Think about you are watching a balloon inflate, however as a substitute of slowing down because it will get greater, it retains increasing quicker and quicker. That is primarily what scientists found about our universe in 1998 utilizing exploding stars referred to as supernovae. They discovered that some unknown pressure, which was subsequently named “darkish vitality” was pushing area itself aside at an accelerating charge. Now, after analyzing over 2,000 of those stellar explosions, researchers have discovered hints that darkish vitality may not be as fixed as we thought. It could really be altering, and probably weakening over time.
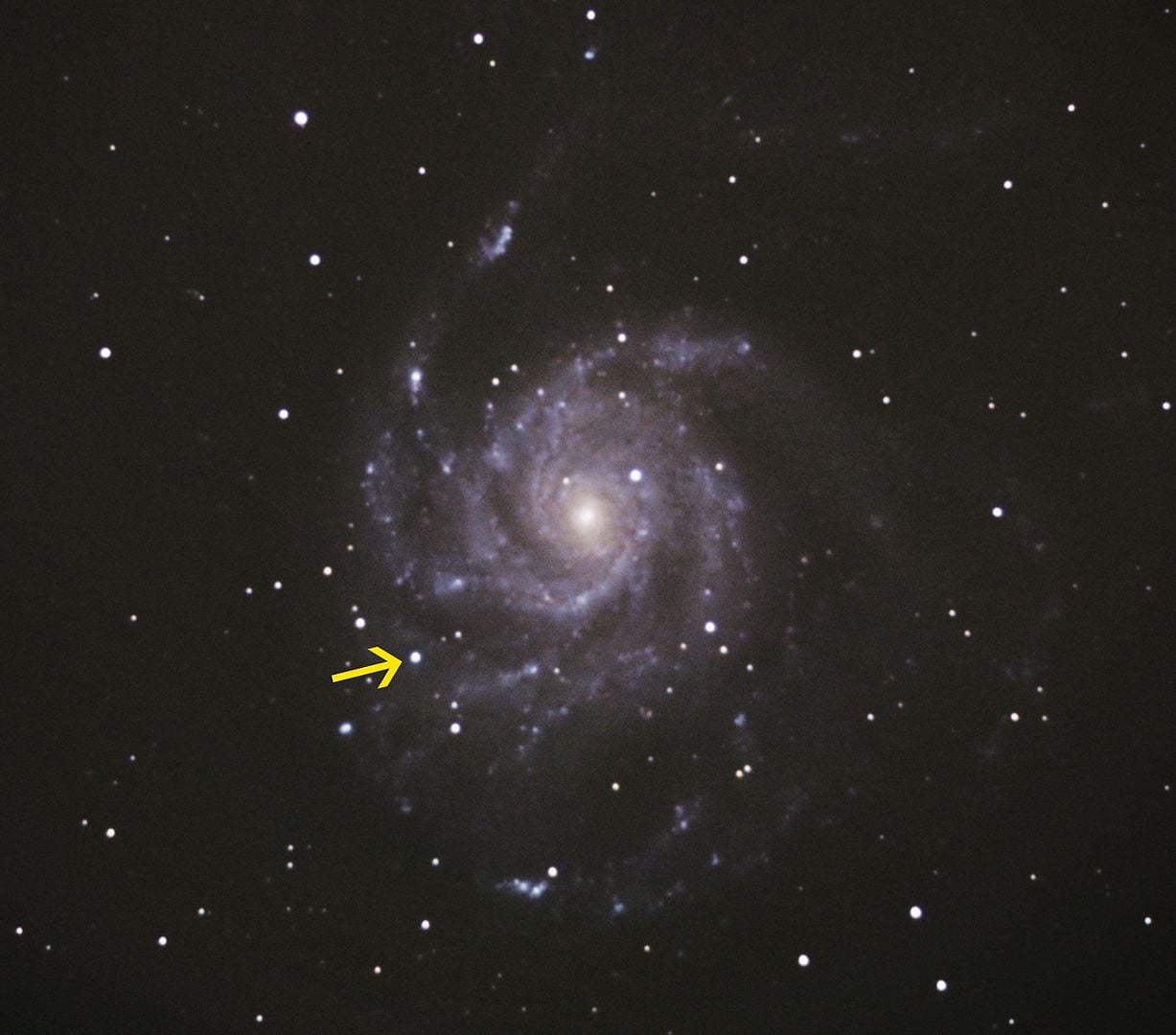 A supernova was captured within the Pinwheel Galaxy in 2011 and named SN2011fe (Credit score : Thunderf00t)
A supernova was captured within the Pinwheel Galaxy in 2011 and named SN2011fe (Credit score : Thunderf00t)
Sort Ia supernovae are extremely brilliant explosions that happen when a particular kind of lifeless star, referred to as a white dwarf, accumulates an excessive amount of materials and explodes. They’re so brilliant that they are often seen throughout billions of sunshine years, and crucially, all of them shine with roughly the identical brightness.
This predictability of the brightness makes them good “commonplace candles” for measuring distances in area. Similar to you can estimate how distant a streetlight relies on how brilliant it seems, astronomers can calculate how far these supernovae are from Earth. However this is the important thing, by additionally measuring how a lot the sunshine from these explosions has been stretched or redshifted by the enlargement of area, it’s potential to determine how briskly the universe was increasing at totally different instances prior to now.
Since that Nobel Prize profitable discovery in 1998, astronomers have noticed greater than 2,000 Sort Ia supernovae utilizing totally different telescopes and strategies. However there was an issue, evaluating knowledge from totally different sources was like making an attempt to check measurements taken with totally different rulers. Every telescope and survey had its personal calibrations and variations.
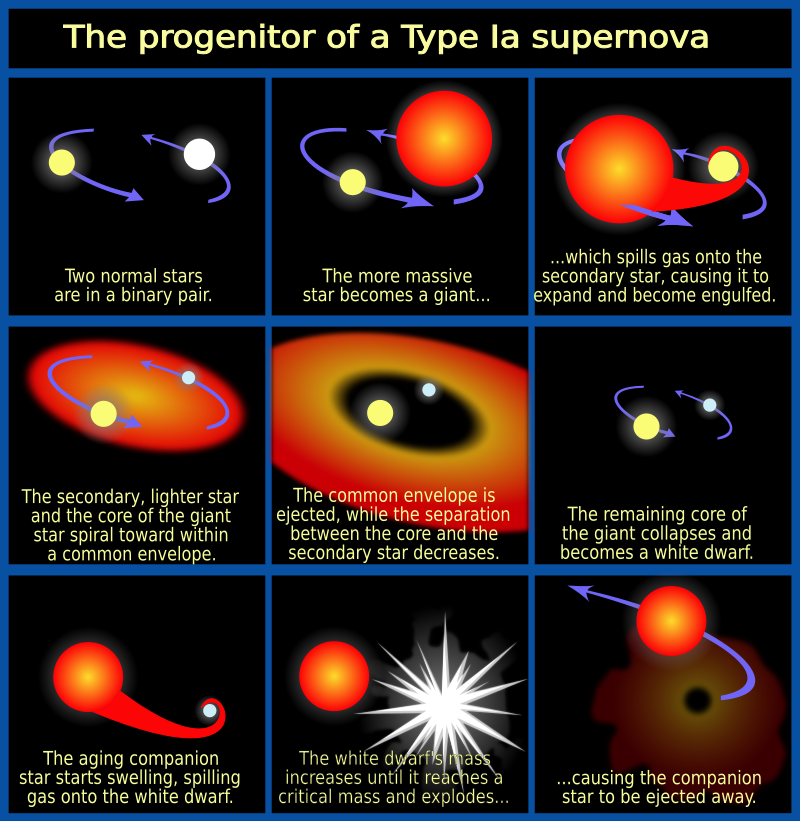
Schematic of the Sort 1a supernova course of (Credit score : NASA, ESA and A. Feild (STScI))
To unravel this, a world workforce referred to as the Supernova Cosmology Challenge spent years creating one thing referred to as “Union3”, the most important standardised dataset of supernovae ever assembled. They painstakingly analysed 2,087 supernovae from 24 totally different datasets, adjusting for all of the variations between telescopes and surveys to place every little thing on the identical scale. When the workforce analysed this huge, standardised dataset utilizing statistical strategies, they discovered one thing intriguing. The info means that darkish vitality may not have stayed fixed all through historical past.
“Darkish vitality makes up nearly 70% of the universe and is what drives the enlargement, so whether it is getting weaker, we might count on to see enlargement gradual over time” – David Rubin, the research’s lead creator from the College of Hawaii.
This potential change in darkish vitality has big implications for the last word destiny of our universe. At present, researchers work with a mannequin referred to as Lambda CDM, the place darkish vitality (Lambda) stays fixed over time and counteracts the gravitational pull of matter (chilly darkish matter, or CDM). But when darkish vitality is definitely weakening then the mannequin may play out very in another way. If darkish vitality wins over gravity, the universe continues increasing without end, probably resulting in a “Large Rip” the place area expands so quick that even atoms get torn aside. If gravity wins, the enlargement may decelerate, cease, and even reverse right into a “Large Crunch” the place every little thing collapses again collectively. In the event that they stability, the universe may attain a gentle state.
What makes this discovery significantly thrilling is that it is not coming from only one supply. A separate research referred to as the Darkish Power Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), which research how galaxies cluster collectively, is seeing comparable hints that darkish vitality is likely to be evolving.
The researchers aren’t able to definitively declare that darkish vitality is altering—the proof, whereas intriguing, is not fairly sturdy sufficient but. Over the following yr, they plan so as to add a number of hundred extra supernovae to their dataset, which ought to present much more exact measurements. Trying additional forward, new telescopes just like the Vera C. Rubin Observatory and the Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope are anticipated to find tens of hundreds of further supernovae over the approaching decade.
Supply : Largest supernova dataset hints dark energy may be changing over time

