Discovering an exoplanet in a star’s liveable zone all the time generates curiosity. Every of those planets has an opportunity, even when it is an infinitesimal one, of internet hosting easy life. Whereas the opportunity of detecting life on these distant planets is distant, discovering them nonetheless teaches us about exoplanet populations and photo voltaic system architectures.
When TESS discovered three planets orbiting the M-dwarf L 98-59 in 2019, then a fourth planet in 2021, the detections generated curiosity. Now {that a} fifth planet has been detected, a super-Earth within the liveable zone, the system is garnering renewed curiosity.
The invention is reported in analysis that can seem in The Astronomical Journal titled “Detailed Architecture of the L 98-59 System and Confirmation of a Fifth Planet in the Habitable Zone.” The lead creator is Charles Cadieux, a researcher on the College of Montreal and Trottier Institute for Analysis on Exoplanets (IREx). The paper is at the moment out there on arxiv.org.
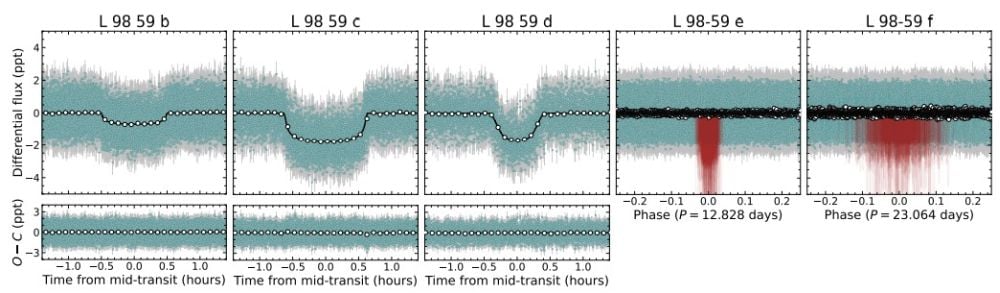 This determine exhibits transit knowledge from TESS for the three innermost planets within the system, and radial velocity measurements for the 2 outermost planets. Picture Credit score: Cadieux et al. 2025.
This determine exhibits transit knowledge from TESS for the three innermost planets within the system, and radial velocity measurements for the 2 outermost planets. Picture Credit score: Cadieux et al. 2025.
L 98-59 is an M3V star, a purple dwarf, about 34.5 light-years away. It has about 0.3 photo voltaic lots and measures about 0.31 photo voltaic radii. Its first three planets, L 98-59 b, c, and d, have been discovered by TESS with the transit technique. The opposite two planets, e and f, have been discovered with the radial velocity (RV) and transit timing variations (TTV) strategies.
“These new outcomes paint essentially the most full image we’ve ever had of the fascinating L 98-59 system,” mentioned lead creator Cadieux in a press release. “It’s a strong demonstration of what we are able to obtain by combining knowledge from house telescopes and high-precision devices on Earth, and it provides us key targets for future atmospheric research with the James Webb House Telescope [JWST].”
Whereas the doubtless liveable planet is intriguing, the general structure of the system is perhaps much more intriguing. The system is a tightly-packed grouping of terrestrial planets with some dramatic compositional variations, regardless of their shut proximity to one another. The system is paying homage to the TRAPPIST-1 system found in 2016/17, which incorporates seven terrestrial planets. Its discovery generated a wave of curiosity within the house science and exoplanet neighborhood.
“Multiplanetary techniques supply a singular alternative to check the outcomes of planetary formation and evolution inside the similar stellar setting,” the authors write of their paper. “One speculation is that planet formation round metal-rich M dwarfs could favor large planets in ‘single’ configurations, whereas decrease metallicity (and fewer huge disks) might result in a number of rocky planets in secure, compact, and coplanar preparations.”
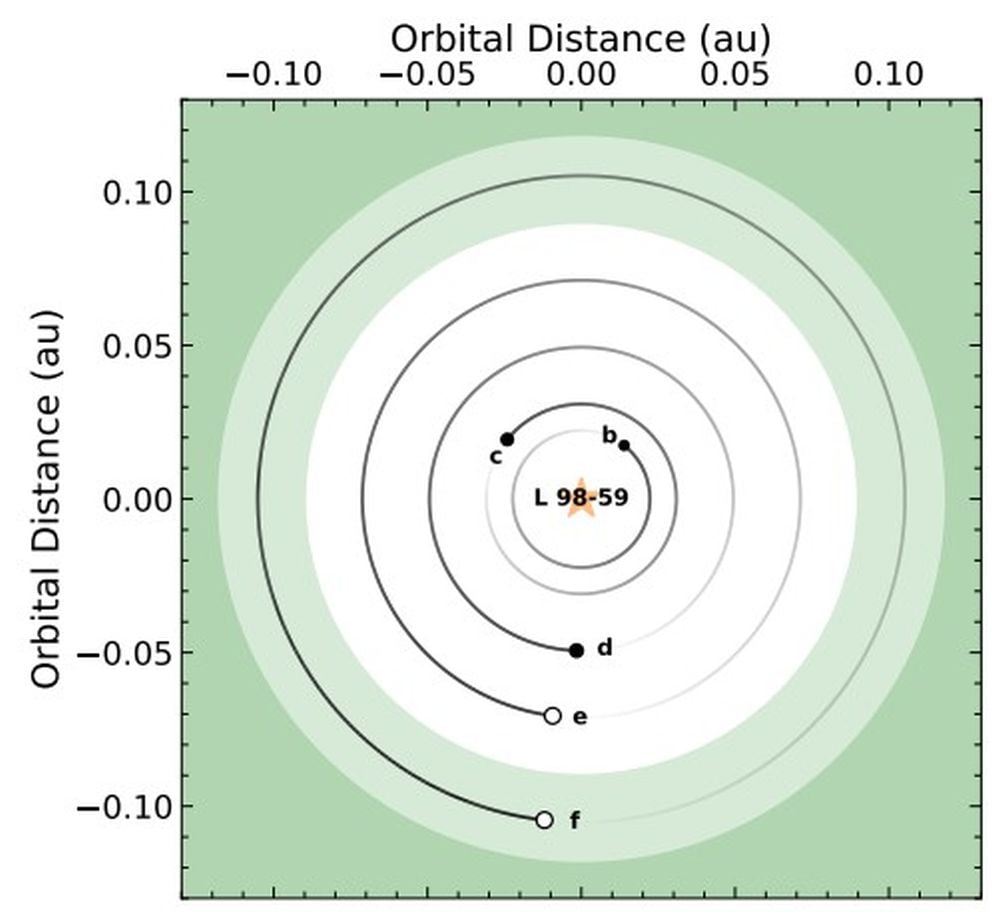 Above view of the L 98-59 planetary system. The Liveable Zone is proven in inexperienced for runaway/most greenhouse (conservative) and pale inexperienced for early current Venus/early Mars (optimistic).Picture Credit score: Cadieux et al. 2025.
Above view of the L 98-59 planetary system. The Liveable Zone is proven in inexperienced for runaway/most greenhouse (conservative) and pale inexperienced for early current Venus/early Mars (optimistic).Picture Credit score: Cadieux et al. 2025.
The innermost planet, L 98-59 b, has an Earth-like density, however is just about 84% its mass and half its dimension. It is a uncommon sub-Earth with well-understood parameters. It takes solely about 2.25 Earth days to orbit its star, and atmospheric research suggests it is perhaps a really volcanically energetic world as a consequence of tidal heating.
L 98-59 c can also be possible volcanic as a consequence of tidal heating. It is about 1.3 Earth radii and two Earth lots, and completes an orbit in about 3.7 Earth days. L 98-59 d has about 1.6 Earth radii, about 1.6 Earth lots, and an orbital interval of about 7.4 days. It could be a water world, or hycean world. The fourth planet, L 98-59 e, has about 1.4 Earth radii, a minimal mass of about 2.8 Earth lots, and an orbital interval of about 12.8 days.
The newly-detected planet, L 98-59 f, is within the optimistic liveable zone of the star. It has a minimal mass of about 2.80 Earth lots, about 1.4 Earth radii, and follows a 28 day orbit.
One of many fascinating issues about this technique is that they comply with close to round orbits. This implies they’re amenable to atmospheric spectroscopic research by the JWST or different telescopes. Observations additionally present that the three inside transiting planets have rising water-mass fractions with orbital distance.
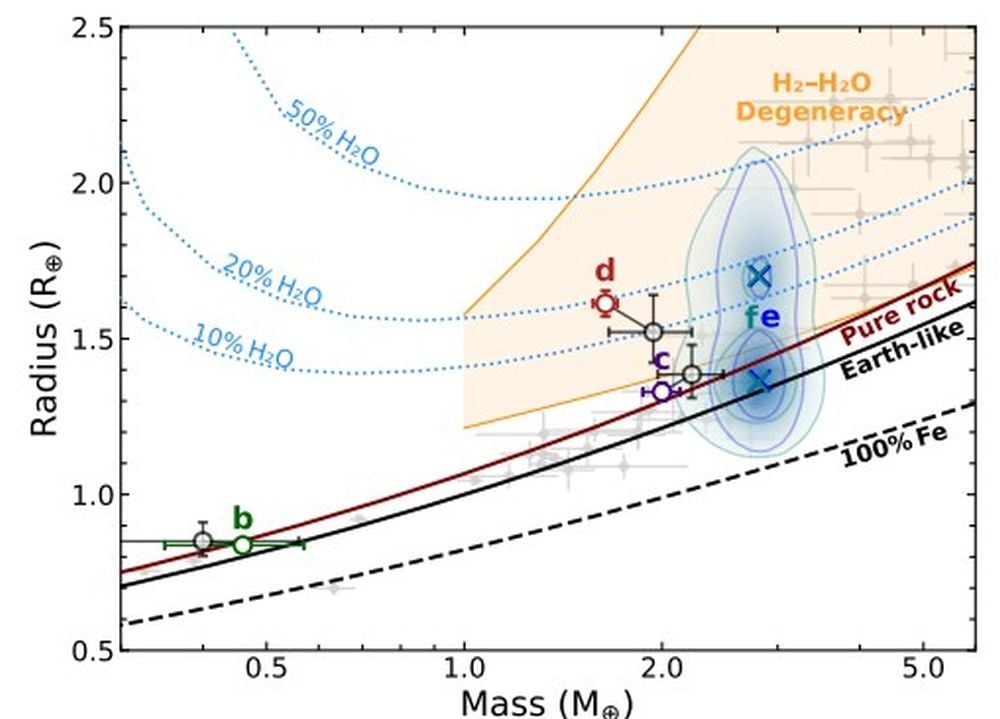 This determine exhibits Mass–radius constraints on the L 98-59 planets (b: inexperienced, c: purple, d: purple, e: blue, f: teal) with different exoplanets round M dwarfs within the background (grey factors). Exoplanet mass on the x-axis and radius on the y-axis. The orange area delimits a degeneracy (H2- or H2O-rich) in composition. “The planets round L 98-59 are seemingly displaying various compositions,” the authors write. Picture Credit score: Cadieux et al. 2025.
This determine exhibits Mass–radius constraints on the L 98-59 planets (b: inexperienced, c: purple, d: purple, e: blue, f: teal) with different exoplanets round M dwarfs within the background (grey factors). Exoplanet mass on the x-axis and radius on the y-axis. The orange area delimits a degeneracy (H2- or H2O-rich) in composition. “The planets round L 98-59 are seemingly displaying various compositions,” the authors write. Picture Credit score: Cadieux et al. 2025.
“With its variety of rocky worlds and vary of planetary compositions, L 98-59 affords a singular laboratory to deal with among the subject’s most urgent questions: What are super-Earths and sub-Neptunes made from? Do planets type in another way round small stars? Can rocky planets round purple dwarfs retain atmospheres over time?” mentioned René Doyon, co-author of the research, who’s a professor on the College of Montreal and the Director of IREx.
“Discovering a temperate planet in such a compact system makes this discovery notably thrilling,” mentioned lead creator Cadieux. “It highlights the outstanding variety of exoplanetary techniques and strengthens the case for learning doubtlessly liveable worlds round low-mass stars.”
Exoplanet habitability round low mass M-dwarfs is a contentious thought. Since they’re so dim, their liveable zones are near the celebs. This creates a few potential obstacles to habitability as scientists perceive it.
Due to their proximity to their stars, these planets could also be tidally-locked. It is tough to say whether or not that is a critical barrier to habitability, or if an exoplanet’s ambiance would one way or the other unfold the warmth round. It is potential that liveable zones on these planets are restricted to a pole-to-pole terminator zone across the planet’s floor that’s temperate.
M-dwarfs are additionally recognized for his or her highly effective flaring, which may strip atmospheres away. With out an environment, an exoplanet is unlikely to be liveable, although scientists cannot utterly get rid of the likelihood.
Alternatively, M-dwarfs are extraordinarily long-lived stars that burn their gasoline very slowly. Which means they provide long-lived stability to any planets of their liveable zones.
This technique will little question appeal to additional consideration from the exoplanet science neighborhood. Actually, additional research with the JWST is already underway. “The atmospheric characterization of the L 98-59 planets is already underway with JWST, utilizing each transmission and emission spectroscopy,” the authors write. ” Such complete characterization is vital to advancing our understanding of planet formation and evolution round low-mass stars.”
“With these new outcomes, L 98-59 joins the choose group of close by, compact planetary techniques that we hope to know in larger element over the approaching years,” says Alexandrine L’Heureux, co-author of the research and Ph.D. scholar on the College of Montreal. “It’s thrilling to see it stand alongside techniques like TRAPPIST-1 in our quest to unlock the character and formation of small planets orbiting purple dwarf stars.”

