Probably the greatest issues about satellites is the truth that they may give us a view of Earth that solely astronauts can see with their very own eyes.
As lovely as satellite tv for pc photographs of our planet is perhaps to have a look at, nonetheless, they’re way over only a fairly image — they’re essential for scientific analysis.
Take, as an illustration, this completely mesmerizing video by NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio, which exhibits orange plumes erupting from the floor of Earth and swirling across the planet. Mesmerizing, sure, however finally regarding — these plumes illustrate how carbon dioxide entered and moved via Earth’s environment from January 2020 to March 2020.
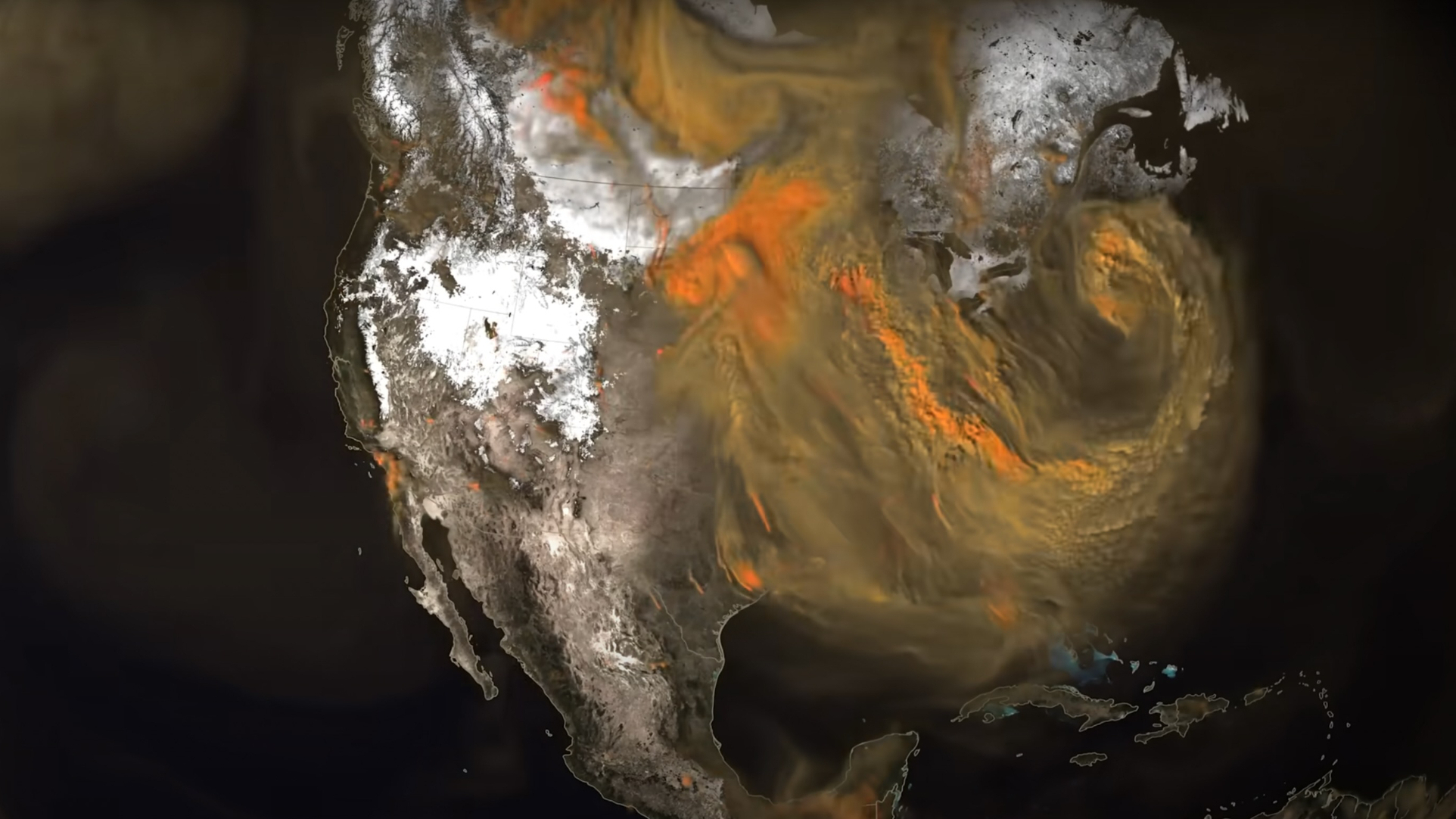
Created utilizing NASA Goddard’s Goddard Earth Observing System (GEOS) climate mannequin — which is 100 instances higher-resolution than normal climate fashions — this visualization makes use of billions of information factors noticed from each house (as an illustration, from NASA’s Terra and Suomi Nationwide Polar-orbiting Partnership satellites) and land.
Whereas the mannequin usually analyzes climate programs, local weather scientists recommended utilizing GEOS to have a look at carbon dioxide. “We had this chance to say: Can we tag alongside and see what actually high-resolution CO2 seems like?” Goddard local weather scientist Lesley Ott mentioned in a statement. “We had a sense we have been going to see plume constructions and issues that we have by no means been in a position to see once we do these coarser-resolution simulations.”
For those who check out the video, you may see these plume constructions are certainly extremely seen — they arrive from a wide range of sources, from energy crops to wildfires to cities. You may also discover a pulsing rhythm to the plumes.
For particular plumes emanating from fires, the pulses are as a result of daytime flare-ups, which usually lower in a single day. However on a world scale, you are basically seeing crops respiratory. In the course of the day, Earth’s crops take in carbon dioxide throughout photosynthesis, however at night time, when photosynthesis doesn’t happen, they “inhale” oxygen and “exhale” carbon dioxide, identical to animals.
You may additionally discover that a few of the carbon dioxide swirls and strikes across the globe — this exhibits how climate disperses the fuel all through the environment, finally creating one thing of an insulating layer that traps warmth. Our carbon dioxide emissions are a big driver of local weather change, particularly the planet’s rising common temperature.
By finding out carbon dioxide via such high-resolution fashions, local weather scientists can higher predict local weather developments and develop methods to mitigate its antagonistic results. “As policymakers and as scientists, we’re making an attempt to account for the place carbon comes from and the way that impacts the planet,” mentioned Ott. “You see right here how every little thing is interconnected by these completely different climate patterns.”

