A close-by dwarf galaxy might educate astrophysicists one thing new about darkish matter and black holes. It is named Segue 1 and it is about 75,000 mild years away. Segue 1 is among the Milky Method’s smallest and dimmest satellite tv for pc galaxies. It has about 600,000 photo voltaic plenty and is simply as brilliant as about 300 Suns.
Which means the tiny galaxy has a really excessive mass-to-light ratio, which means that it might be dominated by darkish matter. However new analysis factors in a unique path. It exhibits that somewhat than being held collectively by darkish matter, an enormous black gap at its middle is retaining the tiny dwarf intact.
The analysis is titled “Modeling the “Dark-matter Dominated” Dwarf Galaxy Segue 1 with a Supermassive Black Hole,” and it is printed in The Astrophysical Journal Letters. The lead creator is Nathaniel Lujan, a graduate pupil on the College of Texas at Austin.
“Darkish matter and black holes play vital—and sometimes overlapping—roles in galactic dynamics,” the researchers write of their letter. Neither darkish matter nor black holes emit mild, however their mixed large gravitational strengths affect the light-emitting our bodies of their vicinities: stars. So the motions and dynamics of stars inform astronomers lots about black holes and darkish matter.
However since each gravitational forces are current, it takes actual effort to find out how the forces from a galaxy’s black gap and darkish matter are intertwined. “This work illustrates a dynamical modeling method for disentangling these two influences in a delicate case, the dwarf galaxy Segue 1,” the authors clarify.
The character of darkish matter is mysterious as a result of we do not know what it truly is. Black holes are additionally mysterious, however much less so. Because the researchers level out, we all know that the majority large galaxies host a supermassive black gap of their facilities. The lone recognized exception is M33. Astronomers suppose that dwarf galaxies and irregular galaxies might lack them.
“The dwarf spheroidal galaxy, Segue 1, is assumed to have one of many largest ratios of darkish matter to stellar mass,” the authors write. That enormous element of unseen, dominant mass might be found by watching the way in which stars transfer. However the identical factor is true of black holes. The researchers used fashions to attempt to perceive how these forces are at play.
“Our work might revolutionize the modeling of dwarf galaxies or star clusters to incorporate supermassive black holes as an alternative of simply darkish matter halos,” stated Nathaniel Lujan, a graduate pupil at UTSA who led the analysis.
The work Lujan is referring to comes from a joint effort between College of Texas Austin and UT San Antonio. The 2 campuses ran an astronomy course that supplied a chance for college students from each campuses to work with highly effective computer systems and superior modelling aimed toward finding out how gravity impacts galaxies. Astrophysicists Karl Gebhardt (UT Austin) and Richard Anantua (UTSA) ran the course collectively.
“We designed this course to foster collaboration between our two universities,” stated Gebhardt. “Initially, the undertaking was to mannequin the gravitational dynamics inside Segue 1. That it resulted in a major discovery is an actual testomony to the expertise of those college students and their decided, onerous work.”
The scholars ran hundreds of laptop fashions of the movement of stars in Segue 1. The simulations have been primarily based on a number of components, particularly the mass of a black gap and the quantity of darkish matter. Their objective was to land on a mannequin that would clarify the movement of the dwarf galaxy’s stars as noticed by the Keck Observatory.
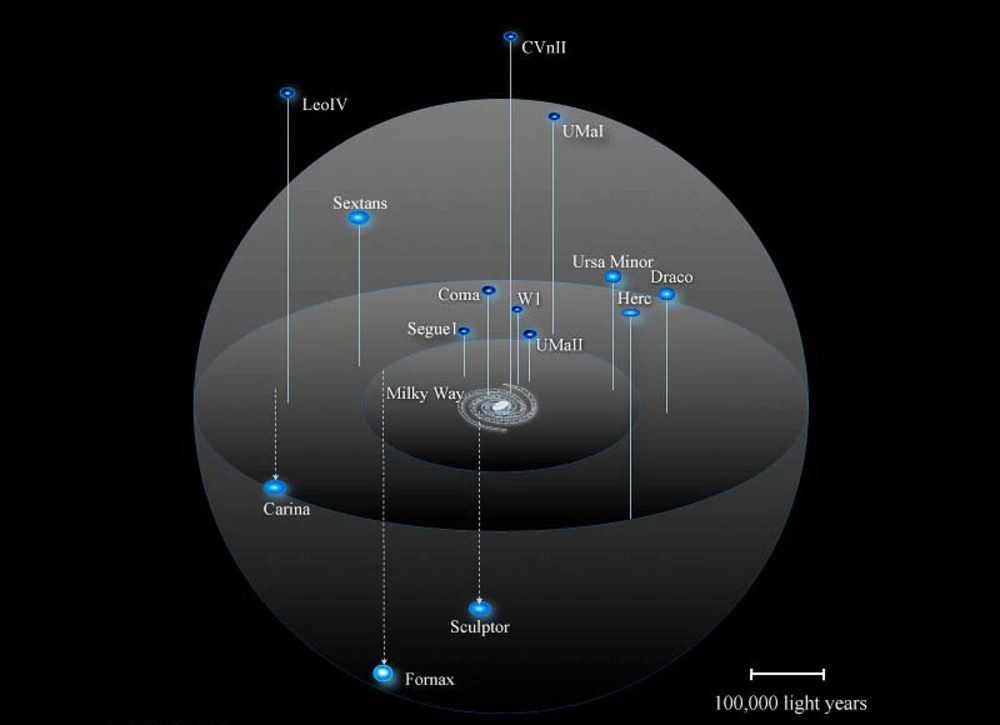 *This picture exhibits the Milky Method and several other of its satellite tv for pc dwarf galaxies, together with Segue 1. Picture Credit score: J. Bullock/M. Geha/R. Powell*
*This picture exhibits the Milky Method and several other of its satellite tv for pc dwarf galaxies, together with Segue 1. Picture Credit score: J. Bullock/M. Geha/R. Powell*
Segue 1 could be very near the Milky Method, and our galaxy’s gravity is stripping stars from the dwarf galaxy, totally on the periphery. Step one was to find out which stars within the galaxy are transferring due to the Milky Method’s tidal stripping. As soon as these have been recognized, they have been eliminated in order to not confuse the outcomes.
From there, the researchers mapped the speeds and instructions of the remaining stars. They discovered that stars in Segue 1’s central area have been whipping across the middle in tight, quick circles. This can be a clear signal {that a} black gap is current, and it was how scientists found the supermassive black gap within the Milky Method.
The fashions containing a number of darkish matter did not match what they have been seeing. Fashions with each darkish matter haloes and black holes got here nearer. The conclusion was clear: the spheroidal dwarf galaxy Segue 1 contained a black gap. “The popular mannequin has a central black gap and a darkish halo,” the authors write.
Discovering a black gap did not contradict all the pieces astronomers learn about dwarf galaxies. They’ve discovered black holes in some dwarf galaxies, however just a few proportion of them have confirmed black holes of their facilities.
The scale of the black gap is what’s stunning.
Black holes in dwarf galaxies lie within the intermediate black gap (IMBH) mass vary, someplace between about 100 and 100,000 photo voltaic plenty. However the black gap in Segue 1 is much extra large. The researchers estimate that it incorporates about 450,000 photo voltaic plenty, exceeding the 100,000 photo voltaic plenty of the galaxy’s stars. In many of the galaxies we all know of, the mass of the central black gap does not exceed that of the celebs. Within the Milky Method, for instance, the SMBH has about 4.3 million photo voltaic plenty, whereas the celebs make up as a lot as 60 billion photo voltaic plenty.
“There’s a sturdy relation between the mass of the black gap and the mass of the host galaxy. The black gap in Segue 1 is considerably bigger than what is anticipated,” defined Gebhardt. “If this massive mass ratio is frequent amongst dwarf galaxies, we must rewrite how these programs evolve.”
What can clarify the mass of Segue 1’s black gap?
The researchers say that the tiny dwarf galaxy might have as soon as had much more stars however misplaced them to the Milky Method by tidal stripping. What we see within the dwarf galaxy could also be solely the remnant of a as soon as a lot bigger galaxy. “Segue 1 is probably going being tidally stripped at giant radii, and we may be witnessing the remnant nucleus of a extra large system,” the authors clarify of their analysis letter.
One other intriguing chance considerations “Little Red Dots” (LRD), a kind of galaxy that the JWST discovered within the very early Universe. Nearly all of LRDs have accreting black holes which might be rather more large than they need to be, when in comparison with the LRDs general mass. This mirrors what’s noticed in Segue 1. “Alternatively, given the excessive black gap mass relative to the stellar mass, Segue 1 is analogous to the Little Pink Dots seen within the early Universe,” the researchers clarify.
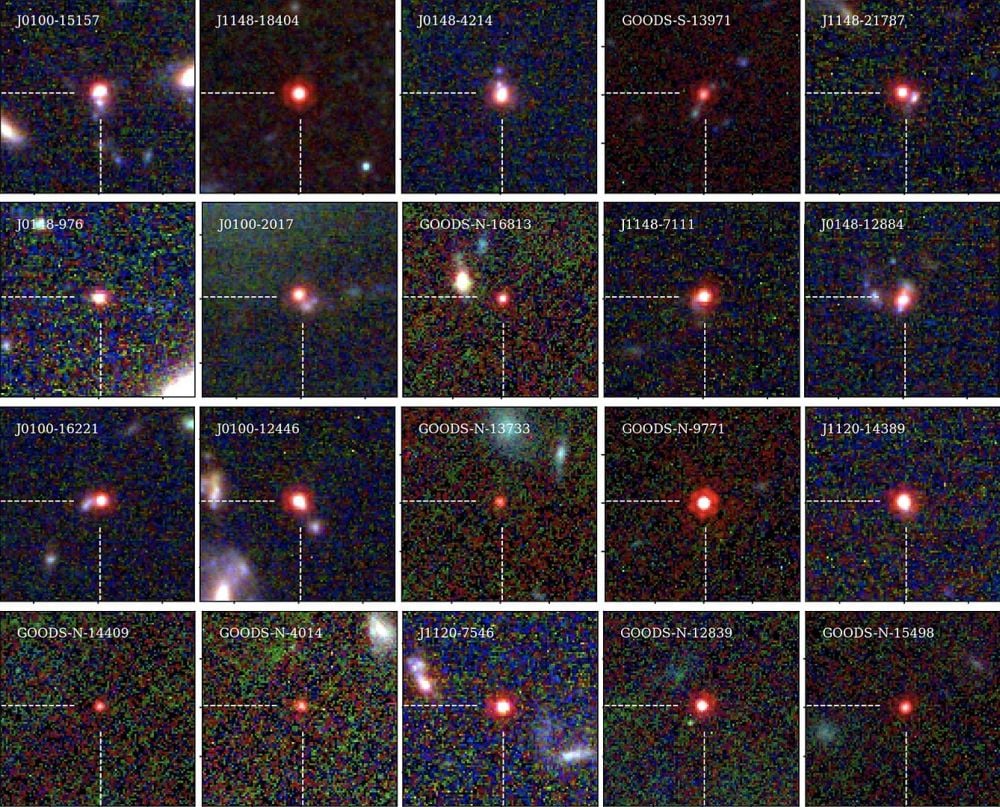 *This picture exhibits a few of the “Little Pink Dots” found by the JWST. Segue 1 is similar to them. Picture Credit score: “Little Pink Dots: An Considerable Inhabitants of Faint Energetic Galactic Nuclei at z ∼ 5 Revealed by the EIGER and FRESCO JWST Surveys” Journal quotation: Jorryt Matthee et al 2024 ApJ 963 129DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad2345URL: CC BY 4.0,
*This picture exhibits a few of the “Little Pink Dots” found by the JWST. Segue 1 is similar to them. Picture Credit score: “Little Pink Dots: An Considerable Inhabitants of Faint Energetic Galactic Nuclei at z ∼ 5 Revealed by the EIGER and FRESCO JWST Surveys” Journal quotation: Jorryt Matthee et al 2024 ApJ 963 129DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad2345URL: CC BY 4.0,
Segue 1 was as soon as considered a darkish matter dominated galaxy, however this analysis contradicts that. “The “dark-matter”-dominated galaxy Segue 1 has most of its mass in materials that’s darkish,” the authors write. “On this case, that materials is primarily within the black gap versus a normal darkish halo.”
The tiny, dim dwarf might be a relic LRD from the early Universe, and if that is the case, so might different dwarf spheroidal galaxies.
“Will probably be illuminating to hold out an analogous investigation with different dwarf spheroidals,” the authors conclude.

