NASA and JPL are working laborious to develop extra autonomy for his or her Mars rovers. Each of their present rovers on Mars—MSL Curiosity and Perseverance—are partly autonomous, with Perseverance being a bit of extra superior. In reality, creating extra autonomous navigation was an specific a part of Perseverance’s mission.
Each rovers use a system known as AutoNav, with Perseverance’s system being extra highly effective and extra well-developed. In the course of the rover’s first yr on Mars, it travelled a complete of 17.7 km, and AutoNav was used to judge about 88% of its route.
One of many principal obstacles to even better autonomous navigation is position-finding. The longer Perseverance drives autonomously, the bigger the error turns into in its understanding of the place it really is on the Martian floor. And if it would not know the place it’s, it might’t precisely plan and navigate a route. It’s, in impact, misplaced.
“Not till we’re misplaced do we start to grasp ourselves.” — Henry David Thoreau
Three totally different methods mix to create Perseverance’s autonomous operations: AutoNav, AEGIS, and OBP. AutoNav makes use of photos and maps to plan routes, and AEGIS, the Autonomous Exploration for Gathering Elevated Science, makes use of onboard wide-angle imagery to pick out remark targets for the rover’s SuperCam instrument. OBP (OnBoard Planner) schedules deliberate operations to cut back the rover’s power consumption. All three methods mix to offer Perseverance better autonomy.
All of those methods and the better operational autonomy they grant the rover are geared toward acquiring most science outcomes.
Perseverance’s autonomy took one other step ahead with the event of Mars International Localization (MGL). There isn’t any GPS on Mars (no less than, not but) so pinpointing its place on the floor is a roadblock to the rover’s better autonomy and higher science outcomes. The system is defined in a convention paper titled “Censible: A Robust and Practical Global Localization Framework for Planetary Surface Missions.”
“That is type of like giving the rover GPS. Now it might decide its personal location on Mars,” mentioned JPL’s Vandi Verma, chief engineer of robotics operations for the mission. “It means the rover will be capable to drive for for much longer distances autonomously, so we’ll discover extra of the planet and get extra science. And it might be utilized by nearly every other rover touring quick and much.”
Perseverance’s longest autonomous drive is 699.9 meters over three days. Place uncertainty prevents it from extending that distance. The farther it drives autonomously, the bigger its place uncertainty turns into.
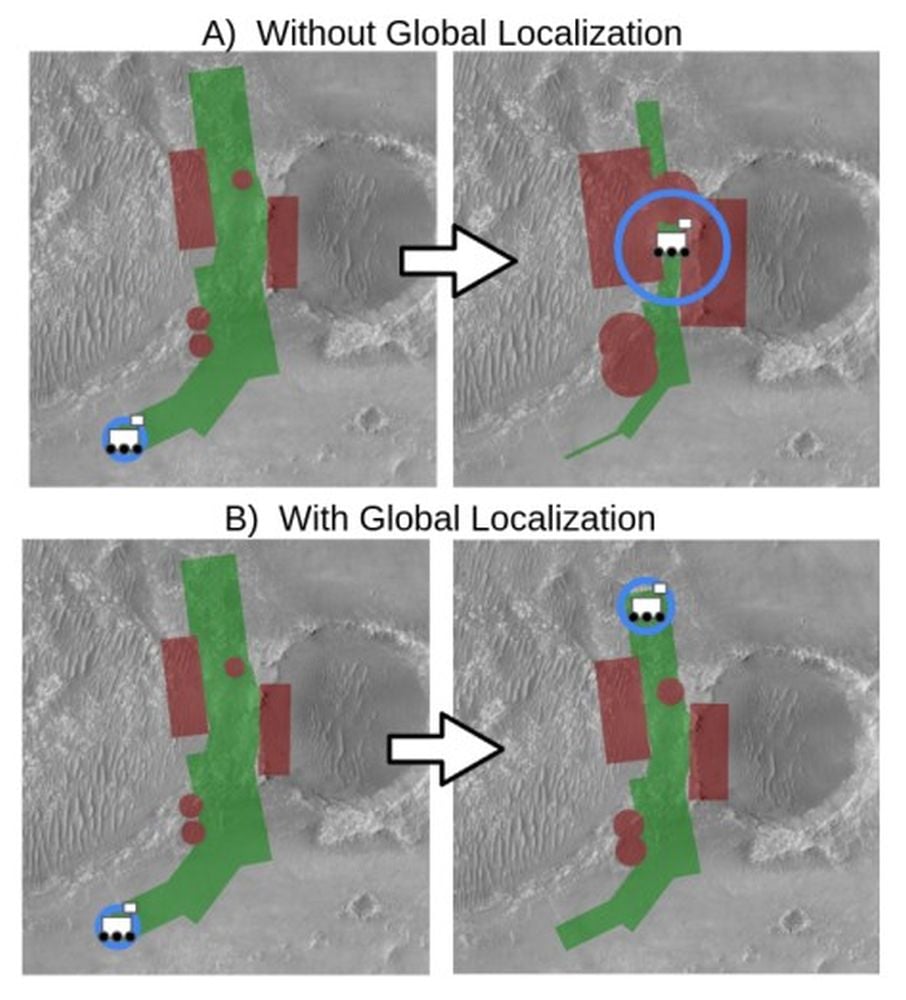 *This determine exhibits what occurred when Perseverance tried an extended drive via a slim hall on Sol 385. The blue circles present how the rover’s place uncertainty grows over time with out MGL. The purple polygons and circles present identified hazards close to its route. As soon as the uncertainty turns into giant sufficient, the potential footprint of the hazards additionally grows, and the rover is basically misplaced and may’t proceed with out human intervention. Within the backside panels exhibiting MGL’s impact, the error would not develop as giant, the hazard footprint would not develop close to as giant, and the rover can journey additional with out assist. Picture Credit score: Nash et al. 2026. ICRA*
*This determine exhibits what occurred when Perseverance tried an extended drive via a slim hall on Sol 385. The blue circles present how the rover’s place uncertainty grows over time with out MGL. The purple polygons and circles present identified hazards close to its route. As soon as the uncertainty turns into giant sufficient, the potential footprint of the hazards additionally grows, and the rover is basically misplaced and may’t proceed with out human intervention. Within the backside panels exhibiting MGL’s impact, the error would not develop as giant, the hazard footprint would not develop close to as giant, and the rover can journey additional with out assist. Picture Credit score: Nash et al. 2026. ICRA*
Within the present navigation system, Perseverance drives till its place error accumulates and turns into too giant to journey safely anymore. Then it takes a 360 diploma panoramic picture. That is the place a human being intervenes by manually matching the rover’s place to a worldwide map.
“People have to inform it, ‘You’re not misplaced, you’re secure. Maintain going,’” Verma mentioned. “We knew if we addressed this drawback, the rover might journey a lot farther day-after-day.”
This new technique is extra highly effective. It nonetheless includes a 360 panorama of the rover’s present location, however no human intervention is required. The picture is a monochromal purple picture, which most intently matches that of the HiRISE photos from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
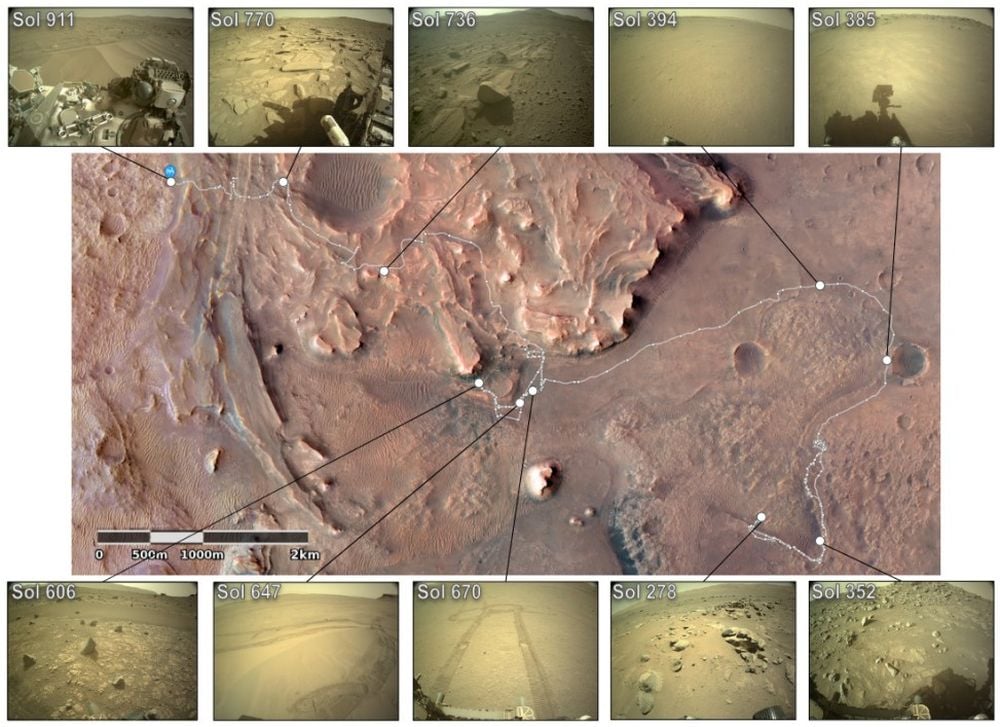 *Every white dot on this picture represents one of many 264 panoramic photos Perseverance captured in Jezero Crater. They seize the rover’s total mission as much as Sol 911 as travelled via a number of terrain sorts. Picture Credit score: Nash et al. 2026. ICRA*
*Every white dot on this picture represents one of many 264 panoramic photos Perseverance captured in Jezero Crater. They seize the rover’s total mission as much as Sol 911 as travelled via a number of terrain sorts. Picture Credit score: Nash et al. 2026. ICRA*
This new improvement is partly due to Perseverance’s sidekick, the Ingenuity Helicopter. Ingenuity was a exceptional success. It accomplished 72 flights over three years earlier than struggling rotor harm and ending its mission in January, 2024. With its demise, a strong microprocessor onboard Perseverance that was devoted to speaking with Ingenuity grew to become accessible. Perseverance can now pinpoint its floor location to inside 10 inches, and it solely wants about two minutes to take action.
Utilizing that tiny digital mind, the system employs an algorithm to match onboard terrain maps created by orbiters with panoramic photos from Perseverance’s cameras. This lets the rover discover its location with out human intervention. Perseverance used this method with nice success on two days of regular operations. As soon as on February 2nd, and as soon as on February sixteenth. The system has the potential to enormously enhance the space Perseverance can cowl with out human intervention. Since it might additionally carry out scientific observations with some autonomy, MGL has the potential to pay huge scientific dividends.
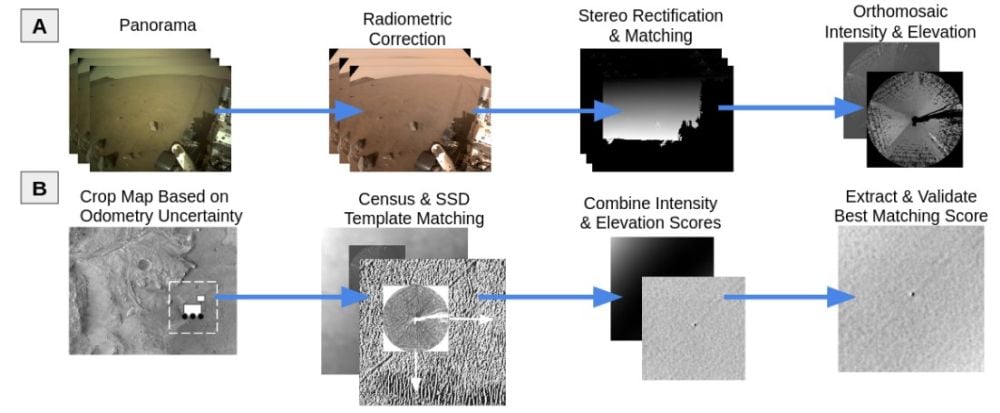 *These panels give a high-level view of the worldwide localization framework. Within the prime row, rover photos are reworked to match the orbital map. Within the backside row, the algorithm matches the rover photos to the orbital map. Picture Credit score: Nash et al. 2026. ICRA*
*These panels give a high-level view of the worldwide localization framework. Within the prime row, rover photos are reworked to match the orbital map. Within the backside row, the algorithm matches the rover photos to the orbital map. Picture Credit score: Nash et al. 2026. ICRA*
“It allows the rover to be commanded to drive for probably limitless drive distances with out requiring localization from Earth,” the authors write within the convention paper. The system will be utilized to different robotic missions in response to the authors. “Past Perseverance, absolute place estimation is vital for future planetary robotic missions.”
This animation exhibits how the system works. It lets Perseverance pinpoint its location utilizing an onboard algorithm that matches terrain options in navigation digital camera pictures (the round picture, known as an orthomosaic) to these in orbital imagery (the background). Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech.
“We’ve given the rover a brand new skill,” mentioned Jeremy Nash, a JPL robotics engineer who led the group engaged on the challenge below Verma. “This has been an open drawback in robotics analysis for many years, and it’s been tremendous thrilling to deploy this answer in house for the primary time.”


