There is no such thing as a denying the superior predictive energy of Albert Einstein’s 1915 idea of gravity, basic relativity — but, the idea nonetheless has inconsistencies on the subject of calculating its impact on huge distances. And new analysis suggests these inconsistencies might be the results of a “cosmic glitch” in gravity itself.
Within the 109 years because it was first formulated, basic relativity has remained our most interesting description of gravity on a galactic scale; repeatedly, experiments have confirmed its accuracy. This idea has additionally been used to foretell points of the universe that might later be observationally confirmed. This contains the Massive Bang, the existence of black holes, the gravitational lensing of sunshine and tiny ripples in spacetime known as gravitational waves.
But, just like the Newtonian idea of gravity that it surpassed, basic relativity could not provide us the complete image of this enigmatic power.
“This mannequin of gravity has been important for all the pieces from theorizing the Massive Bang to photographing black holes,” Robin Wen of the College of Waterloo’s Mathematical Physics Orogram stated in an announcement. “However once we attempt to perceive gravity on a cosmic scale, on the scale of galaxy clusters and past, we encounter obvious inconsistencies with the predictions of basic relativity.”
Associated: ‘Quantum gravity’ might assist unite quantum mechanics with basic relativity ultimately
“Gravity turns into round one % weaker when coping with distances within the billions of sunshine years,” Wen stated. “We’re calling this inconsistency a ‘cosmic glitch.’ It is virtually as if gravity itself stops completely matching Einstein’s idea.”
The cosmic glitch described by the workforce would require an alteration in a worth known as the gravitational fixed. This alteration would happen as calculations strategy the “superhorizon,” or the utmost distance gentle might have traveled because the origin of the universe.
This adjustment could be performed, the workforce says, by including a single extension to the usual cosmological mannequin. This mannequin is named the lambda chilly darkish matter mannequin. As soon as full, the admendment ought to clear up inconsistencies in measurements at cosmological scales with out affecting the present profitable makes use of of basic relativity.
What’s basic relativity and will or not it’s incorrect?
The invention of basic relativity was so revolutionary as a result of, moderately than describe gravity as a mysterious power, it posited that gravity arises from the curvature of the very cloth of house and time, united as a single entity known as “spacetime.” And this curvature, Einstein realized, is formed by objects with mass.
Think about putting balls of accelerating mass on a stretched rubber sheet. A tennis ball would trigger a tiny, virtually imperceptible dent; a cricket ball would create a extra pronounced dent; and a bowling ball would spur an enormous curve that probably attracts anything on the sheet towards it. It is the identical idea with objects in house, although the curvature of spacetime exists in 4 dimensions, so there are some fairly key variations. Nonetheless, moons have much less mass than planets, planets lower than stars, and stars lower than galaxies — thus, the gravitational influences of those celestial our bodies will increase respectively.
Einstein’s idea of gravity was like a successor to Newtonian idea, although the latter nonetheless serves fairly properly on terrestrial scales and is correct sufficient to get rockets to the moon. But, Einstein’s idea might clarify issues that Newton’s couldn’t, such because the quirky orbit of Mercury across the solar.
Newton wasn’t precisely incorrect about gravity — he simply wasn’t proper on scales of planets, stars and galaxies.
Is basic relativity incorrect, although?
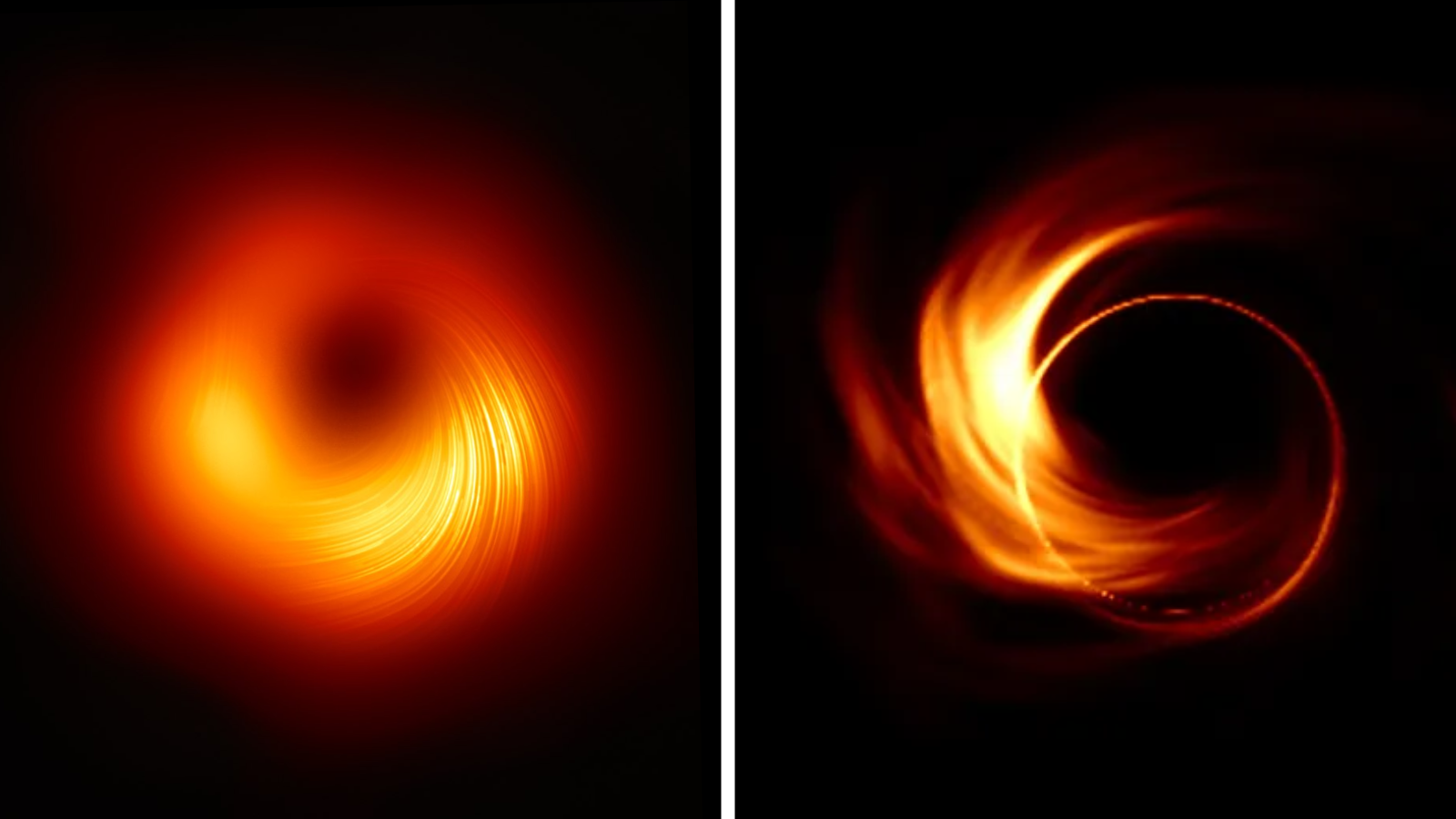
Properly, in all probability not. As a idea, it has been too correct in predicting points of the universe we did not find out about. As an illustration, the primary picture of a black gap captured by the Occasion Horizon Telescope was revealed to the general public in April 2019. This picture was type of stunning due to how carefully the looks of the supermassive black gap M87* resembled predictions of basic relativity.
Nonetheless, scientists are conscious there are a number of points with basic relativity that will require its eventual revision. As an illustration, the idea would not unite with quantum mechanics; one of the best description we’ve of physics on basic ranges smaller than the atom. That is primarily as a result of there may be presently no quantum idea to explain gravity.
So, evidently changes to basic relativity at some stage to “prolong” its attain to the smallest scales of the universe — and in line with this workforce, the vastest scales — appear inevitable.
For many years, researchers have tried to create a mathematical mannequin that helps basic relativity overcome its inconsistencies, and College of Waterloo utilized mathematicians and astrophysicists have been deeply engaged on this quest.
Change basic relativity? What!
If the thought of revising basic relativity appears tantamount to heresy, think about that this would not be the primary time that its associated theories needed to be adjusted.
Shortly after Einstein first launched the idea, he and others expanded upon it to develop an equation to explain the state of the universe. On account of basic relativity, this equation predicted that the universe ought to be altering. The problem with this was the scientific consensus on the time stated the universe was static. And, whereas Einstein was no stranger to throwing the established order into flux, he occurred to agree with this non-changing cosmic image.
To make sure basic relativity predicted a static universe, Einstein added a “fudge issue” that he later described as his “biggest blunder,” This is named the cosmological fixed, and is represented by the Greek letter lambda. The fixed can be faraway from thought when Edwin Hubble satisfied Einstein that the universe is non-static. It is increasing, he argued. And so far as we all know at the moment, Hubble was certainly right.
Lambda, nevertheless, would truly make a comeback. It’d begin serving a distinct operate on the finish of the twentieth century, when astronomers found that not solely is the universe increasing, however it’s doing so at an accelerating price.

“Virtually a century in the past, astronomers found that our universe is increasing,” Niayesh Afsharid, a College of Waterloo professor of astrophysics and a researcher on the Perimeter Institute, stated within the assertion. “The farther away galaxies are, the quicker they’re shifting, to the purpose that they appear to be shifting at almost the velocity of sunshine, the utmost allowed by Einstein’s idea. Our discovering means that, on these very scales, Einstein’s idea may be inadequate.”
The College of Waterloo workforce’s suggestion of a “cosmic glitch” modifies gravity at huge distances and extends Einstein’s mathematical formulation to deal with this whereas not “overthrowing” the idea.
“Consider it as being like a footnote to Einstein’s idea,” Wen stated. “When you attain a cosmic scale, phrases and situations apply.”
The researchers behind this cosmic glitch idea counsel that future observations of the large-scale construction of the universe and a common “fossil” area of radiation known as the cosmic microwave background (CMB) from an occasion that occurred shortly after the Massive Bang might make clear whether or not a cosmic glitch in gravity is liable for present “cosmic tensions.”
This might embody the explanation that quantum idea provides a worth for lambda that could be a staggering issue of 10¹²¹ (10 adopted by 120 zeroes) higher than astronomical observations appear to point out (no surprise some physicists name it “the worst theoretical prediction within the historical past of physics!”).
“This new mannequin would possibly simply be the primary clue in a cosmic puzzle we’re beginning to clear up throughout house and time,” Afshordi concluded.
The workforce analysis seems within the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics.

