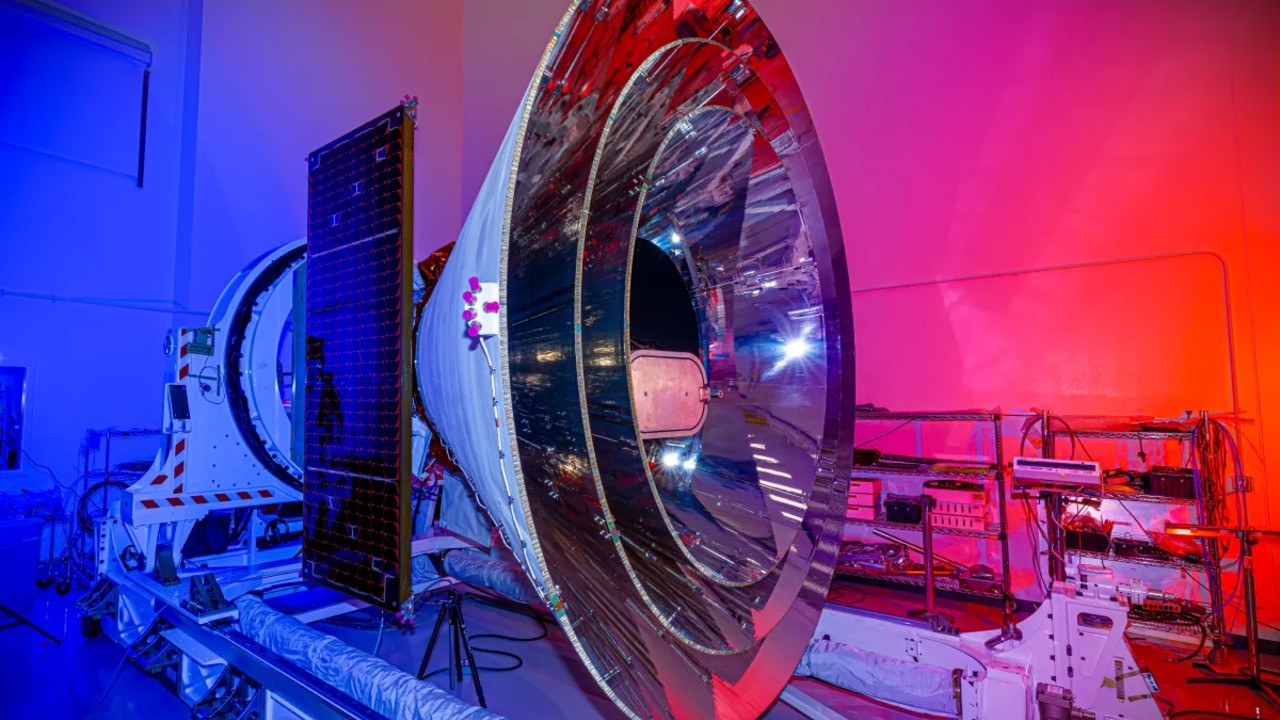
An formidable NASA mission to map the sky in 3D utilizing a space-based observatory now has a goal launch date of late February 2025.
NASA’s compact car-sized observatory, referred to as Spectro-Photometer for the Historical past of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer (or simply SPHEREx for brief), will map the hundreds of thousands of stars and galaxies seen from our planet in each path, “like scanning the within of a globe,” in keeping with an company statement. The satellite tv for pc will launch right into a polar orbit atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg House Drive Base in California.
Utilizing the sky map, SPHEREx has three scientific targets to attain. First, by measuring the distribution of a whole lot of hundreds of thousands of galaxies, NASA seeks to know extra about an historical cosmic occasion referred to as inflation, when the universe elevated exponentially simply fractions of a second after the Large Bang. If the observatory is profitable, scientists might achieve improved perception into the physics underlying inflation and what drove the phenomenon.
Secondly, NASA is on the lookout for a extra full image of objects and sources radiating all through the recognized universe. The observatory will collect knowledge that may allow scientists to measure the “collective glow” of distant galaxies, together with gentle from hidden galaxies which have by no means been noticed individually earlier than.
Lastly, the SPHEREx mission will search our personal galaxy, the Milky Approach, for components wanted for all times, together with carbon dioxide and water. If SPHEREx finds them, it might give scientists a clue to how probably it’s for these components to be current when new planets type.
Scientists at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) developed and constructed SPHEREx, which has a deliberate lifespan of two years. Throughout this time, SPHEREx ought to produce two maps per 12 months, in keeping with JPL.
SpaceX gained the contract for the launch again in 2021. The 329-lb (178 kilograms) spacecraft will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket from House Launch Advanced 4E at Vandenberg Air Drive Base in California, with NASA’s Launch Companies Program at Kennedy House Middle in Florida managing the launch. JPL heads the general mission, together with operations, techniques engineering, integration, and testing.
A secondary payload for a similar Falcon 9 launch is a constellation of 4 small satellites, representing NASA’s PUNCH mission (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere). The satellites are headed to low Earth orbit. They will observe the solar’s outer layer, the corona, to check how mass and power remodel into photo voltaic wind.

