Metallicity is a basic a part of the Universe. The Large Bang created largely hydrogen, the only and lightest factor, and a tiny little bit of helium, the second lightest factor. These components collect collectively in giant portions to kind stars. For rocky planets to kind, stars needed to kind first.
Stars forge the heavier components—known as metals in astronomy—by way of nucleosynthesis, then unfold these metals out into interstellar area. In consequence, rocky planets like Earth can ultimately kind. The important thing factor right here is time.
As generations of stars reside and die, the metallicity of their house galaxy slowly rises. Because the metallicity rises, various kinds of planets can kind. Even various kinds of rocky planets. That is the important thing thought behind new analysis.
The analysis is titled “Effect of Galactic Chemical Evolution on Exoplanet Properties,” and it is printed in The Astrophysical Journal Letters. The lead writer is Jason Steffen, affiliate professor with the College of Nevada Las Vegas Division of Physics and Astronomy. The analysis produces a brand new mannequin that tries to seize the complexity of cosmochemistry over time and the way it impacts planet formation.
“Supplies that go into making planets are fashioned inside stars which have completely different lifetimes,” mentioned lead writer Steffen in a press release. “These findings assist clarify why older, rocky planets are much less dense than youthful planets just like the Earth, and in addition counsel that the required components for all times didn’t arrive unexpectedly.”
All of us love our resplendent Earth, the place life thrives in each possible area of interest and a blue sky comforts us with its calming gentle. It might look like it was designed for us. However the actuality is that Earth, like each different planet, is principally fashioned from the wreckage of dying stars. However stars die on completely different timescales in response to their lots, and that impacts the kind of wreckage, or planetary constructing blocks, accessible. That in flip determines the character of the planets that kind.
 *This artist’s illustration exhibits a younger star with its protoplanetary disk. Planets kind in these disks, and so they’re chemically enriched by earlier stars. The diploma and kind of chemical enrichment determines many features of kind of rocky planets that may kind. Picture Credit score: NASA-JPL*
*This artist’s illustration exhibits a younger star with its protoplanetary disk. Planets kind in these disks, and so they’re chemically enriched by earlier stars. The diploma and kind of chemical enrichment determines many features of kind of rocky planets that may kind. Picture Credit score: NASA-JPL*
The better a star’s mass, the heavier the metals it produces, and the earlier it produces them. Decrease mass stars producer lighter metals however they seem later, since decrease mass stars have longer lifetimes. So when heavy mass stars die after only some million years, they enrich their environment with components like oxygen, silicon, and magnesium. These components make up the majority of a rocky planet’s outer layers. About three quarters of Earth’s crust is oxygen and silicon, for instance. The mantle is basically oxygen, silicon, magnesium, and iron.
“We discover that the early abundances of components fashioned from the evolution and dying of high-mass stars (reminiscent of oxygen, silicon, and magnesium) yields planets with bigger mantles and smaller cores. The later addition of components produced in low-mass stars (reminiscent of iron and nickel) causes the planet cores to turn into comparatively bigger,” the authors write of their analysis letter.
This leads to much less dense planets orbiting older stars in comparison with youthful stars. That is what scientists have discovered within the recognized exoplanet inhabitants. “These outcomes are broadly in step with latest observations of planet properties from stars of various ages,” the authors clarify.
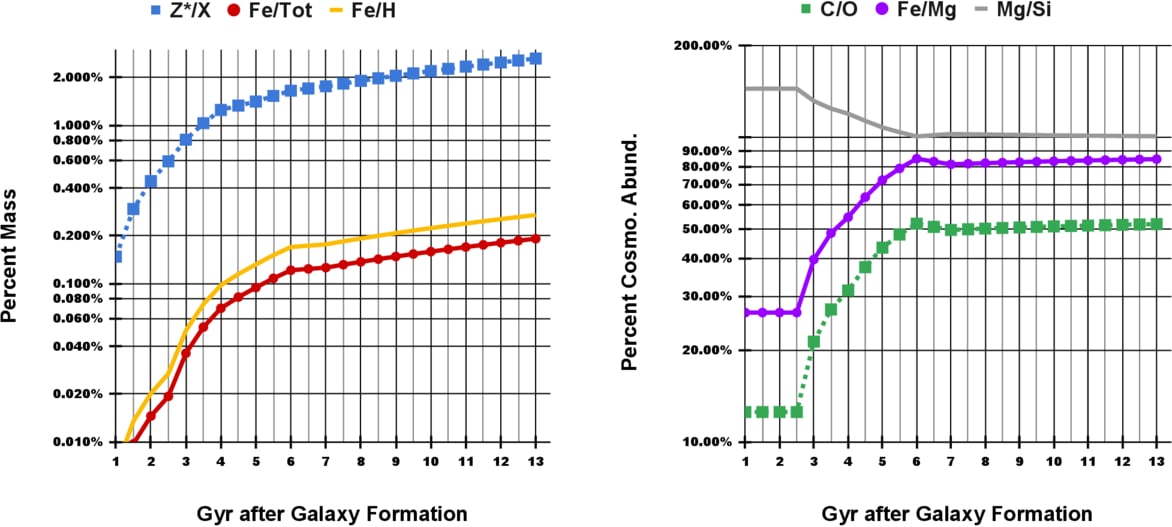 *These graphs from the analysis present how cosmochemistry in a galaxy adjustments over time. They present the “change within the preliminary chemical composition by way of essential elemental ratios,” the authors clarify.The left graph exhibits the preliminary p.c lots in blue, the ratio of iron over complete components in purple, and the ratio of iron over hydrogen in yellow. The appropriate graphs exhibits preliminary p.c cosmological abundances of choose elemental ratios, together with carbon/oxygen in inexperienced, iron/magnesium in purple, and magnesium over silicon in inexperienced. Picture Credit score: Steffen et al. 2025. ApJL*
*These graphs from the analysis present how cosmochemistry in a galaxy adjustments over time. They present the “change within the preliminary chemical composition by way of essential elemental ratios,” the authors clarify.The left graph exhibits the preliminary p.c lots in blue, the ratio of iron over complete components in purple, and the ratio of iron over hydrogen in yellow. The appropriate graphs exhibits preliminary p.c cosmological abundances of choose elemental ratios, together with carbon/oxygen in inexperienced, iron/magnesium in purple, and magnesium over silicon in inexperienced. Picture Credit score: Steffen et al. 2025. ApJL*
The above graphs are complicated however essential.
The Fe/Mg ratio is essential as a result of it will possibly hint the anticipated mass ratio between a rocky planet’s crust and mantle. The Mg/Si ratio is likewise essential. It predicts the kind of volcanic rock on the planet. If the rock is depleted in Si, it possible has a thick crust that inhibits extrusive volcanoes and plate tectonics, each considered essential for habitability. “Our outcomes counsel that early planets have larger Mg/Si ratios, which make Si-depleted planets with thick crusts,” the authors write.
Earth’s habitability depends on quite a few components, together with its iron core. That is the place our planet’s protecting magnetic protect originates, and the analysis exhibits that iron content material was decrease earlier within the Milky Method’s historical past. This suggests that habitability may very well be extra possible later in a galaxy’s lifetime.
“Planets that kind round early-generation stars within the Milky Method could have decrease iron content material, implying that planets round these stars could have smaller cores,” the authors clarify.
The takeaway is that the components needed for a liveable rocky planet can be found at completely different instances. A really younger galaxy is unlikely to kind many liveable planets. However the development is not essentially uniform and easy.
The principle conclusions are that denser planets kind as a galaxy evolves, and on the identical time their radii lower. Additionally, because the Fe/Mg and C/O ratios quickly lower between 2 and 6 gigayears, there is a lower in Mg/Si. The quantity of iron accessible doubles between 1 and 5 gigayears, then stays fixed afterward. Additionally, enrichment by completely different stellar sources can change the [core mass fraction]( of planets by as a lot as 10%.
“One implication of those findings is that the circumstances for all times don’t begin instantly,” says Steffen. “Loads of the weather wanted for a liveable planet, and for dwelling organisms, are made accessible at completely different instances all through galactic historical past.”
The authors clarify that their mannequin will be prolonged as our understanding of rocky exoplanets advances. Missions just like the JWST, PLATO, and others will generate a extra correct understanding of rocky exoplanet properties.
“Such extensions will set up a extra correct understanding of the altering properties of planets over time and switch rocky planets into probes of the Galaxy’s historical past,” the authors conclude.

