Think about a crew of astronauts headed to Mars. About 140 million miles away from Earth, they uncover their spacecraft has a cracked O-ring. However as a substitute of counting on a dwindling cache of spare elements, what if they might merely fabricate any half they wanted on demand?
A workforce of Berkeley researchers, led by Ph.D. scholar Taylor Waddell, could have taken a large leap towards making this feature a actuality. On June 8, they despatched their 3D printing know-how to area for the primary time as a part of the Virgin Galactic 07 mission.
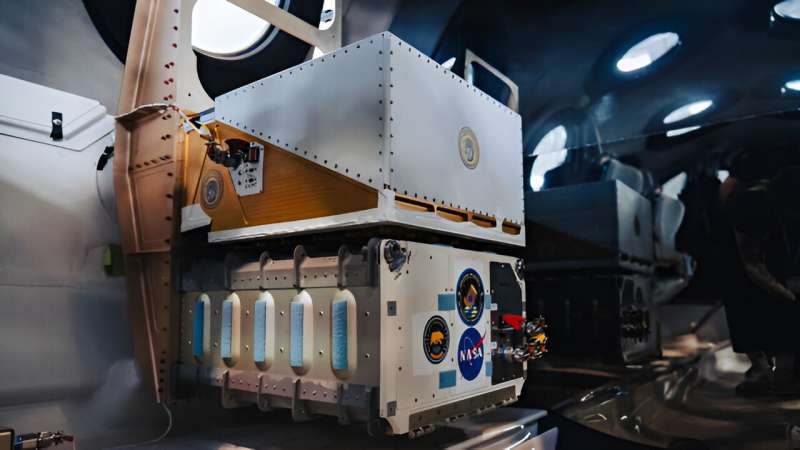
Their next-generation microgravity printer—dubbed SpaceCAL—spent 140 seconds in suborbital area whereas aboard the VSS Unity area aircraft. In that quick time span, it autonomously printed and post-processed a complete of 4 take a look at elements, together with area shuttles and benchy collectible figurines from a liquid plastic referred to as PEGDA.
“SpaceCAL carried out properly below microgravity circumstances in previous assessments aboard parabolic flights, but it surely nonetheless had one thing to show,” stated Waddell. “This newest mission … allowed us to validate the readiness of this 3D printing know-how for area journey.”
He added, “We hope that sometime it might be used to fabricate every part from elements and instruments for spacecraft to new contact lenses and dental crowns for crew members.”
3D printing, also referred to as additive manufacturing, has advanced significantly because it was first patented within the Nineteen Eighties. Hayden Taylor, affiliate professor of mechanical engineering, led a workforce of UC Berkeley and Lawrence Livermore Nationwide Laboratory (LLNL) researchers that invented Computed Axial Lithography (CAL) know-how in 2017.
This new sort of additive manufacturing, which makes use of gentle to form stable objects out of a viscous liquid, expanded the vary of printable geometries and considerably elevated the pace at which 3D elements could possibly be printed. And it functioned properly in microgravity circumstances, opening the door to purposes associated to area exploration.
CAL know-how can be what introduced Waddell to Berkeley to pursue his Ph.D. in mechanical engineering. As an undergraduate on the College of Wisconsin, Madison, and a Pathways Engineer at NASA, Waddell turned captivated by 3D printing—from its seemingly magical means to rework an thought right into a bodily type, to its affordability and accessibility.
Upon studying about CAL, he reached out to Taylor and shortly discovered himself at Berkeley. There, he spent numerous hours in Taylor’s lab, working with different scholar researchers on new methods to leverage this know-how for the larger good.
Reaching new heights
CAL stands other than different 3D printing applied sciences due to its unbelievable pace—creating elements in as little as 20 seconds—and effectivity. By enabling astronauts to print elements rapidly in an emergency and on demand, CAL doubtlessly eliminates the necessity to carry hundreds of spare elements on long-duration area missions.
“You may cut back that upmass, make these missions go quicker and cut back threat by bringing manufacturing applied sciences with you,” stated Waddell.
As well as, CAL’s distinctive means to print properly in microgravity circumstances permits engineers to discover the bounds of 3D printing from area.
“With CAL, we had been in a position to show—first on these zero-G[ravity] missions and now on this spaceflight—that we will print elements in microgravity that aren’t doable on Earth,” stated Waddell.
So far, CAL has proven that it may well efficiently print with greater than 60 totally different supplies on Earth, resembling silicons, glass composites and biomaterials. In response to Waddell, this versatility may come in useful for each the cabin and the crew.
“So, with the cabin, in case your spacecraft is breaking down, you possibly can print O-rings or mechanical mounts and even instruments,” he stated. “However CAL can be able to repairing the crew. We are able to print dental replacements, pores and skin grafts or lenses, or issues personalised in emergency medication for astronauts, which is essential in these missions, too.”
Sometime, CAL could also be used to print much more refined elements, resembling human organs. LLNL has obtained a grant from NASA to check this know-how on the Worldwide House Station.
“They’ll principally do bioprinting on the House Station,” stated Waddell. “And the lengthy, long-term purpose is to print organs up in area with CAL, then carry them again all the way down to Earth.”
Subsequent, Waddell and his colleagues hope to start work with NASA on growing and validating a single object that might assist crew well being and wellness, like a dental crown for an astronaut or a surgical wound closure software.
“These experiments are actually centered on pushing know-how for the betterment of everybody,” stated Waddell. “Despite the fact that it is for area, there are all the time tons of the way it may well profit individuals again right here on Earth.”
It is also the kind of know-how that the Berkeley House Middle envisions being developed at its new 36-acre campus at present below improvement. The Berkeley House Middle can be a house for innovation and entrepreneurship, bringing collectively applied sciences developed by NASA and UC Berkeley, and commercialized via personal business.
“Think about a spot the place personal corporations can take innovations like these created by Taylor Waddell and make it doable for these vital discoveries to interrupt out of the lab and into the general public realm,” stated Darek DeFreece, a regent emeritus of the College of California and the pinnacle of UC Berkeley’s efforts to develop the Berkeley House Middle. “We had been cheering as we watched the historic Virgin Galactic 07 flight.”
A collaborative effort
In some ways, the June 8 area mission was a end result of years of analysis by all the scholars in Hayden Taylor’s nanoscale manufacturing lab. Collectively, they’re pushing the boundaries of a comparatively new know-how to see what is feasible.
“This mission is constructed on a workforce of many, many individuals,” stated Waddell, together with scholar researchers Dillon Balk, Skyler Chan, Sean Chu, Brian Chung, Ameera Elgonemy, Jacob Gottesman, Anthony Moody, Jake Nickel, Dylan Potter, Austin Portinause, Anusri Sreenath and Audrey Younger.
He additionally credit his advisor for offering essential assist and the chance to take an lively function within the evolution of CAL know-how.
“Hayden is likely one of the finest PIs on the market. He offers me the duty to decide on the place I need to push this analysis,” stated Waddell. “Together with his final three SpaceCAL missions, he lets me lead them, from deciding who to rent and what we need to analysis to planning the entire journey. He actually lets me be the place I am most passionate and use him because the useful resource to make that occur.”
Virgin Galactic performed a pivotal function in taking this mission to the subsequent stage. “The workforce at Virgin Galactic helped us every step of the way in which, particularly in the course of the week getting ready for the rocket launch,” stated Waddell.
“There have been lots of glorious engineers and passionate individuals who needed to guarantee that we had been profitable.”
Quotation:
Engineers ship 3D printer into area (2024, July 4)
retrieved 5 July 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.

