
NASA held a media occasion on December 5 to debate the findings concerning the Artemis 1 Orion heatshield points that occurred throughout its reentry after a profitable check flight together with NASA Administrator Invoice Nelson, Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, Affiliate Administrator Jim Free, Artemis II Mission Commander Reid Wiseman, and Moon To Mars Program head Amit Kshatriya. Additionally mentioned had been updates to the Artemis II Orion crew module’s electrical and life-support methods because the spacecraft is ready for Artemis II.
Artemis 1 launched on November 16, 2022 from Kennedy House Middle’s LC-39B. In the course of the mission’s 25 days, 10 hours, 53 minutes, SLS despatched Orion on a path that noticed it go farther than any man-rated spacecraft within the historical past of spaceflight. On December 11, Orion, utilizing a skip-reentry, reentered the Earth’s environment protected by its 16 foot diameter Avcoat ablative heatshield that hit the environment at 32-times the pace of sound and bore these velocities and heating for over 3,600 miles to land inside 2 miles of the USS Portland, its restoration ship. Nonetheless, there have been areas of the Orion heatshield that didn’t behave as anticipated throughout Orion’s reentry again to Earth.

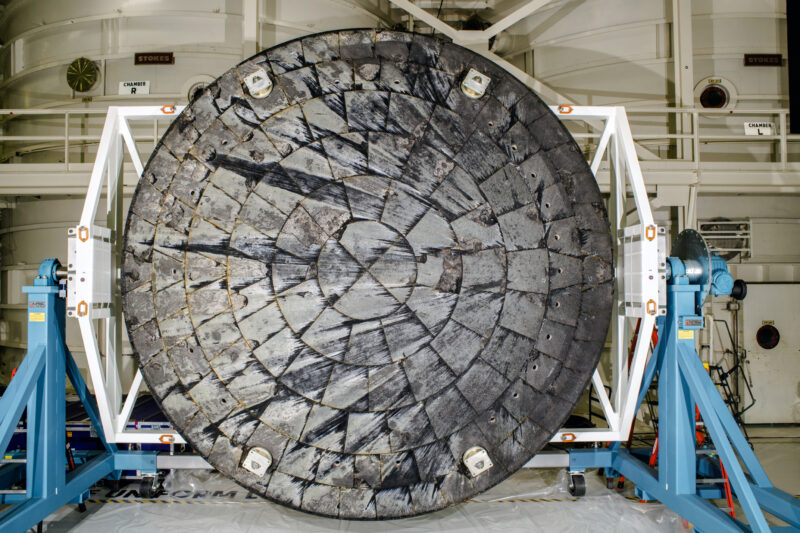
In a tour de drive presentation, Amit Kshatriya, NASA’s Deputy Affiliate Administrator and head of NASA’s Moon to Mars program workplace gave a presentation on what occurred to the Artemis 1 Orion’s heatsheild and the steps taken to grasp why. As he stated, an ablative heatshield like Orion’s is designed to burn, or char, throughout reentry. Many of the warmth of reentry is eliminated by what NASA calls the “radiative shock” that happens in entrance of the spacecraft because it travels via the environment. The remainder of the warmth of reentry is eliminated by convection via charing of the heatshieldt’s outer layer. This char layer of the ablator on the heatshield is designed to progressively recede, or burn-away, in order that the fabric beneath protects the spacecraft through the excessive warmth skilled throughout reentry. The heatshield is just not designed for areas which are charring to break-off, as occurred throughout reentry of the Artemis 1 Orion spacecraft. There have been about 100 areas of Orion’s heatshield the place the char layer that protects Orion broke-off in ways in which NASA had not anticipated.

The Orion heatshield had wonderful efficiency, in response to NASA. However not like intervals up to now that led to the lack of the Challenger and Columbia crews, in response to Kshatriya, NASA of right this moment doesn’t consider surprising habits of one thing so crucial as a heatshield signifies that it’s nonetheless behaving inside margin. NASA determined it was crucial to get a full technical understanding of the “transported liberation phenomena”, as NASA calls it, that led to the lack of char.
In response to Mr. Kshatriya, the Orion program head, Howard Hu, stood-up a heatshield tiger workforce run by Johnson House Middle’s Luis Saucedo that was a multi-disciplinary group consisting of thermal safety methods, aerothermal dynamics, aerothermal testing evaluation, thermal testing evaluation, stress evaluation, materials testing, with further specialists brought-in from the Division of Protection, Division of Vitality, throughout industries and international locations. In response to Kshatriya, “…Saucedo…carried out what’s in my estimation within the 20-years I’ve been within the company is without doubt one of the most opulent items of engineering evaluation that I’ve been part of. Their work was substantial, important, and very spectacular.” The Orion heatshield tiger workforce, “…led to advances enabling an understanding of Orion’s heatshield materials loss properties and its interplay within the aerothermal setting, created new applied sciences check and non-destructive analysis strategies to watch the heatshield’s aerothermal setting interactions in NASA’s arc jet services, which had been upgraded as a part of this work.”

As soon as the Orion heatshield tiger workforce’s report was accomplished, a full verification was accomplished by an outdoor group, led by Paul Hill, who can be a key advisor serving on the Aerospace Security Advisory panel, that was made-up of specialists brought-in from throughout business each US and worldwide. The intent was give NASA confidence that it actually understood the surprising habits of Artemis 1’s Orion heatshield throughout reentry. This group was unanimous in its settlement of the evaluation as to the foundation causes of the Orion heatshield’s habits.
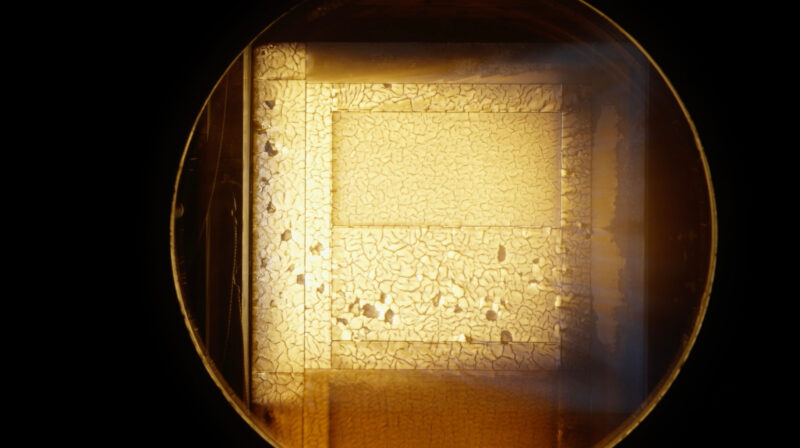
Throughout reentry, the ablative materials has to supply gases underneath pyrolysis, that’s burning away of fabric in a excessive thermal setting with out oxygen. As Kchatriya stated, NASA realized that as a part of that response, the permeability of the Avcoat heatshield materials is crucial. The perception into what occurred didn’t come till NASA checked out areas of the the Avcoat materials the place the burning-away of the char layer stopped through the dwell-time of the skip reentry, that’s the interval of the skip reentry throughout which Orion was experiencing much less thermal loading. Throughout this era, the manufacturing of gases from the Avcoat materials was greater than the permeability, which is the flexibility of the fabric to permit circulation of gases, allowed. The elevated strain because of the greater manufacturing of gases throughout the Avcoat materials that would not readily escape due to the fabric’s permeability led to a distinction in strain that resulted in cracks “in airplane with the outer mildew line” of the Orion crew module. In some circumstances, these cracks made their approach all the best way to the bond-line, or the place among the 186 Avcoat heatshield meet different blocks.
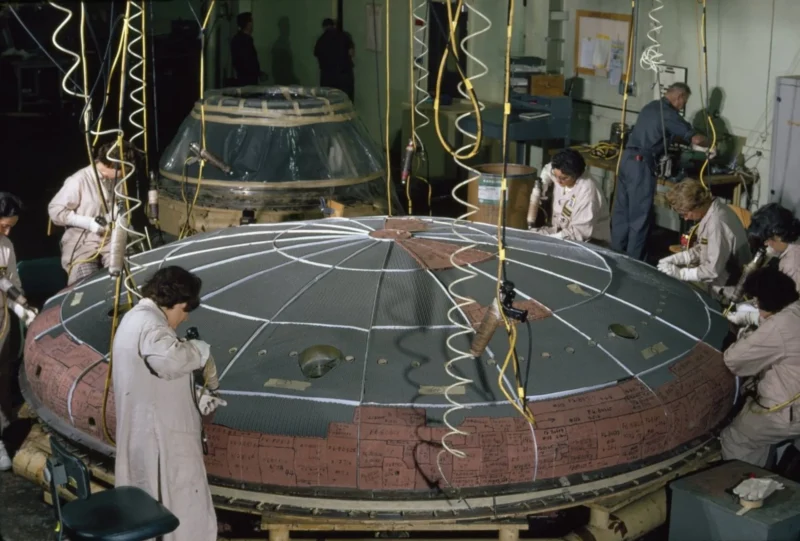

One query on many individuals’s minds is why the Apollo command module heatshield, in addition to the EFT-1 Orion crew module’s heatshield, didn’t expertise Avcoat points. The heatshields of those spacecraft included Avcoat hand-filled in a honeycomb construction. Containing the Avcoat materials inside honeycomb cells abbreviated propagation of any crack propagations from progressing past every honeycomb cell. However the price of a heatshield constructed by hand is pricey and susceptible to its personal errors, comparable to voids from incomplete fills. There’s additionally the mass penalty of the honeycomb construction itself. NASA’s present Orion heatshield design using Avcoat brick is supposed to win-back that honeycomb mass and have the ability to produce large Orion spacecraft heatshields on a inexpensive and extra fast method.
Due to the Orion heatshield check program, NASA now is aware of the best way to produce Avcoat with the wanted permeability requirements and has, in response to Kshatriya, sized-up manufacturing functionality leading to a 50% leap within the manufacturing price to shortly produce Avcoat heatshields at a price NASA wants. NASA thinks the qualification of the reformulated Avcoat will probably be accomplished inside a yr. Within the meantime, since NASA totally understands, “…not solely the interplay of the Avcoat materials and the setting but in addition the built-in interplay of the way it performs on the spacecraft,” NASA goes to fly the present heatshield on the Artemis 2 Orion spacecraft as a result of it feels that there’s no higher technique to be taught than to fly.
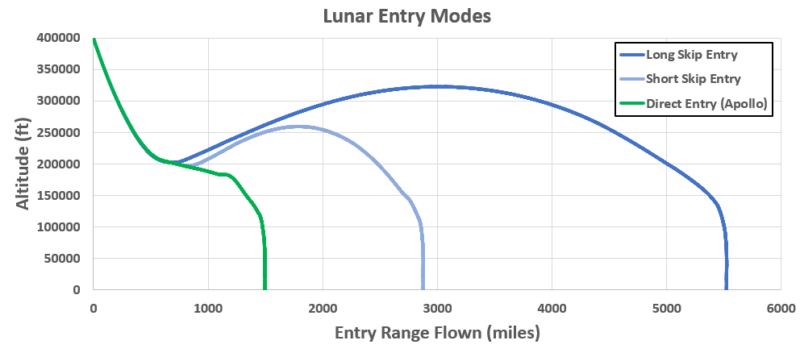
The present Artemis 2 Orion heatshield has an identical Avcoat formulation to Artemis 1’s Orion. There are two methods to stop the Avcoat heatshield points that occurred throughout Artemis 1 Orion’s reentry: change-out the Artemis 2 Orion heatshield with one utilizing the newly formulated Avcoat blocks; or change the reentry setting. NASA has chosen the latter choice, that’s to alter the reentry setting. As a result of NASA is utilizing an equatorial free-return trajectory to ship the Artemis 2 astronauts to the Moon, it might management the reentry setting and achieve this safely and has chosen this path in an effort to proceed to maneuver the Artemis 2 program ahead. Artemis 2 Mission Commander Reid Wiseman said that the Artemis 2 crew is totally behind NASA’s choice.
Making the wanted modifications to the Artemis 2 mission’s reentry steering, together with resolving a handful of points within the efficiency and integration of the Orion spacecraft, will delay the September 2025 launch of Artemis 2 to April 2026. There are points with {the electrical} system of the Orion spacecraft throughout an abort.
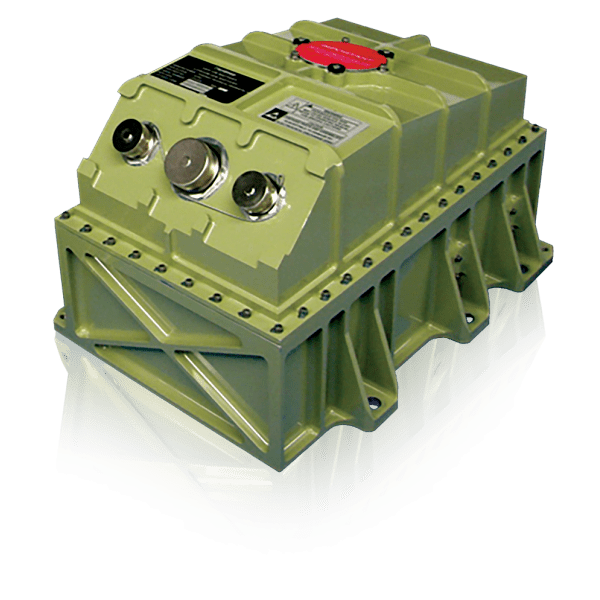

It was found that the 2 main and two back-up EaglePicher 120-volt Li-ion batteries on the Orion spacecraft, that are answerable for communications, navigation, propulsion and thermal management, weren’t, as defined by Dep. Assoc. Admin. Kshatriya, capable of tolerate the extraordinary setting skilled throughout an abort utilizing the launch abort system. Every of the 120-volt Li-ion batteries, in response to EaglePicher, comprise 32 EaglePicher 30 Ah prismatic, lithium-ion cells. Since all the abort methods on the Orion spacecraft, together with the launch abort system, will probably be lively on Artemis 2, NASA has been working to guarantee that all the electrical system points throughout abort are resolved. Fixing the batteries has taken a while and concerned a whole rework in how the batteries are mounted and mechanically secured within the Orion spacecraft. Kshatriya called-out the wonderful work by EaglePicher Technologies in Joplin, Missouri, the provider of the Orion spacecraft batteries, enabled the whole and high quality to repair. Remedying the battery repair was made troublesome find very excessive reliability parts because of the excessive fragile nature of the area parts provide chain. Apparently, Kshatriya talked about that NASA has a protracted historical past with EaglePicher and that its batteries had been those that saved the Apollo 13 crew as soon as the gasoline cells had been misplaced. After the Apollo 13 command module was shut-down, it and its EaglePicher batteries spend days being cold-soaked in area. As a result of the Apollo 13 batteries could possibly be powered-up, the Apollo 13 crew was capable of efficiently reenter and splash-down.

Resolving points with the Orion Setting Management Life-Help System (ECLSS) has taken longer than deliberate. A problem was introduced in early 2024 within the ECLSS involving the management system of the valves for the carbon dioxide removing system. One other ECLSS challenge was the sealing materials on the valves being deformed and inflicting over-board leakage. Each of those ECLSS points have been mounted. NASA continues to check the Orion ECLSS via a number of failure paths, to in essence beat it onerous, to make sure that it can work as wanted for the Artemis 2 and future crews. Since all the points concerning Orion’s batteries, ECLSS, and heatshield have been resolved, NASA has determined to go ahead with stacking the Artemis 2 launch automobile and Orion spacecraft.
NASA is utilizing the time till the spring 2026 launch of the Artemis 2 mission to work with its industrial companions to retire threat for the Artemis 3 touchdown mission, ought to SpaceX’s Starship be prepared.

