Mars could also be generally known as the Crimson Planet, however underneath the correct cosmic situations, its skies shimmer emerald with auroras — and for the primary time, scientists suppose they will predict the spectacle.
Having the ability to predict Martian auroras, which consequence from photo voltaic storms that additionally unleash dangerous radiation, may present future astronauts with essential warning and time to take cowl, scientists say.
Auroras happen when charged particles from the solar slam right into a planet’s ambiance and collide with atoms and molecules there, resulting in a glow. On Earth, our magnetic subject funnels these particles towards the poles, giving rise to the famous northern and southern lights. But Mars lost its global magnetic field long ago, a change that also helped transform it from a wet world into the dry planet we see today. With no shield to steer solar particles, the entire nightside sky can glow with diffuse green light, caused by oxygen atoms less than 60 miles (about 100 kilometers) above the surface.
In March 2024, NASA’s Perseverance rover made skywatching history by capturing the first visible-light aurora on Mars, marking the first time such a phenomenon had been observed from the ground of another world.
Last week at the Europlanet Science Congress–Division for Planetary Sciences (EPSC–DPS) meeting in Helsinki, Finland, Elise Knutsen, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Oslo, reported a second detection and described new instruments her crew developed to forecast when auroras will seem.
“The truth that we captured the aurora once more demonstrates that our methodology for predicting aurorae on Mars and capturing them works,” Knutsen mentioned in a statement.
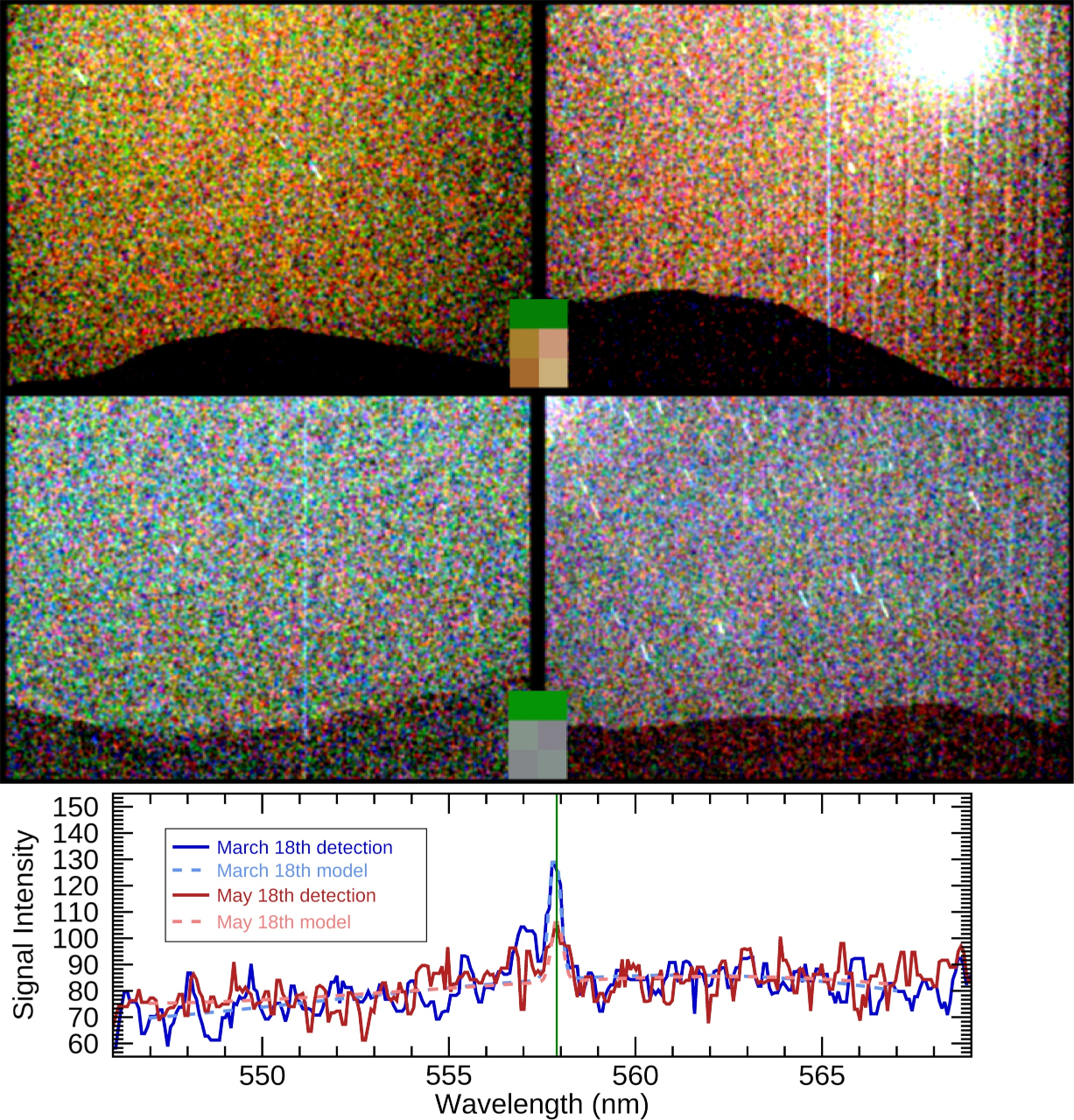
In contrast to on Earth, the place aurora forecasting advantages from a long time of information, predicting Martian auroras remains to be a trial-and-error science. As a part of the brand new research, Knutsen and her crew programmed Perseverance’s cameras to look at the sky after photo voltaic eruptions generally known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs) blasted within the course of Mars. These huge outbursts hurl billions of tons of charged particles into house — and the quicker the CME, the extra doubtless it’s to spark an aurora.
However rover observations should be scheduled about three days upfront, as mission groups on Earth want time to plan, validate and transmit instructions to Mars. This forces researchers to make educated bets on which storms are promising sufficient to focus on, in line with the assertion.
Between 2023 and 2024, the crew tried eight occasions. The primary makes an attempt got here up empty as a result of the CMEs weren’t sturdy sufficient. Later, nevertheless, by specializing in quicker, extra intense storms, the researchers succeeded in capturing two situations of glowing inexperienced auroras, in line with the assertion.
Nonetheless, not each highly effective CME produced a lightshow. “Statistically there’s additionally a level of randomness to those issues, so typically we’re simply unfortunate,” Knutsen mentioned within the assertion.
“Predicting the aurora on Earth all the way down to minute precision is not an actual science both.”

