
The hunt for alien life and its radio indicators from past our photo voltaic system remains to be arising dry. However, it is not for lack of on the lookout for doable superior civilizations.
A latest search led by Jean-Luc Margot of UCLA’s Earth, Planetary, & House Sciences Division scanned stars inside just a few hundred light-years of Earth. Margot and his workforce seemed for radio signatures of superior civilizations in a sampling of “TESS Objects of Curiosity.” TESS is the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite tv for pc doing an all-sky survey of close by stars and their doable planets. The paper is revealed on the arXiv preprint server.
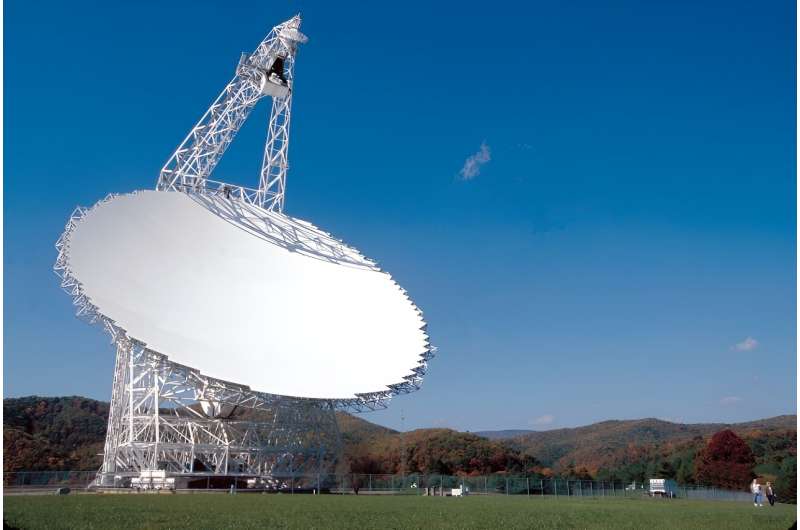
Margot is founding father of UCLA SETI’s “Are Alone within the Universe?” challenge. It seems to be for proof of different civilizations within the universe and pulls info from radio emissions which may determine them. From 2020 to 2023, Margot’s workforce pointed the Inexperienced Financial institution Telescope towards the TESS objects to seize radio emissions coming from a selected area of area. The workforce used the L-band receiver on the scope, which scans a area of the spectrum between 1.15 and 1.73 GHz. That is a narrowband “window” the place they counsel it may be doable to detect alien indicators in the event that they exist.
It might be thrilling to discover a “wow!” sign from one other civilization. However, that did not occur this time. The workforce wrote a paper detailing their work, and concluded, “Based mostly on our observations, we discovered that there’s a excessive likelihood (94.0%–98.7%) that fewer than ~0.014% of stars sooner than M8 inside 100 percent host a transmitter that’s detectable in our search.” That is a quite definitive conclusion that close by stars aren’t sending cosmic “hiya” greetings in our course.
What would superior civilizations use to speak throughout area?
The hunt for extraterrestrial signatures from superior civilizations is a comparatively younger science. The primary searches started within the mid-Twentieth century. Since then, SETI astronomers have discovered search methods utilizing obtainable radio telescopes. However, it nonetheless faces some bodily realities.
It is no shock that communications throughout the gulfs of area are tough. There is a time lag, in fact. A sign we ship to Proxima Centauri saying “Howdy” would take simply over 4 years to get there on the pace of sunshine. If anyone exists there, they’d despatched a “Hello neighbor” again to us—once more on the pace of sunshine. After all, it takes one other 4 years or so to journey between us. That is eight years to ascertain a connection.
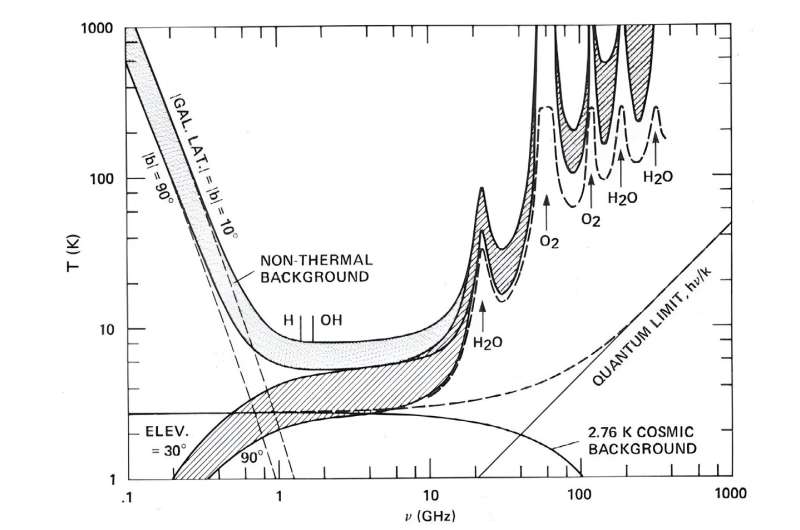
Take into account additionally that indicators need to move by no matter “stuff” exists in area, like fuel and dirt. These take up some types of radiation. Nevertheless, radio indicators get by fairly properly, which makes them a sensible choice for an interstellar greeting. Subsequent, you need to contemplate what frequencies to make use of. It seems these between 1 and 10 GHz are fairly helpful as a result of they keep away from the galaxy’s “hum” at decrease frequencies. At increased frequencies, our personal ambiance (and possibly these of different planets) can drown out any indicators.
So, astronomers assume that one other technologically superior civilization may use that vary, too. After all, there are additionally language variations and cultural assumptions, which might form any messages. However, at the least having a frequency vary helps get the hunt going.
What the workforce did
Of their SETI search, Margot’s workforce reasoned that they’d have to pattern for emissions made by technologically savvy beings. They wrote, “The seek for technosignatures supplies a chance to acquire strong detections with unambiguous interpretations. An instance of such a technosignature is a narrowband (say, <10 Hz at gigahertz frequencies) sign from an emitter positioned past the photo voltaic system. Detection of a sign with these traits would offer ample proof for the existence of one other civilization as a result of pure settings can’t generate such indicators.”
In different phrases, they wished to exclude pure emissions from the pattern. These can be radio indicators created by naturally occurring occasions and objects. In our personal photo voltaic system, for instance, Jupiter has sturdy radio emissions. So does the solar, and Earth does, too, for that matter, however we will exclude these simply. Outdoors of the solar and planets, pulsars give off sturdy indicators, as do star-forming areas, and supernova remnants. And, in fact, there are very energetic emitters akin to quasars and the areas round black holes. All of these sources need to be omitted from any surveys on the lookout for techno-signatures.
So, the GBT captured emissions from round 11,680 stars and their planetary methods that lay between 5,385 and 18,173 light-years away. The observations occurred throughout two-hour periods on April 22, 202, April 28, 2021, Could 22, 2022, and Could 13, 2023. They did two scans of about 2.5 minutes every on chosen pairs of sources. Then, they processed the information, which included about 37 million narrowband detections of emissions. The ensuing conclusion was that there aren’t any superior civilizations close by which are transmitting in that vary of frequencies.
Are we alone? Crowdsourcing the search
The search by Margot and his workforce additionally incorporates citizen scientists from around the globe in a challenge referred to as “Are We Alone within the Universe?” The collaboration has netted greater than 300,000 classifications of radio indicators within the close by neighborhood despatched in by greater than 10,000 volunteers.
As well as, Margot provides a SETI course at UCLA for graduate college students. The attendees be taught to collect and analyze information from radio telescopes concerned within the search. It is an eye-opening exploration of the completely different disciplines concerned within the seek for extraterrestrial intelligence. They embrace sign processing expertise, data-gathering, telecommunications, statistics, and information science.
Whereas the newest seek for indicators confirmed no proof of technological civilizations in our near-Earth neighborhood, it does ship an essential message: in the event that they’re “on the market” they aren’t in that sampling. As in a lot of science, the shortage of a conclusive sign is simply as essential as a conclusive one. For one factor, it researchers additionally want to differentiate between indicators from area and indicators from expertise right here on Earth. Sorting these out is a vital a part of any search paradigm.
The complete train additionally allowed the workforce to refine its pipelines of knowledge and processing algorithms. That will likely be helpful sooner or later if, and when, a sign is discovered that would point out clever life on the market. And, there may be nonetheless lots of sky to discover within the hunt for technologically superior civilizations.
Extra info:
Jean-Luc Margot et al, A Seek for Technosignatures Round 11,680 Stars with the Inexperienced Financial institution Telescope at 1.15-1.73 GHz, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2308.02712
Quotation:
Astronomers scan 11,680 close by stars for indicators from superior civilizations (2023, August 15)
retrieved 15 August 2023
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

