Round three many years in the past, we weren’t sure that different stars had planets orbiting them. Scientists naturally thought there can be, however that they had no proof. Now, not solely do we all know of greater than 6,000 confirmed exoplanets, however we will watch as child planets take form round distant stars.
When stars type, they’re surrounded by rotating disks of fuel and mud referred to as protoplanetary disks. Planets type in these disks, and in recent times, ALMA (Atacama Giant Millimeter/submillimeter Array has examined many of those disks. It is made headlines by discovering telltale indicators of planets forming, as they appear to clear orbital paths within the disks.
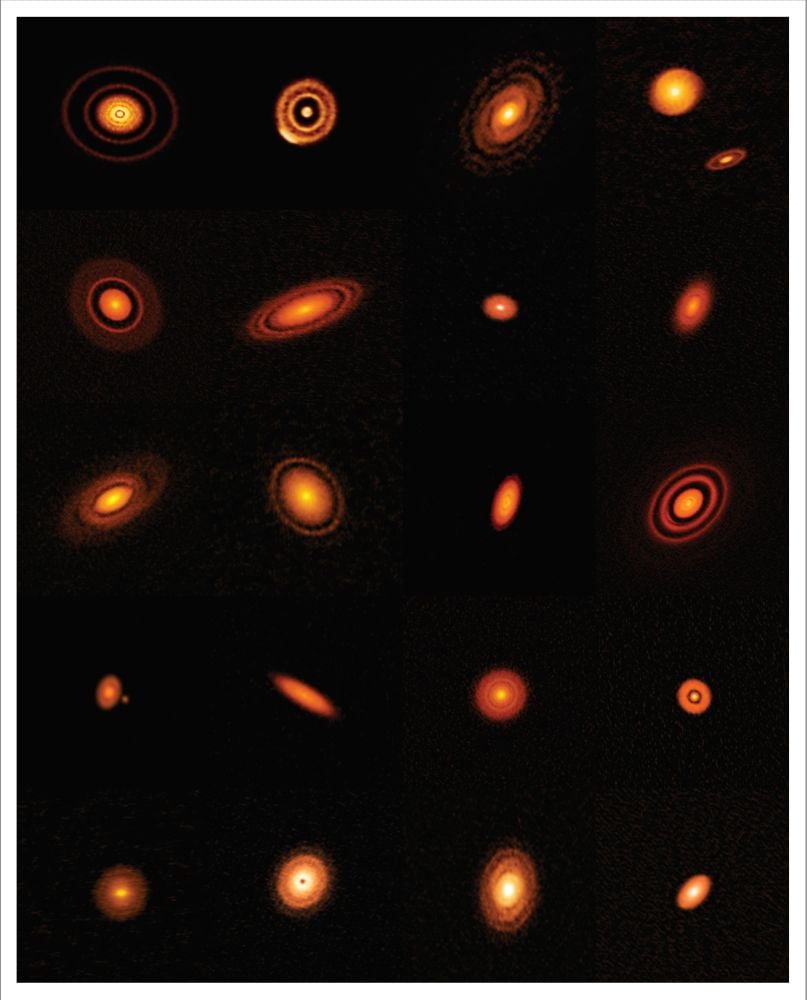 This picture exhibits among the protoplanetary disks imaged by ALMA. The gaps and rings present the place planets are forming and creating lanes within the fuel and mud. Picture Credit score: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), S. Andrews et al.; NRAO/AUI/NSF, S. Dagnello
This picture exhibits among the protoplanetary disks imaged by ALMA. The gaps and rings present the place planets are forming and creating lanes within the fuel and mud. Picture Credit score: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), S. Andrews et al.; NRAO/AUI/NSF, S. Dagnello
Different telescopes have studied these younger protoplanetary disks, too, and uncovered their very own proof of planets forming. Astronomers working with the ESO’s Very Giant Telescope (VLT) and its SPHERE instrument discovered spiral arm patterns within the disk across the star HD 135344B. Whereas these patterns counsel the presence of a planet, there was no direct proof.
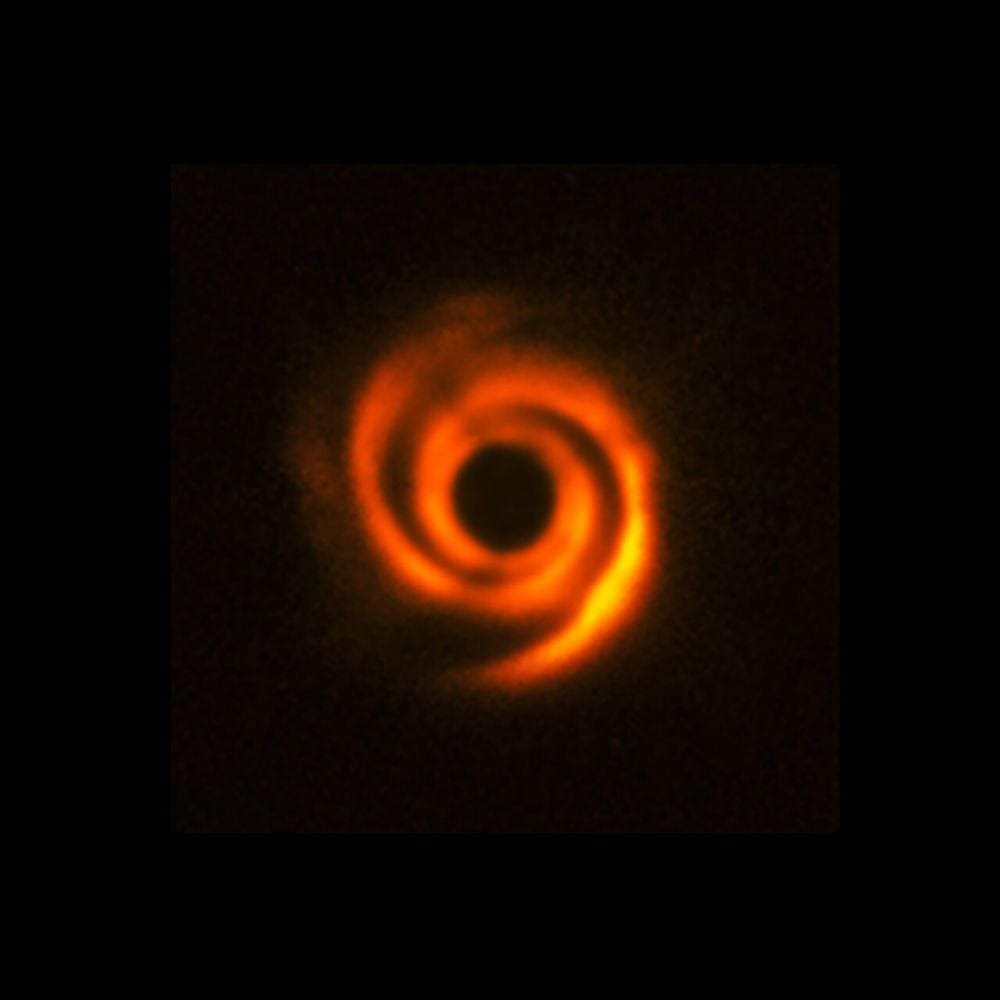 The SPHERE instrument on the ESO’s Very Giant Telescope noticed these spiral arm patterns round HD 135344B. This instrument instructed the presence of a planet, however did not present any direct proof that one was there. The central black area exhibits how the star itself is blocked by the telescope’s coronagraph. Picture Credit score: ESO/T. Stolker et al.
The SPHERE instrument on the ESO’s Very Giant Telescope noticed these spiral arm patterns round HD 135344B. This instrument instructed the presence of a planet, however did not present any direct proof that one was there. The central black area exhibits how the star itself is blocked by the telescope’s coronagraph. Picture Credit score: ESO/T. Stolker et al.
Now astronomers working with one other of the VLT’s devices, the Enhanced Decision Imager and Spectrograph, might have discovered direct proof of a fuel big forming across the star. The invention is introduced in a analysis letter titled “Unveiling a protoplanet candidate embedded in the HD 135344B disk with VLT/ERIS” printed in Astronomy and Astrophysics. The lead writer is Francesco Maio, a doctoral researcher on the College of Florence, Italy.
“Excessive-angular-resolution observations in infrared and millimeter wavelengths of protoplanetary disks have revealed cavities, gaps, and spirals,” the authors write of their analysis. “One proposed mechanism to elucidate these buildings is the dynamical perturbation brought on by big protoplanets.”
Previous research examined the disk round HD 135344B. ALMA observations revealed spiral arms and hints of an enormous planet forming, and different options like a blob. This analysis has refined these observations with extra highly effective devices.
“We recognized the beforehand detected S1, S2, S2a spiral arms and the “blob” options southward of the star,” they added. In addition they discovered a brand new level supply on the base of the S2 spiral arm. They determine it as a fuel big with about 2 Jupiter plenty.
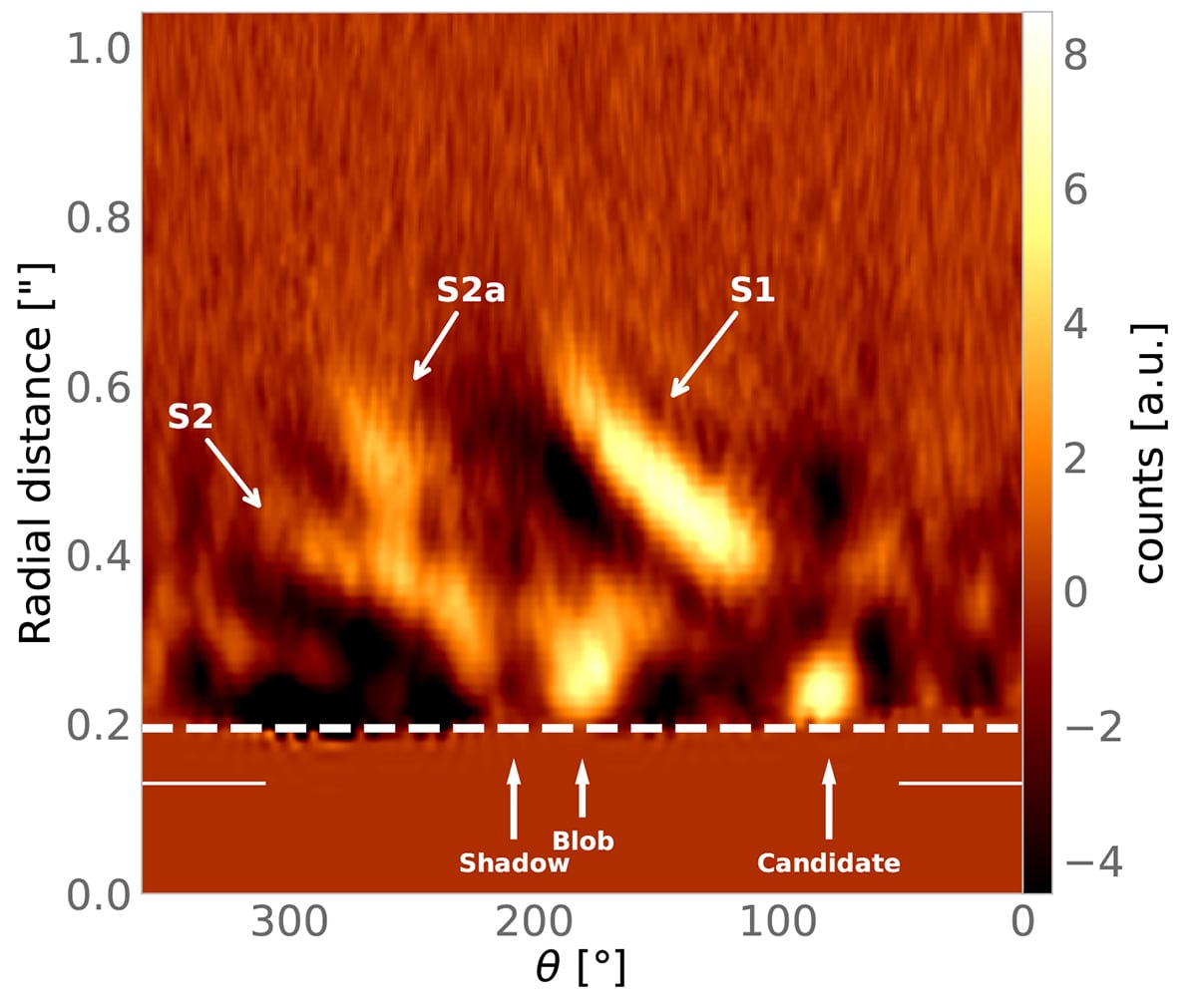 This determine exhibits the 2 spiral arms and the candidate companion. The shadow, marked by the arrow, can also be evident, together with a completely shadowed area highlighted by the horizontal stable line. This visualization of the shadows additional confirms the prolonged nature of the blob south of the star and highlights that it’s a part of the S2 spiral interrupted by the shadow. Picture Credit score: Maio et al. 2025. A&A
This determine exhibits the 2 spiral arms and the candidate companion. The shadow, marked by the arrow, can also be evident, together with a completely shadowed area highlighted by the horizontal stable line. This visualization of the shadows additional confirms the prolonged nature of the blob south of the star and highlights that it’s a part of the S2 spiral interrupted by the shadow. Picture Credit score: Maio et al. 2025. A&A
These observations are markedly totally different from earlier observations exhibiting the telltale gaps carved out by exoplanets. With these photographs, researchers might solely deduce that planets created them. And in relation to spirals, there have been different potential explanations, too. “Spiral arms will also be defined by different mechanisms not involving an exterior perturber,” the researchers write, explaining that gravitational instability might doubtlessly create the arms, as might shadows. A 2021 paper defined that asymmetries in circumstellar disks can forged shadows on different areas of the disk. These shadows create areas of low strain that would set off the formation of spirals.
However this time, astronomers have detected mild alerts from the planet itself.
“What makes this detection doubtlessly a turning level is that, in contrast to many earlier observations, we’re capable of instantly detect the sign of the protoplanet, which remains to be extremely embedded within the disc,” says Maio, who is predicated on the Arcetri Astrophysical Observatory, a centre of Italy’s Nationwide Institute for Astrophysics (INAF). “This offers us a a lot larger degree of confidence within the planet’s existence, as we’re observing the planet’s personal mild.”
This method is 440 mild years away, and the planet is about twice as massive as Jupiter. It is about as distant from its star as Neptune is from the Solar (~4.5 billion km).
A distinct group of researchers have additionally found spiral arms within the disk round one other star. It is named V960 Mon, and the researchers used the ERIS instrument on the VLT to look at it. They are saying they found a companion object forming within the disk, and their discovery is in The Astrophysical Journal Letters. It is titled “VLT/ERIS Observations of the V960 Mon System: A Dust-embedded Substellar Object Formed by Gravitational Instability?” and the lead writer is Anuroop Dasgupta from the European Southern Observatory.
“V960 Mon is an FU Orionis object that exhibits sturdy proof of a gravitationally unstable spiral arm that’s fragmenting into a number of mud clumps. We report the invention of a brand new substellar companion candidate round this younger star,” the researchers report. It is deeply embedded within the disk, and is near some beforehand reported clumps within the disk round V960 Mons. “This candidate might characterize an actively accreting, disk-bearing substellar object in a younger, gravitationally unstable setting,” they write.
The article could possibly be a million years outdated and have 660 Jupiter plenty.
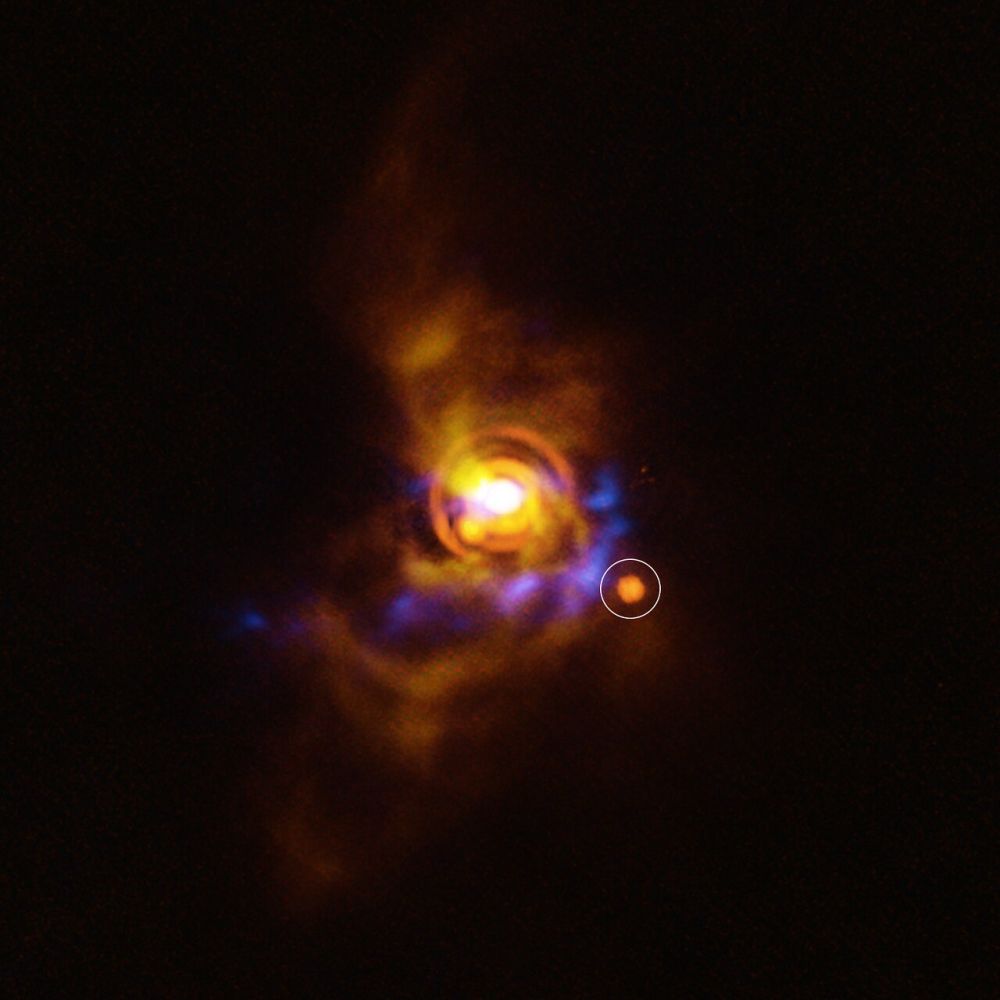 This picture exhibits a doable companion orbiting the younger star V960 Mon. Earlier evaluation of the disc confirmed that it accommodates clumps of unstable materials that would collapse to type a companion object. The brand new candidate discovered right here could possibly be both a planet or a brown dwarf. Picture Credit score: ESO/A. Dasgupta/ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)/Weber et al.
This picture exhibits a doable companion orbiting the younger star V960 Mon. Earlier evaluation of the disc confirmed that it accommodates clumps of unstable materials that would collapse to type a companion object. The brand new candidate discovered right here could possibly be both a planet or a brown dwarf. Picture Credit score: ESO/A. Dasgupta/ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)/Weber et al.
This work provides to previous research that recognized spiral arms round V960 Mons. That analysis additionally discovered clumps that could possibly be parts of the spiral present process gravitational instability and probably forming planets. “Estimating the mass of
solids inside these clumps to be of a number of Earth plenty, we advise this statement to be the primary proof of gravitational instability occurring on planetary scales,” these authors wrote.
That analysis set the stage for Dasgupta and his co-researchers to seek for and discover extra direct proof of a companion forming within the disk.
“That work revealed unstable materials however left open the query of what occurs subsequent. With ERIS, we got down to discover any compact, luminous fragments signaling the presence of a companion within the disc — and we did,” says Dasgupta. Nevertheless, they are not certain if it is a planet or a brown dwarf.
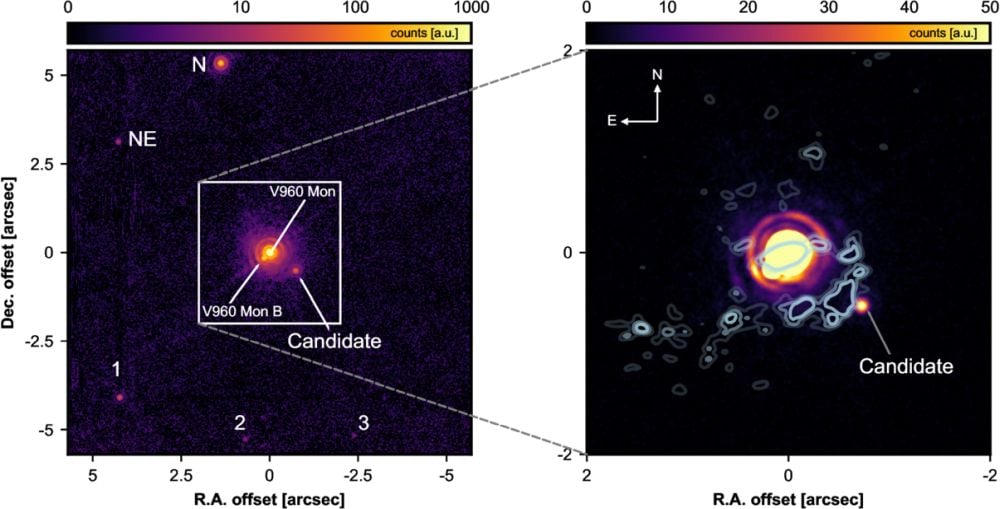 This can be a VLT/ERIS picture of V960 Mon. The left panel exhibits the binary star embedded in its setting, marking the detection of V960 Mon N and V960 Mon NE. The best panel exhibits a zoom-in onto V960 Mon, overlaid with ALMA contours, and the candidate object. Picture Credit score: ESO/A. Dasgupta/ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)/Weber et al.*
This can be a VLT/ERIS picture of V960 Mon. The left panel exhibits the binary star embedded in its setting, marking the detection of V960 Mon N and V960 Mon NE. The best panel exhibits a zoom-in onto V960 Mon, overlaid with ALMA contours, and the candidate object. Picture Credit score: ESO/A. Dasgupta/ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)/Weber et al.*
This detection is essential as a result of if it is confirmed, it could possibly be the primary direct proof of planets forming by gravitational instability (GI). The core accretion principle is extra broadly accepted, however gravitational instability might higher clarify how Jupiter mass planets might type rapidly, and farther from their stars.
These two techniques and their spirals are linked with GI. Astronomers assume they help the GI formation mannequin, however differentiating between the 2 processes in distant disks is difficult.
The hunt to look at planets as they’re nonetheless forming is linked to our sturdy want to know how our planet shaped. Mental curiosity drives us to take a look at our environment and marvel how every thing received this manner. There are a lot of unresolved questions on how Earth shaped, and by watching as different planets type, we might be able to uncover some solutions.
“We’ll by no means witness the formation of Earth, however right here, round a younger star 440 light-years away, we could also be watching a planet come into existence in actual time,” stated Maio.

