Astronomers have noticed the distant energetic galaxy OJ 287 for a few years. It is a BL Lac object, a sort of energetic galactic nuclei identified for his or her excessive variability. They show speedy and pronounced variability of their brightness throughout a number of wavelengths.
In easy phrases, an energetic galactic nuclei is a supermassive black gap (SMBH) that is actively accreting materials. SMBHs exert an awfully highly effective affect on their environment. Observing the formation and propagation of jets that come from SMBHs are one method to perceive how they dominate their environments. Amongst different results, these jets warmth up close by gasoline clouds, stifling their star formation.
New observations with a radio interferometer named Radioastron House VLBI revealed the presence of an uncommon ribbon-like jet of fabric emanating from the middle of OJ 287. The observations and outcomes are in a latest paper titled “Revealing a ribbon-like jet in OJ 287 with RadioAstron.” The lead writer is Dr. Thalia Traianou from Heidelberg College, and the paper is revealed in Astronomy and Astrophysics.
The RadioAstron Space VLBI mission combines a spaceborne radio telescope with 27 ground-based radio telescopes worldwide to create a big digital telescope. Utilizing interferometry, it creates a digital radio telescope that is 5 instances Earth’s diameter. This offers RadioAstron exceptionally excessive spatial decision, permitting the telescope to see into OJ 287’s core. Over a number of years of observations, it discovered an extended, sinuous, ribbon-like jet of plasma that twists and turns because it reaches into area.
Whereas this jet has been noticed earlier than, and is the location of a historic detection of a particularly energetic shock, that is the primary time astronomers have noticed the twists and turns. “For the primary time, as a consequence of a good geometrical place of the jet in tandem with excessive knowledge high quality, we detect a number of sharp bends that kind a “ribbon-like” jet construction that extends right down to 1 mas,” the authors write of their analysis article.
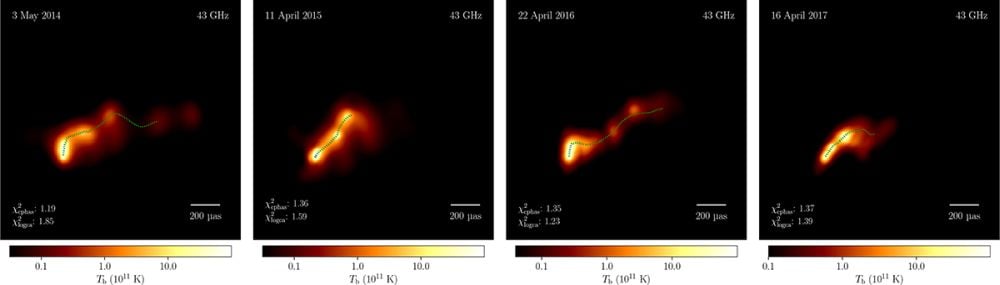 These are multi-epoch VLBI photos of OJ 287 noticed on Might 3, 2014, April 11, 2015, April 22, 2016, and April 16, 2017. The ridgelines, delineating the jet’s axis for every epoch, are overlaid as dashed lime traces, with a black define for enhanced visibility. This picture sequence clearly reveals the jet’s evolution over the 4 years. Picture Credit score: Traianou et al. 2025. A&A
These are multi-epoch VLBI photos of OJ 287 noticed on Might 3, 2014, April 11, 2015, April 22, 2016, and April 16, 2017. The ridgelines, delineating the jet’s axis for every epoch, are overlaid as dashed lime traces, with a black define for enhanced visibility. This picture sequence clearly reveals the jet’s evolution over the 4 years. Picture Credit score: Traianou et al. 2025. A&A
RadioAstron detected extra than simply the ribbon-like jet. It additionally additionally discovered areas throughout the jet with temperatures larger than 10 trillion Kelvin. That is extraordinarily sizzling. The Solar’s core is about 15 million Kelvin, for comparability, that means that the recent areas within the jet are 660,000 instances hotter. This temperature is much like the Universe solely microseconds after the Large Bang, when all matter existed as quark-gluon plasma.
In addition they discovered the emergence of a brand new jet part. It is a new shock wave within the jet that slammed right into a pre-existing stationary shock. It coincides with the historic detection of a large outburst of power in 2017 that launched trillion-electron-volt gamma rays from OJ 287.
“We captured the delivery of a jet part and watched it journey down this lovely ribbon till it hit a shock wave and produced probably the most energetic gamma rays ever detected from this supply,” mentioned lead writer Traianou in a press release.
The brand new RadioAstron observations of OJ 287’s twisted jet could assist clarify a long-standing puzzle.
Astronomers have been observing OJ 287 for effectively over a century, logging the item’s brightness variations. They observe an uncommon 60-year cycle, and a shorter 12-year cycle of extraordinarily luminous flares. The cyclical variations recommend that the galaxy hosts a pair of black holes. This might not solely create the cycle, however may additionally clarify why the jet is twisted like a ribbon. If two black holes are orbiting one another, their movement may twist the jet.
“These periodic variations are defined effectively by a supermassive black gap binary (SMBHB) mannequin through which a secondary supermassive black gap follows a precessing, eccentric orbit round a extra huge major,” the authors clarify. “Flares are generated every time a smaller part crosses the first’s accretion disk.”
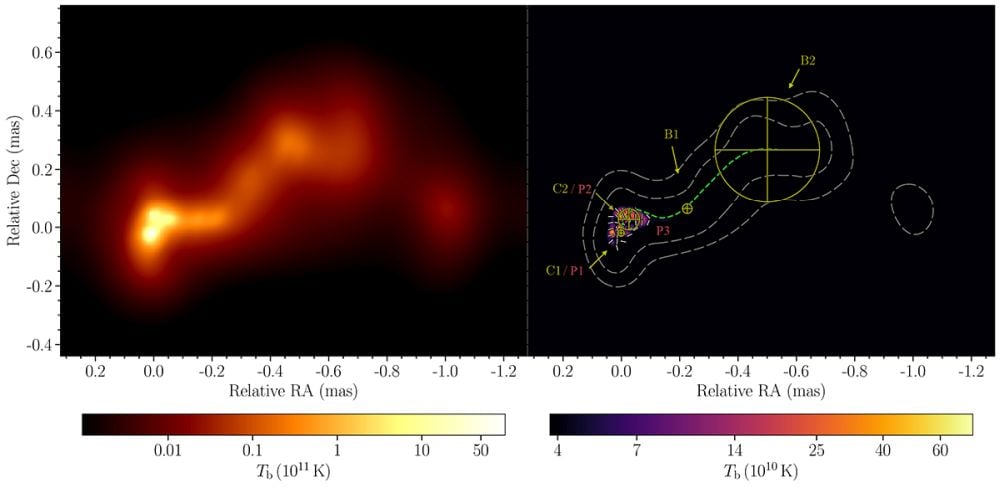 These photos of OJ 287 are from April 25, 2016. The picture on the left reveals brightness temperature. The picture on the best reveals complete depth contours. P1, P2, and P3 are polarized options, and the central dashed inexperienced curve traces the jet ridgeline. Yellow circles C1 and C2 mark the areas of the black holes. Picture Credit score: Traianou et al. 2025. A&A
These photos of OJ 287 are from April 25, 2016. The picture on the left reveals brightness temperature. The picture on the best reveals complete depth contours. P1, P2, and P3 are polarized options, and the central dashed inexperienced curve traces the jet ridgeline. Yellow circles C1 and C2 mark the areas of the black holes. Picture Credit score: Traianou et al. 2025. A&A
Discovering a galaxy with a pair of black holes presents a brand new alternative. Finally, the pair will probably merge and produce gravitational waves. Astronomers have detected these waves from many mergers, so OJ 287 is an opportunity to look at a pair of SMBH earlier than they merge. Whereas RadioAstron led to 2019, observations of OJ 287 with different amenities can be ongoing.
“One of many lovely issues about basic science is the unpredictability of its influence. When electrical energy was found 2 hundred years in the past, nobody may have imagined how deeply it could form fashionable society, mentioned co-author Professor Leonid Curvits from the College of Aerospace Engineering at Delft College of Know-how within the Netherlands. “It’s the identical with our analysis: we don’t know when and what its results can be. However that uncertainty is a part of what makes basic science so thrilling. That mentioned, it’s sure that this RadioAstron research is a prelude to the upcoming transformational discoveries within the new period of multi-messenger astronomy.”

