The Hubble House Telescope is a masterwork of engineering and human ingenuity. Hubble is comparable in dimension and weight to a big college bus, however its contributions to science and astronomy may fill libraries.
Not solely is Hubble considered one of Earth’s premium sources for completely unbelievable, out-of-this-world imagery, it is usually a testomony to human curiosity and willpower. The telescope has been in operation for over 30 years, undergone a complete of 5 servicing missions and delivered practically 250 terabytes of information in contributions to our understanding of the universe.
Scientists started engaged on concepts for a big house telescope in orbit by the top of the Nineteen Sixties, however it might take practically a decade of lobbying and refining plans earlier than funding for the challenge was authorised by the U.S. Congress. It was virtually one other half a decade after that earlier than the telescope obtained its official identify — after famed American astronomer Edwin Hubble. Then, because of the lack of Challenger in January 1986 and the following pause of the house shuttle program, Hubble would wait one more 5 years earlier than reaching orbit.
Deployment

STS-31: April 24-29, 1990
STS-31 crew:
Loren J. Shriver, commander
Charles F. Bolden, pilot
Steven A. Hawley, mission specialist
Bruce McCandless, mission specialist
Kathryn D. Sullivan, mission specialist
Hubble was constructed with a variety of devices onboard, together with the Huge Subject Planetary Digital camera (WFPC), the Goddard Excessive Decision Spectrograph (GHRS), the Faint Object Digital camera (FOC), the Faint Object Spectrograph (FOS) and the Excessive Velocity Photometer (HSP).
Hubble launched on April 24, 1990, stowed contained in the cargo bay of house shuttle Discovery. STS-31 was Discovery’s tenth launch, and it was the thirty fifth house shuttle mission total.
Associated: NASA’s house shuttle: The primary reusable spacecraft
At some point after reaching orbit (April 25), the STS-31 crew deployed Hubble, after which spent many of the period of their mission bringing the telescope into operation. Discovery returned to Earth on April 29, leaving Hubble in an orbit 380 miles (612 kilometers) in altitude, the place it may start awing humanity with the secrets and techniques of the universe.
At the least, that is what was alleged to occur. However the first pictures beamed again to Earth from Hubble — NASA’s $1.5 billion house telescope that took three a long time to succeed in house — had been blurry.
In June 1990, NASA introduced the invention of a spherical aberration on Hubble’s major mirror resulting from a 2-micron mistake within the curvature of the telescope’s major mirror — about 1/50 the width of a human hair. Although small, the defect made the telescope largely ineffective to astronomers. Fortunately, Hubble was designed to be serviceable, and NASA’s finest minds took to the duty.
Servicing Mission 1

STS-61: Dec. 2-13, 1993
NASA’s house shuttle Endeavour launched on Dec. 2, 1993 on the STS-61 mission. The aim was to repair the debilitated house telescope so it may lastly begin seeing straight.
STS-61 crew:
Richard Covey, mission commander
Kenneth Bowersox, pilot
Kathryn Thornton, mission specialist
F. Story Musgrave, mission specialist
Claude Nicollier, mission specialist
Hubble’s engineers designed the telescope particularly to be upgraded. Its giant physique options handrails for astronauts to carry out upkeep and modular elements to facilitate upgrades with the evolution of know-how. This allowed NASA to design and plan fixes to deliver Hubble again into operation after its disastrous begin.
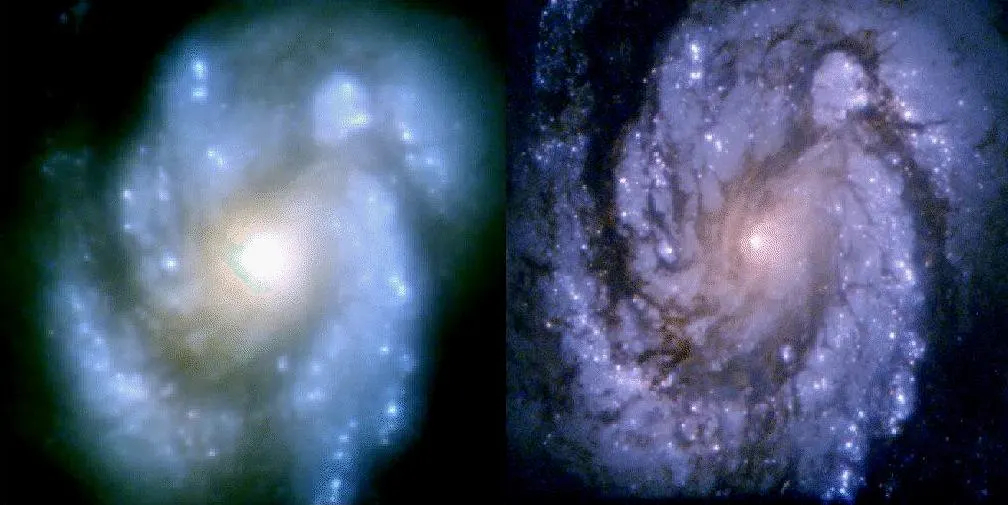
The STS-61 astronauts aboard Endeavor throughout Hubble’s first servicing mission (SM1) spent greater than 35 hours throughout a complete of 5 spacewalks, or EVAs (extravehicular exercise) over the course of as many days to finish their deliberate upgrades. They put in the Corrective Optics House Telescope Axial Alternative (COSTAR) unit rather than the HSP — akin to Hubble getting a brand new pair of glasses to deliver its blurry imaginative and prescient into focus. The WFPC was changed with the WFPC2, which got here with inner corrective optics, and Hubble’s photo voltaic arrays and gyroscopes had been upgraded to enhance the telescope’s monitoring means.
The SM1 mission restored Hubble to operational standing, and because of this, produced one of many telescope’s most iconic pictures.
Associated: 30 years in the past, astronauts saved the Hubble House Telescope
Servicing Mission 2

STS-82: Feb. 11-21, 1997
Discovery lifted off on the STS-82 mission from Launch Advanced-39A, at NASA’s Kennedy House Heart in Florida, on Feb. 11, 1997. In the course of the 10-day flight, 5 EVAs had been carried out to finish the upgrades made to Hubble.
STS-82 crew:
Kenneth Bowersox, mission commander
Scott Horowitz, pilot
Joseph Tanner, mission specialist
Steven Hawley, mission specialist
Gregory Harbaugh, mission specialist
Mark Lee, mission specialist
Steven Smith, mission specialist
Hubble’s second servicing mission, SM2, was much less reparative and extra targeted on what engineers had supposed once they designed the telescope to be serviceable: upgrades and boosting efficiency.
Discovery launched on STS-82 in February 1997, with two new devices for Hubble. The House Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) and Close to Infrared Digital camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) changed Hubble’s GHRS and FOS. The swap expanded the telescope’s imaginative and prescient into near-infrared wavelengths. The mission was additionally profitable in buying and selling out a few of Hubble’s degraded knowledge recorders, in addition to another, secondary {hardware}.
Servicing Mission 3A

STS-103: Dec. 19-27, 1999
Discovery’s third mission to Hubble was an surprising one. In November 1999, the fourth of six gyros used to keep up the telescope’s orientation failed, sending Hubble right into a protecting “protected mode.” Earlier gyros had failed as properly, however with a view to proceed successfully gathering science knowledge, not less than three wanted to be in working order.
STS-103 crew:
Curtis Brown, mission commander
Scott Kelly, pilot
Jean-Francois Clervoy, mission specialist
Michael Foale, mission specialist
John Grunsfeld, mission specialist
Steven Smith, mission specialist
Claude Nicollier, mission specialist
What was initially scheduled in June 2000 as Servicing Mission 3 (SM3) was break up into two missions: An emergency SM3A mission was created for house shuttle Discovery, and STS-102 was added to the launch manifest for December 1999.
Most of the mission’s spacewalks exceeded eight hours, making them a number of the longest EVAs in shuttle historical past. Throughout these prolonged stints navigating Hubble’s handrails, NASA astronauts Steven Smith and John Grunsfeld changed all six gyroscopes contained in the telescope’s Price Sensor Unites (RSUs) and put in a brand new transmitter and knowledge recorder.
Throughout a special EVA, NASA astronauts Michael Foale and Claude Nicollier changed Hubble’s primary pc, growing its processing pace by virtually 20 instances. Additionally they upgraded Hubble’s tremendous steering sensors.
Servicing Mission 3B

STS-109: March 1-12, 2002
The splitting up of SM3 into SM3A and SM3B pushed the upkeep scheduled for June 2000 again to March 2002. House shuttle Columbia launched STS-109 on March 1, with the first aim of delivering and putting in the Superior Digital camera for Surveys (ACS).
STS-109 crew:
Scott Altman, mission commander
Duane Carey, pilot
John Grunsfeld, payload commander and mission specialist
Nancy Currie, mission specialist
Richard Linnehan, mission specialist
James Newman, mission specialist
Michael Massimino, mission specialist
Hubble’s ACS changed the growing older FOC, including 10 instances the imaging energy in comparison with that of its predecessor. Astronauts on SM3B had been additionally tasked with changing Hubble’s photo voltaic arrays, which had been worn by years of radiation and particles.
Although smaller, Hubble’s new photo voltaic arrays offered between 20% and 30% extra energy. Additionally they changed Hubble’s Energy Management Unit (PCU) and added a brand new cooling system to extend the lifespan of NICMOS.
Servicing Mission 4

STS-125: Might 11-24, 2009
STS-125 was the final mission to Hubble. With the house shuttle set to retire two years later, Hubble’s SM4 aimed to improve the house telescope with the applied sciences to assist it final into the twenty first century.
STS-125 crew:
Scott Altman, mission commander
Gregory Johnson, pilot
Michael Good, mission specialist
Megan McArthur, mission specialist
Andrew Feustel, mission specialist
Michael Massimino, mission specialist
John Grunsfeld, mission specialist
House shuttle Atlantis launched on Might 11, 2009, carrying two new devices for the house telescope: the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS) and Huge Subject Digital camera 3 (WFC3).
When astronauts changed the FOC throughout SM3B, the COSTAR instrument that served as Hubble’s glasses grew to become redundant. COS changed COSTAR throughout SM4 and have become a complement to STIS. The place COS’s ultraviolet spectrum detection falls off, STIS can decide up in ultraviolet wavelengths by way of optical to near-infrared gentle. The astronauts additionally managed to restore STIS, which had been inoperable since August 2004, when a failure of its energy provide despatched it into “protected mode.”
A few of Hubble’s most iconic imagery, together with the Hubble Extremely Deep Subject, is attributed to the ACS. In 2007, nonetheless, it additionally suffered {an electrical} failure. Treatments for STIS and ACS had been each comparable to one another within the duties astronauts wanted to carry out to finish their repairs, however had been each very dissimilar to how and the place engineers anticipated astronauts to be performing upkeep on Hubble.
NASA astronauts — together with John Grunsfeld, who had already participated in three Hubble servicing missions — skilled for 2 years to develop the instruments, methods and methods they would want to efficiently restore the house telescope for the final time.
Hubble at the moment
Within the greater than a decade and a half since astronauts final visited Hubble, the telescope has continued to offer wonderful views of the cosmos, however its operation has not been with out its hiccups. As Hubble has aged, NASA mission managers have tightened their working constraints, deriving methods for the observatory to proceed functioning regardless of a number of points.
As new gyros put in throughout servicing missions aged and failed, technicians constructed deeper margins into the elements’ parameters. At this time, the telescope has two functioning gyros and has been shifted to a one-gyro mode to protect the opposite as backup. This presents limitations on a number of the science and observations Hubble could make however has allowed the famed scope to proceed probing the mysteries of the universe.
NASA hopes the brand new working parameters will lengthen Hubble’s life into the 2030s. Nonetheless, that may possible be the top of the highway for the house telescope, functioning devices or not. With out a increase to its altitude from a visiting spacecraft, Hubble will dip right into a decrease and decrease orbit and finally dissipate in Earth’s environment by the mid-2030s.

