Week of January 18
The Orion spacecraft, consisting of the crew module, crew module adapter, and repair module, that can fly 4 astronauts to the Moon on the Artemis II mission within the spring of 2025 is significantly superior over its Artemis I sibling. The variations of the Artemis I and Artemis II Orion spacecraft are deep inside and out of doors the spacecraft.

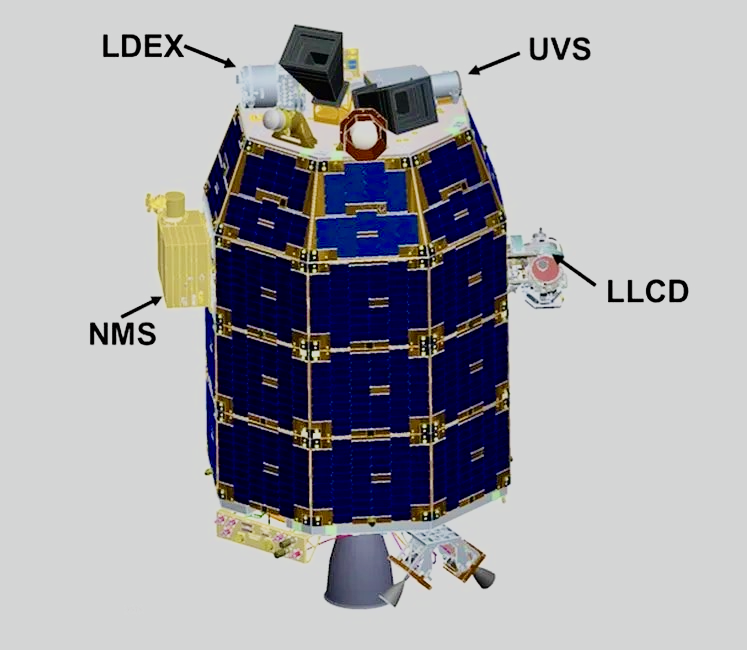
To start with, taking a look at photographs of the Artemis I and Artemis II Orion spacecraft, there are outward variations between the 2 spacecraft. Simply noticeable are two new devices on the Artemis II Orion’s Crew Module Adapter (CMA)1. Highlighted in pink is the Optical Communications System (O2O), the topic of this text.
Optical Communications System (O2O)
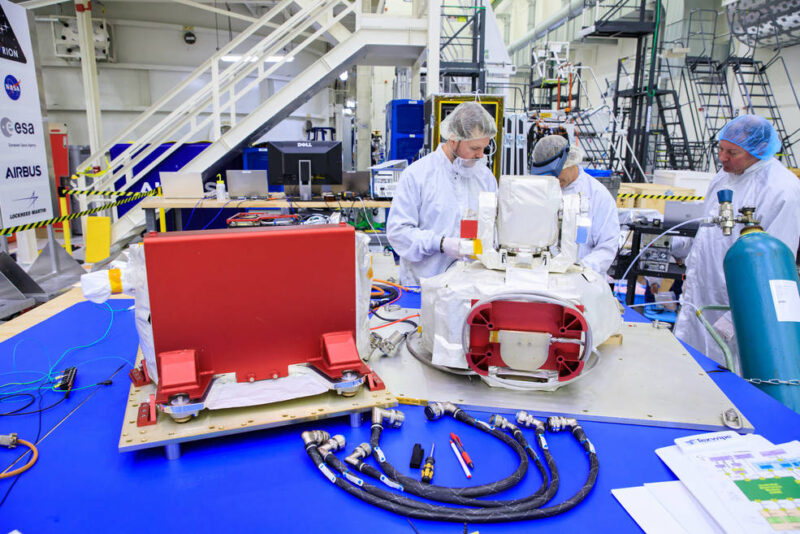

One of many new additions for Artemis II’s Orion spacecraft is the Optical Communications System O2O {hardware}, a DTO (detailed take a look at goal) flying on Artemis II. The Optical Communications System2 is an infra-red laser based mostly communications system that has been in improvement since 2013 by NASA in partnership with the Massachusetts Institute of Know-how’s Lincoln Laboratory.
First gentle for NASA utilizing a laser for two-way communications started in 2013 with the Lunar Laser Communications Demonstration3, part of NASA’s Lunar Environment and Mud Atmosphere Explorer4 spacecraft that was to review the skinny environment of the Moon. MIT’s Lincoln Laboratory constructed the LLCD’s house and floor terminals. The LLCD mounted on LADEE consisted of a ten” (25 cm) cassegrain telescope with a photo voltaic rejection window that allowed the terminal to level proper on the solar with no injury.
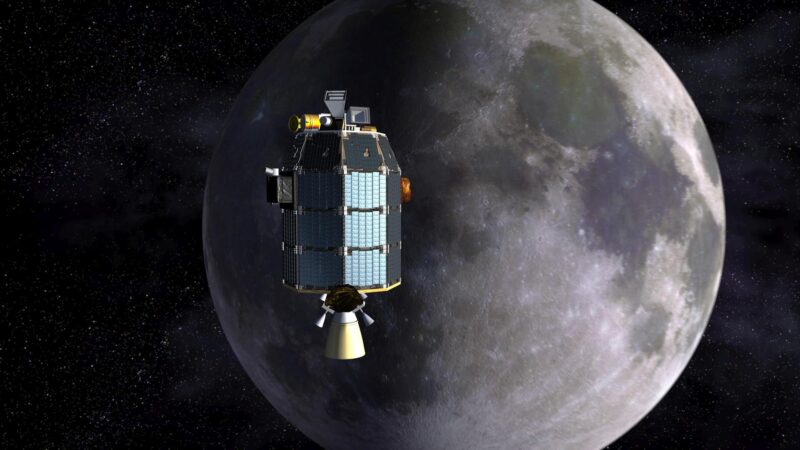

First gentle on October 17, 2013 was historical past making, with a demonstrated information transmission fee of 622 Mbps, which was 6 occasions larger than something beforehand reached within the huge 239,000 miles (385,000 km) distance of the Moon and the receiving terminal in New Mexico. However equally historic was the 20 Mbps add fee from the New Mexico floor station to the LLCD terminal on LADEE, which was 5,000 occasions sooner than any earlier transmission to the Moon. Though LLCD wasn’t deliberate as greater than a technological demonstrator, LLCD was so profitable that on a number of events the LADEE spacecraft’s whole information buffer was downloaded in minutes5.
White radio alerts have served properly of their communications function for the reason that daybreak of house exploration, the LLCD on LADEE confirmed that laser presents the benefit of decrease weight and dimension but having a lot larger information transmission capabilities. The lessened weight and dimension penalty and extra energy are permitting mission designers to game-out new sensors and information for deep house missions that may have been troublesome or worse beforehand.
As soon as LLCD testing was finishing-up, NASA-Glenn was tasked with shifting to the following step, the Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD).
LCRD is made-up of three elements, a geosynchronous-orbit system based mostly on an LLCD-like Lincoln Laboratory design, and two floor terminals. The LCRD geosynchronous orbiting satellite tv for pc was launched on December 7, 2021 and now sits 22,000 miles above the floor of Earth. Since its launch, LCRD has been conducting experiments to refine laser communications in house. However it’s only so helpful as a relay when not getting used to advertise precise missions in house. One thing was wanted to take laser communications to the following stage whereas making wanted adjustments to suitable with LEO spacecraft.
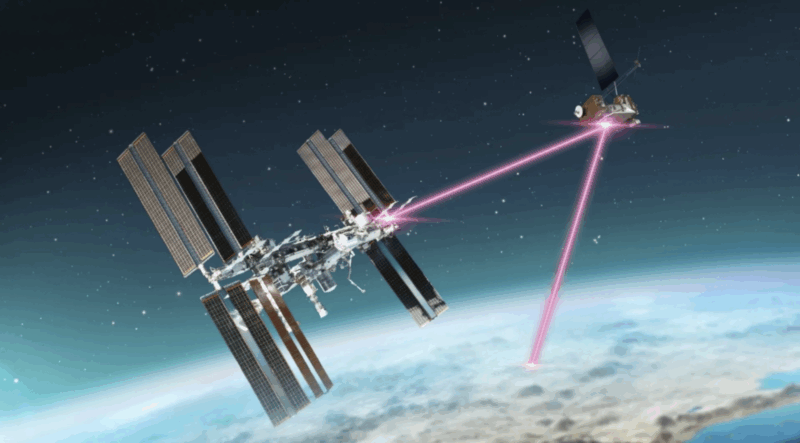
Pretty much as good because the design of the LLCD terminal on LADEE was, the design of LCRD wanted to be up to date resulting from limitations of LLCD. These updates made to the design of LCRD would enhance its design to be used with satellites in LEO. One limitation of LLCD was its “field of vision”, which is the course by which the terminal can level the telescope when LCRD is close by of the LEO satellite tv for pc. Since a LEO satellite tv for pc orbits at a velocity of over 17,000 mph (7.6 km/s), any laser terminal goes to have to maneuver quick to remain locked-on between the LEO satellite tv for pc and the geosynchronous LCRD relay satellite tv for pc. The unique LLCD terminal telescope design was restricted to about 20 levels of movement within the vertical and horizontal frames. A two-axis gimbal was added to the LCRD design that enabled higher pointing by the horizon as a satellite tv for pc strikes by LEO. NASA additionally labored with trade to make the laser terminal, or telescope, extra simply manufactured, leading to MASsOT, the Modular, Agile, Scalable Optical Terminal[^footnote_6]. LEO was certainly the following step for NASA’s laser communications efforts.
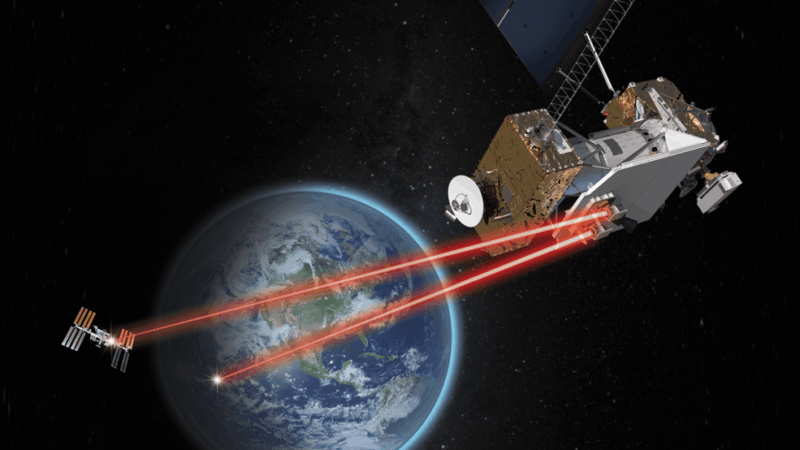
Now enter ILLUMA-T6. NASA’s ILLUMA-T (Integrated LCRD Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal) was launched to ISS on November 9, 2023 on Business Resupply 29 (CR-29). ILLUMINA-T , a partnership of MIT’s Lincoln Lab, NASA’s Communications and Navigation (SCaN), Goddard Area Flight Heart, and Johnson Area Heart, is the primary demonstration of an end-to-end laser communications system. ILLUMINA-T is in regards to the dimension of a house-hold fridge and is rather more succesful than LLCD, as one would count on given the march of know-how.

Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) and NASA’s Hawaiian floor station. Picture Credit score: NASA
Throughout testing on ISS, laser communications have proven a 2x to 6x enchancment over radio frequency based mostly communications within the quantity of knowledge that may be transmitted again to Earth, reaching transmission charges of as much as 1.2 Gbps return and beginning ahead charges of 51-155 Mbps. But additionally essential is the development in safety that the usage of a centered communications system permits. Merely put, RF alerts from house are a lot tougher to focus than a laser beam, making laser a lot more durable for others to tune-into in comparison with RF.
The Artemis II Orion spacecraft will carry its model of ILLUMINA-T, O2O will present 260 Mbps switch speeds permitting the Artemis II astronauts to share excessive decision photographs and video from the Moon. O2O builds upon the successes of NASA’s 2021 Laser Communications Relay Demonstration, LCRD.

