Our information of black holes is incomplete. We all know there are stellar mass black holes which can be created when huge stars collapse on themselves on the finish of their lives of fusion. We all know that supermassive black holes reside within the hearts of galaxies and typically merge with one another. The truth that there are two different hypothetical varieties of black holes which will or could not exist—primordial black holes and intermediate mass black holes—illustrates how our understanding is missing.
The principle purpose for our incomplete information is the difficulties in observing them. Most galaxies appear to host black holes of their facilities, however they’re solely straight observable once they’re accreting materials and emitting mild. These are energetic galactic nuclei (AGN).
A group of astronomers have detected an AGN in a distant dwarf galaxy about 230 million mild years away. In a twist, this black gap does not reside in its galactic heart. As an alternative, its off-center by about 3,200 mild years. It is not the one one.
The invention is in new analysis within the journal Science Bulletin. It is titled “A jetted wandering massive black hole candidate in a dwarf galaxy,” and the lead writer is Yuanqi Liu from the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory.
The brand new discovery is an offset huge black gap that is actively accreting materials like an AGN and can also be producing the signature jets of an AGN. It reveals that black holes can actively accrete materials and develop even when not located within the galactic heart. That is shocking, since galactic facilities are identified to host massive reservoirs of gasoline that black holes feed on.
“Off-nuclear(or offset) energetic galactic nucleus (AGN) are more and more acknowledged as essential laboratories for understanding galactic dynamics and black-hole evolution, with latest research indicating that they’re fairly widespread in varied galaxy populations,” the authors of the brand new analysis write.
 This artist’s illustration reveals an AGN emitting jets and radiation because it accretes gasoline. Whereas sometimes present in galactic facilities, the researchers discovered a black gap/AGN over 3200 mild years from the middle of its dwarf galaxy. Picture Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, Joseph Olmsted (STScI)
This artist’s illustration reveals an AGN emitting jets and radiation because it accretes gasoline. Whereas sometimes present in galactic facilities, the researchers discovered a black gap/AGN over 3200 mild years from the middle of its dwarf galaxy. Picture Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, Joseph Olmsted (STScI)
Astronomers are considering learning black holes in dwarf galaxies. Dwarf galaxies have less complicated evolutionary histories and decrease plenty than massive galaxies just like the Milky Approach. That implies that proof of the processes that formed their black holes’ is healthier preserved than in additional huge galaxies.
Dwarf galaxies even have shallower gravity wells just because they’re much less huge. Analysis reveals that occasions like galaxy mergers or interactions involving a number of different our bodies are sufficient to kick black holes out of the facilities of dwarf galaxies. That is probably what occurred on this case.
This new discovery comes from the Mapping Close by Galaxies at Apache Level Observatory (MaNGA) survey. MaNGA is mapping about 10,000 galaxies, and investigating their inside kinematic buildings and the composition of gasoline and stars. It has recognized 628 dwarf galaxies with candidate AGN. Of these 628 AGN, about 390 of them, or 62%, could also be offset from their galactic facilities.
On this analysis, the group used the Very Long Baseline Array to review a dwarf galaxy named MaNGA 12772-12704. Because the host galaxy reveals no indicators of merger exercise, like tidal tails or double nuclei, they concluded that what they discovered is an offset black gap. The researchers calculated that the black gap has about 300,000 photo voltaic plenty, which means it may very well be within the vary of the elusive intermediate black holes, relying on the definition.
This research reveals that off-center black holes can develop although they don’t seem to be firmly within the galactic heart, the place gasoline is available for them to accrete. The invention is direct proof that helps an alternate methodology of black gap development. Astrophysicists know that black holes can develop via accretion and thru mergers as their host galaxies merge. Gravitational wave observations affirm this. However this research reveals that black holes can turn out to be extra huge with out mergers and while not having to be close to the galactic heart and its gasoline reservoir.
 An artist’s illustration of two black holes merging. Picture Credit score: LIGO/T Pyle
An artist’s illustration of two black holes merging. Picture Credit score: LIGO/T Pyle
“This discovery prompts us to rethink black gap–galaxy co-evolution,” mentioned co-author Tao An in a press release. “Black holes usually are not solely central ‘engines’ however may additionally quietly reshape their host galaxies from the outskirts.”
“The implications are profound particularly for the SMBH formation within the early Universe, the place conventional fashions battle to elucidate the speedy development of SMBHs” to 1 billion plenty the authors clarify of their analysis. The overall mannequin of black gap development in galaxies supposes environment friendly, regular, and sustained development via gasoline that is funneled into the galactic heart.
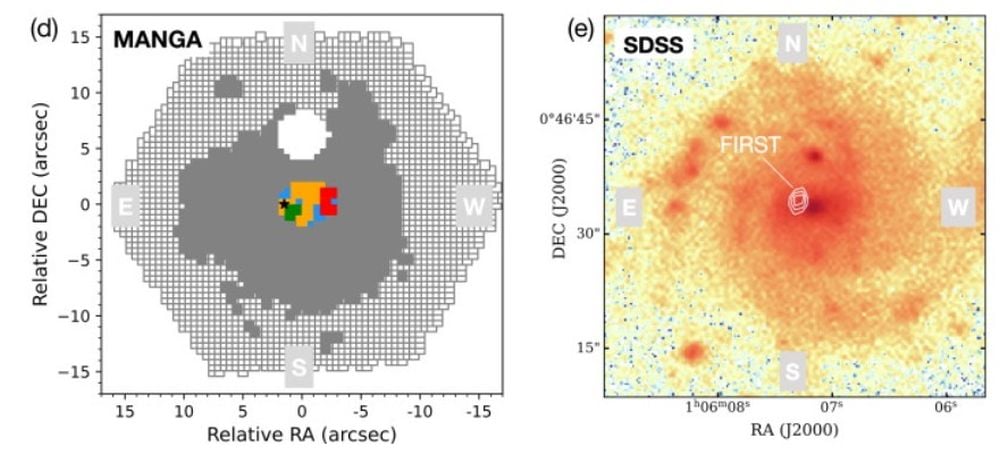 The left panel reveals the spatial distribution of ionization throughout the galaxy, with the black star exhibiting the place of the black gap. The fitting panel reveals SDSS observations in its g-band, used to establish AGN. It additionally reveals radio contours from the FIRST survey, exhibiting that the AGN is offset. Picture Credit score: Liu et al. 2025. Science Bulletin.
The left panel reveals the spatial distribution of ionization throughout the galaxy, with the black star exhibiting the place of the black gap. The fitting panel reveals SDSS observations in its g-band, used to establish AGN. It additionally reveals radio contours from the FIRST survey, exhibiting that the AGN is offset. Picture Credit score: Liu et al. 2025. Science Bulletin.
“MaNGA 12772-12704 suggests another pathway: black holes could develop via accretion occasions distributed all through their host galaxy,” the researchers write. Because the early Universe featured chaotic, gas-rich galaxies, this different pathway could also be much more related.
The invention additionally forces scientists to rethink how AGN suggestions, an essential course of in galaxies, works in low-mass dwarf galaxies. “These observations counsel that even displaced MBHs can drive mechanical suggestions, impacting star formation and gasoline dynamics inside their host galaxies,” the authors clarify of their analysis. “The well-defined jet on this off-nuclear AGN reveals that accretion disk-jet programs, generally seen in highly effective AGN inside huge galaxies, can type and maintain past galactic centre, broadening our insights into AGN physics.”
This discovery helps shift wandering black holes from the hypothetical to the observationally confirmed. As extra highly effective telescopes come on-line, astronomers could discover and make sure extra of them, together with the tons of which can be in limbo as candidates. As soon as astronomers can observe galaxy facilities and buildings with higher accuracy, they could discover that offset AGN usually are not uncommon, not less than in dwarf galaxies.
In consequence, our understanding of black holes, the Universe’s most beguiling objects, will take an enormous step ahead.

