On November twenty seventh, Russia’s Baikonur Cosmodrome skilled a extreme accident that has suspended Russia’s capability to launch payloads and crews to house. Shortly after the Soyuz-MS28 mission launched at 09:27:57 UTC (4:27:57 a.m. EST; 1:27:57 a.m. PST) from Web site 31/6 on the launch heart, drone footage confirmed that the 8U216 cell upkeep cabin was mendacity the other way up within the flame trench. Thankfully, the launch was profitable and the crew it carried – cosmonauts Sergey Kud-Sverchkov and Sergei Mikayev, and NASA astronaut Christopher Williams – arrived safely on the Worldwide Area Station (ISS) just a few hours later.
However, the collapse of this upkeep cabin means Russia’s solely launch web site able to launching missions to the ISS is out of service. Whereas different launch services exist in Russia, such because the Plesetsk Cosmodrome close to Archangel (northern Russia), the Vostochny Cosmodrome in far-eastern Russia, or Gagarin’s Begin at Baikonur, they’re both incapable of reaching the ISS, unable to satisfy crew-launch functionality, or unable to conduct launches in any respect. In consequence, Russia is quickly unable to launch both crews and payloads utilizing Soyuz and Progress spacecraft (respectively) to the ISS in the interim.
In an announcement issued through Telegram, Roscosmos acknowledged the accident whereas emphasizing the success of the mission:
The house rocket launched with out incident. The spacecraft efficiently docked with the Worldwide Area Station. The crew is on board and in good well being. The launch pad was inspected, as is completed earlier than each rocket launch. Injury to a number of launch pad parts was recognized. Injury can happen after launch, so such inspections are obligatory worldwide. The situation of the launch pad is at present being assessed. All vital spare parts can be found for restore, and the injury can be repaired shortly.
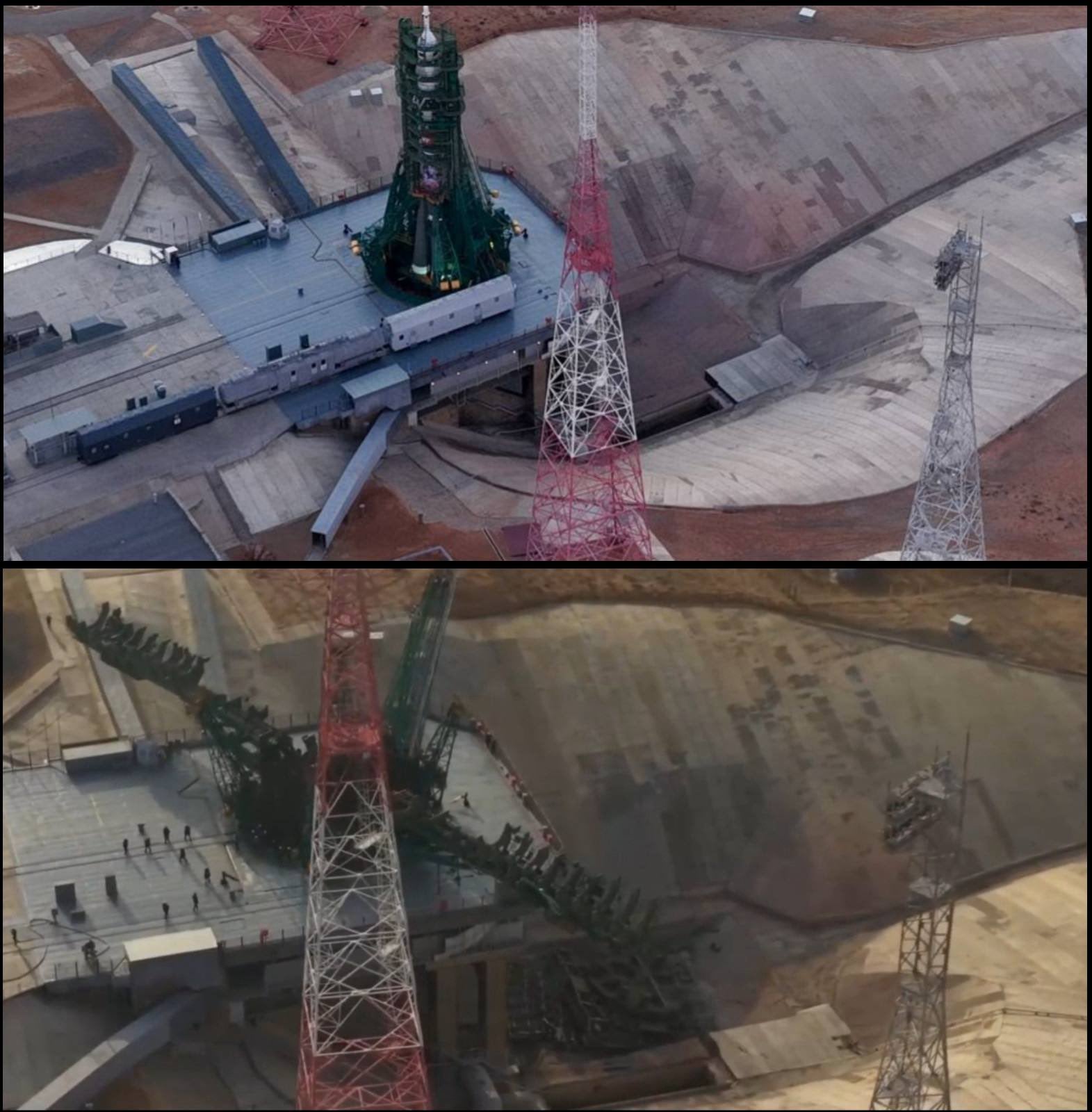 *Drone footage of Web site 31/6 earlier than (above) and after (beneath) launch, displaying the injury to the upkeep cabin. Credit score: Katya Pavlushchenko through X*
*Drone footage of Web site 31/6 earlier than (above) and after (beneath) launch, displaying the injury to the upkeep cabin. Credit score: Katya Pavlushchenko through X*
The 8U216 is a cell, metallic platform weighing over 130 metric tons (144 US tons) that’s prolonged beneath the launch pad throughout launch preparations, together with engine inspection, elimination of protecting covers, and the set up of the “matches” (pyrotechnic gadgets). The construction was initially manufactured in the course of the Sixties, and comparable service cabins are nonetheless being manufactured for different Soyuz launch complexes in Russia right this moment. Based on the launch crew report, the pre-launch preparations had been accomplished with out incident, and the cabin was returned to its nook afterwards.
Nevertheless, post-launch inspections confirmed that the launch precipitated stress variations between the house underneath the launch pad and the nook the place the upkeep cabin is situated. This pulled the service cabin out of the nook and threw it into the flame trench, roughly 20 meters (65.5 ft) beneath. The inspections additionally confirmed that the cabin could not have been correctly mounted in place, or the locks holding it in place failed. Some consultants have acknowledged that the injury to the upkeep cabin was too intensive to restore, and it’ll both have to be changed or rebuilt fully.
As Roscosmos indicated, the mandatory elements can be found in Russia, and NASASpaceFlight just lately famous that sources within the Russian house business have confirmed this. The house company might additionally choose to dismantle the upkeep cabin from Web site 43 on the Plesetsk Cosmodrome, which consists of two launch pads which have been launching R7 rockets because the Sixties. There isn’t a consensus on when Web site 31 can be operational once more, however estimates vary from a number of months to a few years.
This vary in estimates comes down to 2 issues: 1) the idea that the cabin will have to be changed, and a pair of) whether or not different parts had been broken within the accident and likewise have to be repaired/changed. This second merchandise alone would require a number of months of inspection, and Roscosmos might want to carry out a least one uncrewed launch as soon as the upkeep cabin is changed. In any case, this accident signifies that sure deliberate missions must be postponed. This contains the Progress MS-33 cargo launch scheduled for Dec. twenty first, 2025, and will delay the subsequent crewed mission to the ISS, MS-29, scheduled for July 14th, 2026.
 *The upkeep cabin at Web site 31/6. Credit score: TyazhMash/NASASpaceflight.com*
*The upkeep cabin at Web site 31/6. Credit score: TyazhMash/NASASpaceflight.com*
Because of the aforementioned limitations of its different services, Roscosmos won’t be able to shift its flights to different launch websites. And so, Roscosmos has no recourse however to switch the upkeep cabin fully and must postpone all crewed flights to the ISS in the interim. Within the meantime, they might try to launch Progress cargo craft from their Vostochny Cosmodrome, however intensive modifications can be wanted earlier than this will occur. Russia can now not launch crewed craft from the Korou Cosmodrome after Roscosmos withdrew its personnel from the European Spaceport in French Guiana.
The Baikonur Cosmodrome isn’t any stranger to extreme accidents, and that is hardly the worst it has ever seen. That “honor” goes to the Nedelin catastrophe, which occurred on Oct. twenty fourth, 1960, in the course of the testing of a R-16 intercontinental ballistic missile, when the unintentional ignition of its second-stage engines precipitated the missile to blow up. With greater than 54 reported casualties (which weren’t disclosed till many years later), this stays the deadliest catastrophe within the historical past of spaceflight.
However, a disruption in launch functionality is one thing Roscosmos might do with out proper now. Because the invasion of Ukraine in 2022, Russia has confronted worldwide sanctions which have impacted Roscosmos significantly. Other than the numerous business contracts the company has misplaced, there may be additionally the termination of cooperative agreements to develop scientific devices and technical help. On high of that, Roscosmos has both cancelled or had worldwide companions withdraw from a number of profitable joint ventures.
This contains the *ExoMars 2020* mission, a three way partnership with the ESA, and the Venera-D Venus mission, a deliberate collaboration with NASA. Roscosmos has additionally misplaced the launch service contracts it had for 4 ESA missions: the *Galileo M10 and M11* navigation satellites, the Euclid house telescope, and the Earth Cloud, Aerosol and Radiation Explorer (EarthCARE) satellite tv for pc. Initially, these missions had been to be launched utilizing Soyuz rockets, however have since been transferred to different launch suppliers with worldwide companions.
Additional Studying: NASASpaceflight

