We solely have one universe. That’s often loads – it’s fairly huge in spite of everything! However there are some issues scientists can’t do with our actual universe that they will do in the event that they construct new ones utilizing computer systems.
The universes they create aren’t actual, however they’re necessary instruments to assist us perceive the cosmos. Two groups of scientists lately created a few these simulations to assist us find out how our Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope units out to unveil the universe’s distant previous and provides us a glimpse of attainable futures.
Warning: you are actually getting into a cosmic development zone (no laborious hat required)!
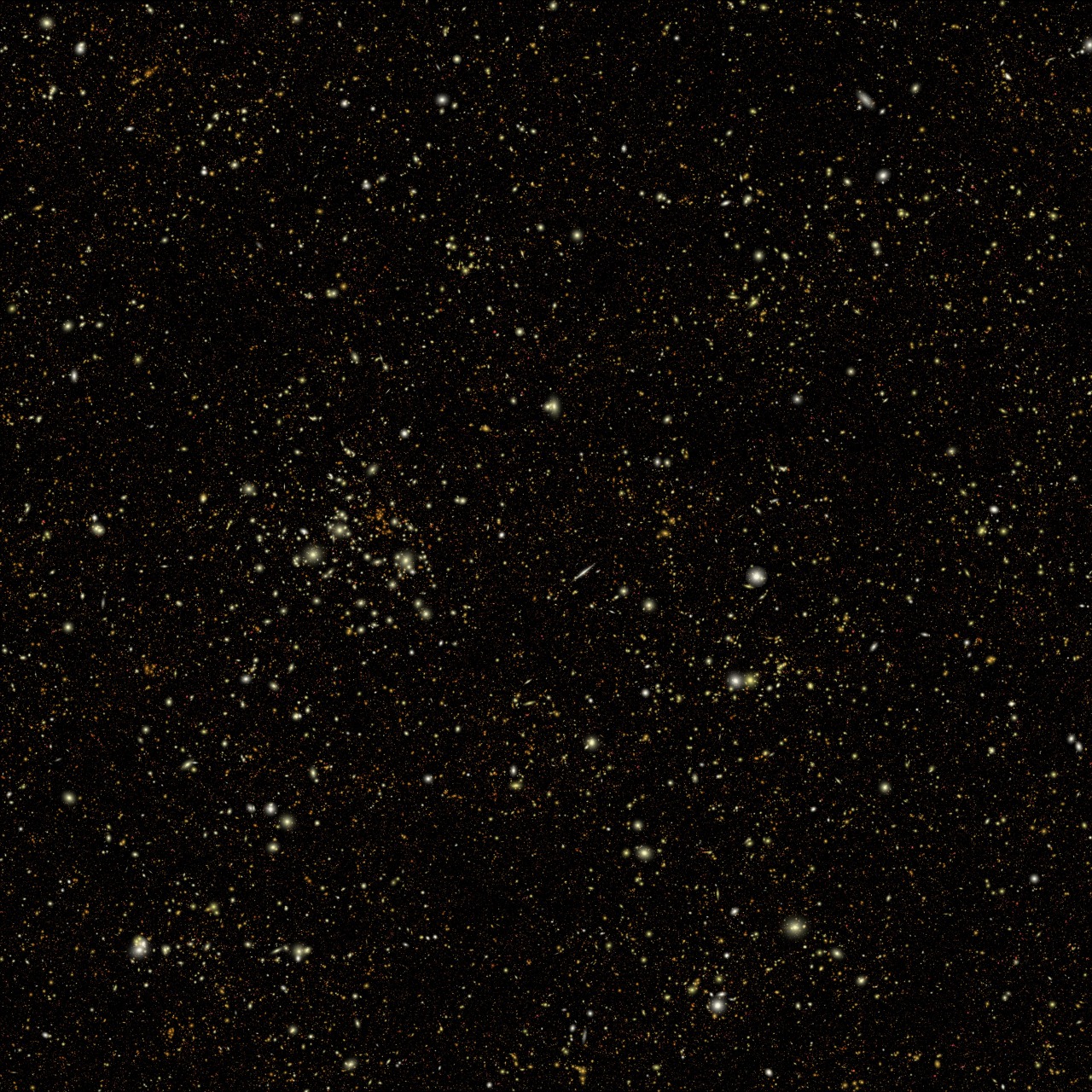
This simulated Roman deep area picture, containing a whole bunch of hundreds of galaxies, represents simply 1.3 p.c of the artificial survey, which is itself only one p.c of Roman’s deliberate survey. The complete simulation is accessible here. The galaxies are coloration coded – redder ones are farther away, and whiter ones are nearer. The simulation showcases Roman’s energy to conduct giant, deep surveys and research the universe statistically in ways in which aren’t attainable with present telescopes.
One Roman simulation helps scientists plan the right way to research cosmic evolution by teaming up with different telescopes, just like the Vera C. Rubin Observatory. It’s primarily based on galaxy and darkish matter fashions mixed with actual knowledge from different telescopes. It envisions an enormous patch of the sky Roman will survey when it launches by 2027. Scientists are exploring the simulation to make remark plans so Roman will assist us be taught as a lot as attainable. It’s a sneak peek at what we may work out about how and why our universe has modified dramatically throughout cosmic epochs.
This video begins by displaying probably the most distant galaxies within the simulated deep area picture in purple. Because it zooms out, layers of nearer (yellow and white) galaxies are added to the body. By learning totally different cosmic epochs, Roman will be capable of hint the universe’s growth historical past, research how galaxies developed over time, and far more.
As a part of the true future survey, Roman will research the construction and evolution of the universe, map darkish matter – an invisible substance detectable solely by seeing its gravitational results on seen matter – and discern between the main theories that try to elucidate why the expansion of the universe is speeding up. It’s going to do it by touring again in time…properly, form of.
Seeing into the previous
Wanting means out into house is type of like utilizing a time machine. That’s as a result of the sunshine emitted by distant galaxies takes longer to achieve us than gentle from ones which might be close by. Once we have a look at farther galaxies, we see the universe because it was when their gentle was emitted. That may assist us see billions of years into the previous. Evaluating what the universe was like at totally different ages will assist astronomers piece collectively the way in which it has remodeled over time.
This animation exhibits the kind of science that astronomers will be capable of do with future Roman deep area observations. The gravity of intervening galaxy clusters and darkish matter can lens the sunshine from farther objects, warping their look as proven within the animation. By learning the distorted gentle, astronomers can research elusive darkish matter, which may solely be measured not directly by its gravitational results on seen matter. As a bonus, this lensing additionally makes it simpler to see probably the most distant galaxies whose gentle they amplify.
The simulation demonstrates how Roman will see even farther again in time due to pure magnifying glasses in house. Large clusters of galaxies are so large that they warp the material of space-time, type of like how a bowling ball creates a properly when positioned on a trampoline. When gentle from extra distant galaxies passes near a galaxy cluster, it follows the curved space-time and bends across the cluster. That lenses the sunshine, producing brighter, distorted photos of the farther galaxies.
Roman will likely be delicate sufficient to make use of this phenomenon to see how even small plenty, like clumps of darkish matter, warp the looks of distant galaxies. That can assist slender down the candidates for what darkish matter might be manufactured from.
On this simulated view of the deep cosmos, every dot represents a galaxy. The three small squares present Hubble’s area of view, and every reveals a special area of the artificial universe. Roman will be capable of shortly survey an space as giant as the entire zoomed-out picture, which is able to give us a glimpse of the universe’s largest buildings.
Developing the cosmos over billions of years
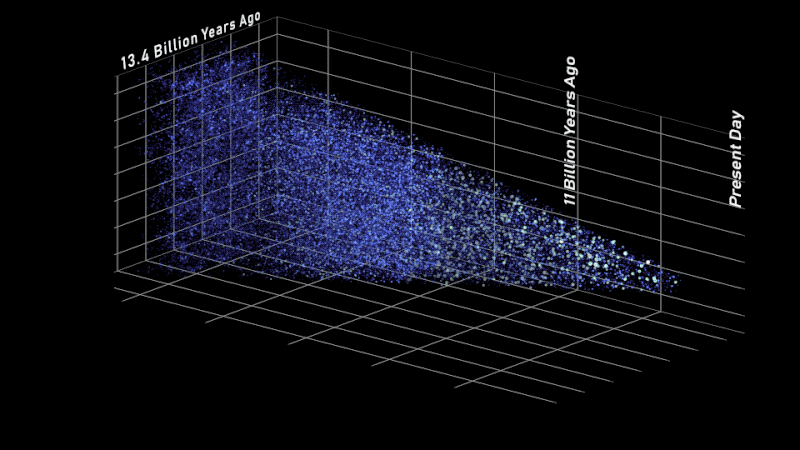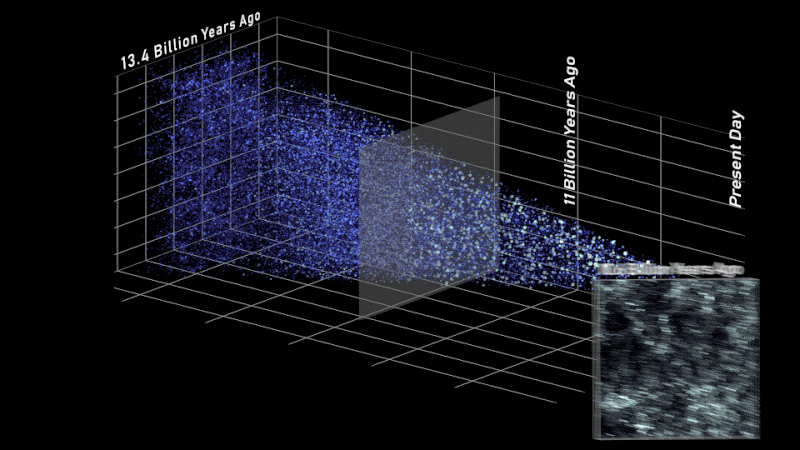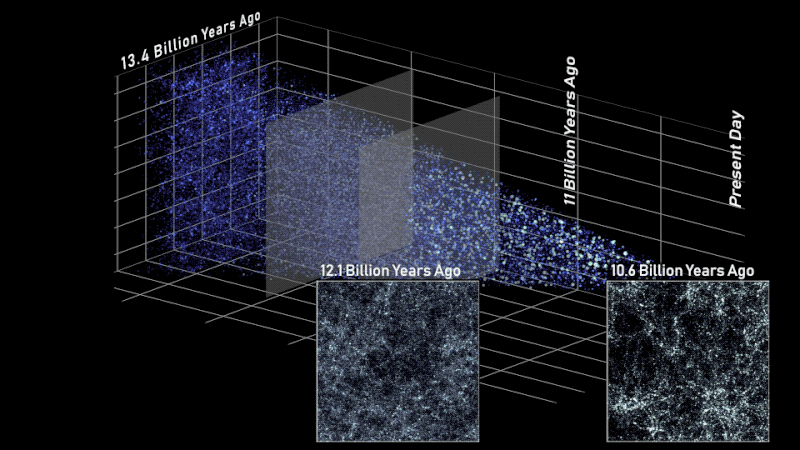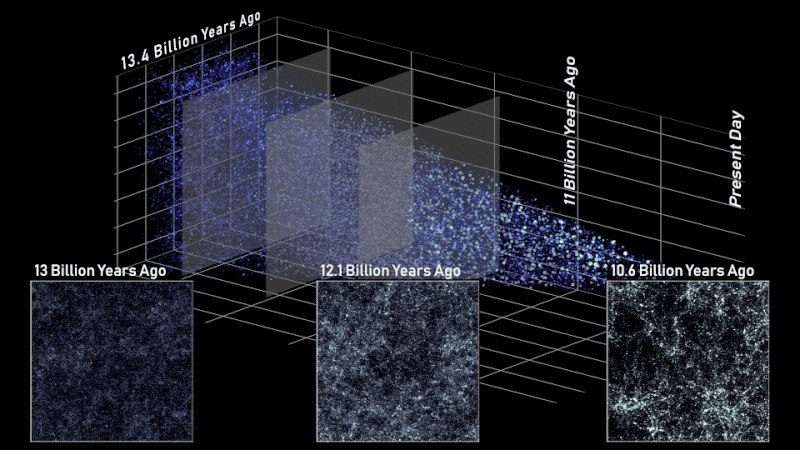
A separate simulation exhibits what Roman may count on to see throughout greater than 10 billion years of cosmic historical past. It’s primarily based on a galaxy formation mannequin that represents our present understanding of how the universe works. That signifies that Roman can put that mannequin to the check when it delivers actual observations, since astronomers can evaluate what they anticipated to see with what’s actually on the market.
On this facet view of the simulated universe, every dot represents a galaxy whose dimension and brightness corresponds to its mass. Slices from totally different epochs illustrate how Roman will be capable of view the universe throughout cosmic historical past. Astronomers will use such observations to piece collectively how cosmic evolution led to the web-like construction we see at this time.
This simulation additionally exhibits how Roman will assist us find out how extraordinarily giant buildings within the cosmos had been constructed over time. For a whole bunch of thousands and thousands of years after the universe was born, it was full of a sea of charged particles that was virtually fully uniform. At the moment, billions of years later, there are galaxies and galaxy clusters glowing in clumps alongside invisible threads of darkish matter that stretch a whole bunch of thousands and thousands of light-years. Huge “cosmic voids” are present in between all of the shining strands.
Astronomers have linked a few of the dots between the universe’s early days and at this time, nevertheless it’s been troublesome to see the massive image. Roman’s broad view of house will assist us shortly see the universe’s web-like construction for the primary time. That’s one thing that will take Hubble or Webb a long time to do! Scientists will even use Roman to view totally different slices of the universe and piece collectively all of the snapshots in time. We’re trying ahead to studying how the cosmos grew and developed to its current state and discovering clues about its final destiny.
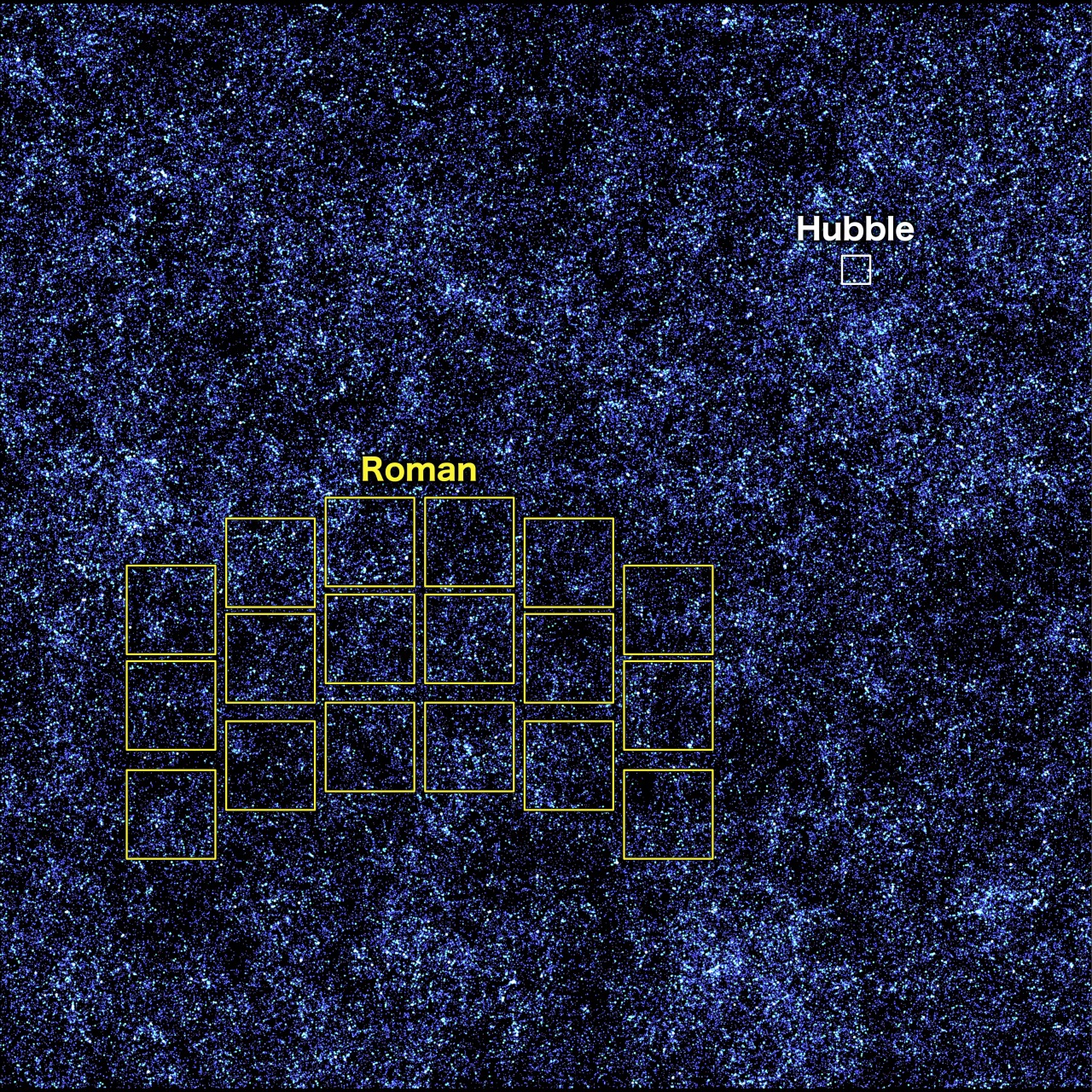
This picture, containing thousands and thousands of simulated galaxies strewn throughout house and time, exhibits the areas Hubble (white) and Roman (yellow) can seize in a single snapshot. It could take Hubble about 85 years to map the whole area proven within the picture on the similar depth, however Roman may do it in simply 63 days. Roman’s bigger view and quick survey speeds will unveil the evolving universe in ways in which have by no means been attainable earlier than.
Roman will discover the cosmos as no telescope ever has earlier than, combining a panoramic view of the universe with a vantage level in house. Every image it sends again will allow us to see areas which might be no less than 100 instances bigger than our Hubble or James Webb house telescopes can see at one time. Astronomers will research them to be taught extra about how galaxies had been constructed, darkish matter, and far more.
The simulations are far more than simply fairly photos – they’re necessary stepping stones that forecast what we will count on to see with Roman. We’ve by no means had a view like Roman’s earlier than, so having a preview helps make sure that we will take advantage of this unbelievable mission when it launches.
Study extra concerning the thrilling science this mission will examine on Twitter and Facebook.
Be sure to observe us on Tumblr in your common dose of house!