In case you might zoom out from Earth far sufficient, our Milky Manner would shrink to only one galaxy amongst roughly fifty neighbours clustered collectively by gravity. These galactic neighbourhoods fluctuate dramatically in dimension, and the most important ones, containing a whole bunch or hundreds of galaxies sure collectively, characterize a number of the most large objects in your complete universe. Their immense scale makes them uniquely beneficial laboratories for testing our understanding of elementary physics.
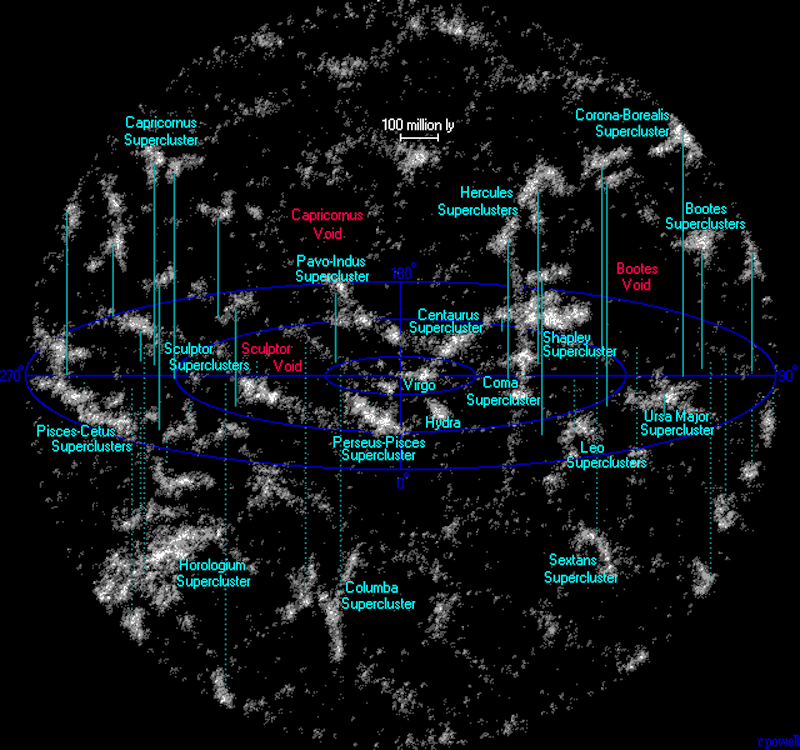 Galactic superclusters, like these within the picture which are the closest clusters to our personal, characterize a number of the largest constructions within the universe (Credit score : Richard Powell)
Galactic superclusters, like these within the picture which are the closest clusters to our personal, characterize a number of the largest constructions within the universe (Credit score : Richard Powell)
A staff led by College of Chicago scientists has now catalogued these colossal constructions utilizing information from the Darkish Power Survey, which spent six years photographing the southern sky from a mountaintop observatory in Chile. By analysing the quantity and distribution of galaxy clusters throughout huge areas of the house, the researchers aimed to probe the invisible forces that form the universe, significantly darkish matter, which pulls galaxies collectively, and darkish power, which drives them aside.
The examine addresses a nagging rigidity in cosmology centred on a quantity referred to as S8, which quantifies how clumpy or structured the universe is. Earlier analysis utilizing a method referred to as weak gravitational lensing had instructed the universe may need barely much less construction right this moment than our greatest theoretical mannequin, Lambda-CDM, predicts primarily based on observations of the early universe. If this discrepancy had been actual, it could point out issues in our elementary understanding, probably requiring physicists to revise our present mannequin.
Nevertheless, the brand new galaxy cluster evaluation tells a special story. The measurements align properly with Lambda-CDM predictions, suggesting our present mannequin stays a very good description of observable actuality. This conclusion issues as a result of it comes from an unbiased methodology. When totally different approaches converge on the identical reply, scientists achieve confidence they’re heading in the right direction.
Galaxy clusters function significantly delicate measuring sticks as a result of their monumental plenty amplify the delicate results of darkish matter and darkish power. But this sensitivity creates challenges, clusters hiding behind each other from our viewpoint can skew calculations, probably main researchers to incorrect conclusions about how a lot darkish matter exists within the universe. The staff believes they’ve efficiently accounted for these and different issues that plagued earlier research.
 Artist impression of the Nancy Grace Roman Telescope will assist to unravel the character of the universe (Credit score : NASA)
Artist impression of the Nancy Grace Roman Telescope will assist to unravel the character of the universe (Credit score : NASA)
The analysis concerned 66 scientists from greater than 50 establishments worldwide, demonstrating the collaborative nature of contemporary cosmology. Trying forward, the subsequent era of large telescopes, together with the Rubin Observatory and the Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope, will dramatically develop the variety of galaxy clusters astronomers can map. Every further cluster gives extra details about the basic forces governing the evolution of our universe.
Supply : Scientists release new survey of the biggest objects in the universe

