Astronauts will check drive NASA’s Orion spacecraft for the primary time throughout the company’s Artemis II check flight subsequent 12 months. Whereas most of the spacecraft’s maneuvers like large propulsive burns are automated, a key check referred to as the proximity operations demonstration will consider the handbook dealing with qualities of Orion.
In the course of the roughly 70-minute demonstration set to start about three hours into the mission, the crew will command Orion via a sequence of strikes utilizing the indifferent higher stage of the SLS (House Launch System) rocket as a mark. The in-space propulsion stage, referred to as the ICPS (interim cryogenic propulsion stage), consists of an roughly two-foot goal that shall be used to judge how Orion flies with astronauts on the controls.
“There are at all times variations between a floor simulation and what an precise spacecraft will fly like in area,” stated Brian Anderson, Orion rendezvous, proximity operations, and docking supervisor throughout the Orion Program at NASA’s Johnson House Middle in Houston. “The demonstration is a flight check goal that helps us scale back threat for future missions that contain rendezvous and docking with different spacecraft.”
After NASA’s Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, and Christina Koch, and CSA (Canadian House Company) astronaut Jeremy Hansen are safely in area, the moon rocket’s higher stage will fireplace twice to place Orion on a excessive Earth orbit trajectory. Then, the spacecraft will mechanically separate from the rocket stage, firing a number of separation bolts earlier than springs push Orion a secure distance away.
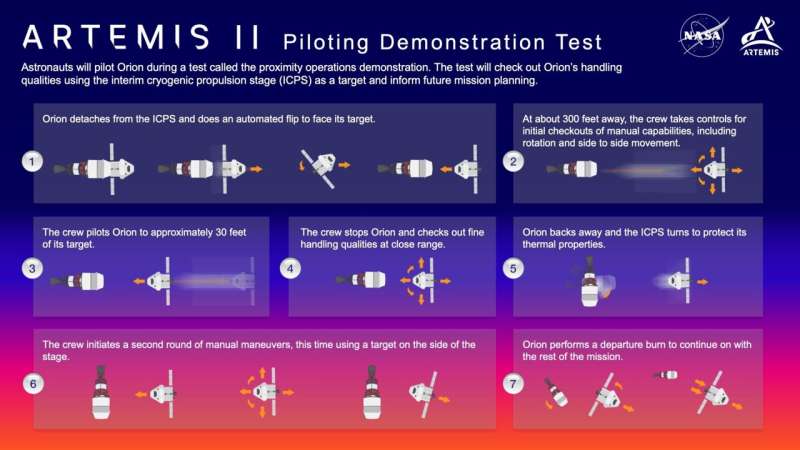
Because the spacecraft and its crew transfer away, Orion will carry out an automatic backflip to show round and face the stage. At roughly 300 toes away, Orion will cease its relative movement. The crew will take management and use the translational and rotational hand controllers and show system to make very small actions to make sure Orion is responding as anticipated.
Subsequent, the crew will very slowly pilot Orion to inside roughly 30 toes of the stage. A two-foot auxiliary goal mounted inside the highest of the stage, just like the docking goal utilized by spacecraft visiting the Worldwide House Station, will information their goal.
“The crew will view the goal through the use of a docking digital camera mounted contained in the docking hatch window on the highest of the crew module to see how effectively aligned they’re with the docking goal mounted to the ICPS,” Anderson stated. “It is a good stand in for what crews will see once they dock with Starship on Artemis III and to the Gateway on future missions.”
About 30 toes from the stage, Orion will cease and the crew will checkout the spacecraft’s nice dealing with qualities to judge the way it performs in shut proximity to a different spacecraft. Small maneuvers carried out very near the ICPS shall be carried out utilizing the response management system thrusters on Orion’s European Service Module.
Orion will then again away and permit the stage to show to guard its thermal properties. The crew will observe the stage, provoke a second spherical of handbook maneuvers utilizing one other goal mounted on the aspect of the stage, strategy inside roughly 30 toes, carry out one other nice dealing with high quality try, then again away.
On the finish of the demonstration, Orion will carry out an automatic departure burn to maneuver away from the ICPS earlier than the stage then fires to re-enter Earth’s ambiance over a distant location within the Pacific Ocean. Throughout Orion’s departure burn, engineers will use the spacecraft’s docking digital camera to assemble exact positioning measurements, which is able to assist inform navigation throughout rendezvous actions on future missions within the lunar atmosphere, the place there is no such thing as a GPS system.
As a result of the Artemis II Orion isn’t docking with one other spacecraft, it isn’t outfitted with a docking module containing lights and due to this fact is reliant on the ICPS to be lit sufficient by the solar to permit the crew to see the targets.
“As with a lot of our exams, it is attainable the proximity operations demonstration will not go precisely as anticipated,” stated Anderson. “Even when we do not accomplish each a part of the demonstration, we’ll proceed on with the check flight as deliberate to perform our main aims, together with evaluating Orion’s methods with crew aboard within the deep area atmosphere and retaining the crew secure throughout the mission.”
The roughly 10-day Artemis II flight will check NASA’s foundational human deep area exploration capabilities, the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft, for the primary time with astronauts and can pave the way in which for lunar floor missions, together with touchdown the primary lady, first particular person of colour, and first worldwide companion astronaut on the moon.
Quotation:
Key check drive of Orion on NASA’s Artemis II to assist future missions (2024, March 20)
retrieved 21 March 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.

