Astronomers have imaged a feeding black hole-powered quasar on the very fringe of the universe, so far-off that it was seen because it appeared lower than 1 billion years after the Huge Bang.
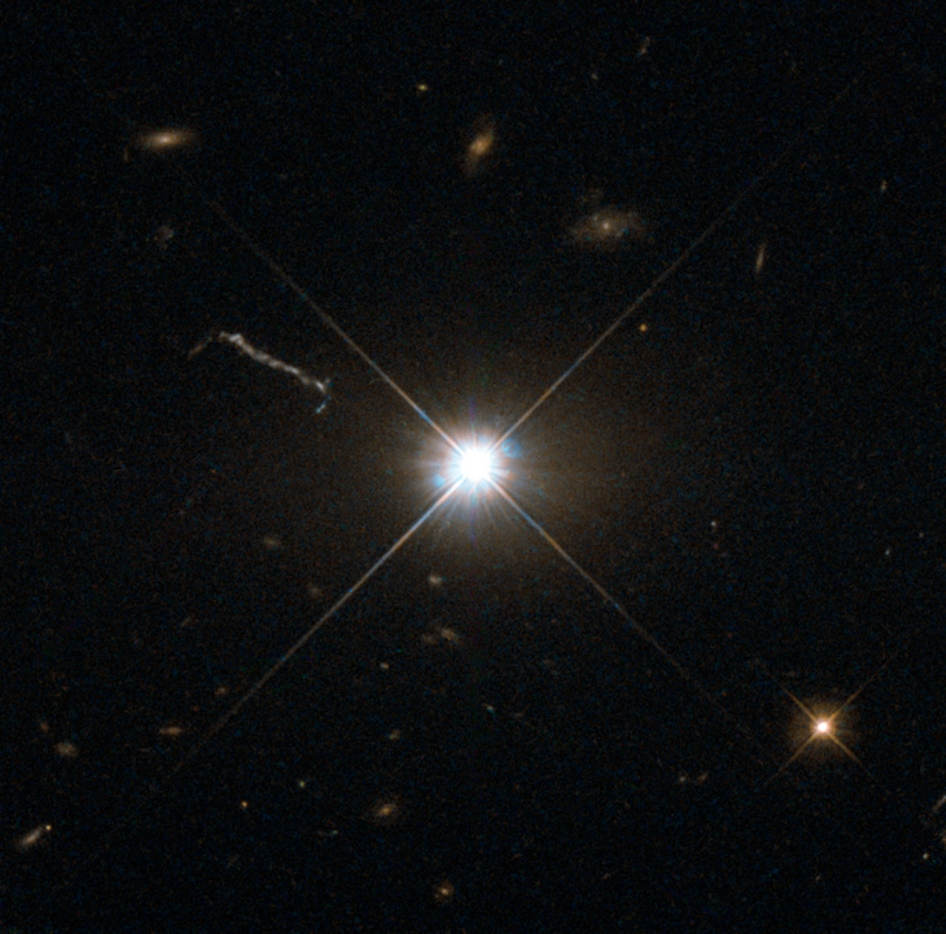
The quasar, designated SDSS J114816.64+525150.3, is powered by a supermassive black gap over 3 billion occasions the mass of the solar positioned within the course of the constellation Ursa Main. It was imaged by the Digital Telescope Undertaking in Italy utilizing its 356 mm (14-inch) aperture robotic unit.
“It is a document end result, to my information: By no means earlier than, the truth is, has a 350mm aperture telescope regarded to date again in area and time,” Digital Telescope Undertaking founder and astrophysicist Gianluca Masi instructed House.com through e-mail. “It’s so far-off that its mild, noticed at present from Earth, began its journey nearly 12.9 billion years in the past, when the universe was lower than 900 million years previous, in comparison with the present age estimated at 13.8 billion years.”
Associated: Brightest quasar ever seen is powered by black gap that eats a ‘solar a day’
SDSS J114816.64+525150.3 represents probably the most distant seen celestial physique within the northern sky that can be observable in seen mild, in line with the astronomer.
When found in SDSS J114816.64+525150.3, this quasar was probably the most distant ever noticed. Within the intervening 20 or so years, astronomers found 8 quasars positioned additional away. This contains P172+18, which stays probably the most distant quasar ever seen, positioned at 13.02 billion mild years away, which means we see it because it was when the 13.8 billion-year-old universe was simply round 780 million years previous.
The distinction is that P172+18 and the opposite extra distant quasars had been recognized in radio mild after which in ultraviolet (UV) to the near-infrared (NIR) mild, all invisible to the human eye, whereas SDSS J114816.64+525150.3 has been seen within the mild that our eyes have advanced to see.

Quasars could be the brightest objects within the universe, however recognizing them in seen mild is a giant deal
SDSS J114816.64+525150.3, like all quasars, owes its brightness and its standing as probably the most energetic object within the sky to the monstrous compact object that sits at its coronary heart: A supermassive black gap that’s greedily consuming matter from its rapid setting.
These black holes can have lots thousands and thousands and even billions of occasions that of the solar. As they eat fuel and dirt from a flattened plate of fabric round them known as an “accretion disk,” their immense gravity generates super tidal forces in that disk. This heats the accretion disk’s fuel and dirt to unbelievable temperatures, leading to it glowing brightly in mild throughout the electromagnetic spectrum.
Along with this, matter that is not gorged on by cosmic titan is channeled to its poles by highly effective magnetic fields. From there, this matter is blasted out as jets touring at close to mild velocity. These jets are additionally accompanied by shiny electromagnetic emissions.
Altogether, this typically makes these areas (also called lively galactic nuclei (AGNs)) brighter than the mixed mild of each star in the whole galaxy that surrounds them.
But, when they’re as distant as billions of light-years away, these highly effective celestial objects are nonetheless powerful to watch. As an illustration, as shiny and highly effective as SDSS J114816.64+525150.3 is, within the sky over Earth, the north star Polaris remains to be a billion occasions brighter as seen from our planet.
Seeing any object this far again in time in seen mild is extraordinarily tough. That’s as a result of as mild (electromagnetic radiation) travels, it’s redshifted, transferring nearer to the infrared area of the electromagnetic spectrum. The longer mild travels, the extra excessive this redshift impact is.

“Because of the enlargement of the universe, electromagnetic radiation experiences the so-called redshift, a cosmological impact that determines a shift in the direction of the purple finish of the noticed wavelength, extra pronounced the farther the supply is,” Masi said in a statement. “On this quasar the extent of the phenomenon is such that the majority of its mild is shifted into the infrared, with solely a tiny fraction remaining within the excessive purple facet of the seen area. The only a few recognized quasars farther away are observable solely within the infrared.”
The detection of this excessive object at these super distances exemplifies the usefulness of the Digital Telescope Undertaking, based in 2006, and its remotely managed robotic telescopes.
Among the many initiatives, different observational targets have been comets, supernovas, eclipses, and meteor showers, delivering pictures of those celestial our bodies to thousands and thousands of individuals throughout the globe. Even so, the commentary of SDSS J114816.64+525150.3 could be the Digital Telescope Undertaking’s best achievement up to now.
“Our instrument has succeeded within the unbelievable feat of immortalizing probably the most distant celestial physique within the northern sky observable on the wavelengths of seen mild, on the fringe of the universe,” Masi concluded.

