Telescopes positioned each on the bottom and in area proceed to dazzle us with unbelievable pictures of the universe. We owe these sharp vistas to a collection of sensible astronomers, together with Andrea Ghez – an astrophysicist and professor at UCLA – and the “Mom of Hubble,” Nancy Grace Roman.
Do you know that stars don’t really twinkle? They solely seem like they do as a result of their gentle has to journey by our turbulent ambiance to achieve our eyes. Because the ambiance shifts and swirls round, the sunshine from distant stars is barely refracted, or bent, in several instructions. Generally it’s directed proper at us, however typically it’s directed a bit to the facet.
It’s like somebody’s shining a flashlight towards you however transferring it round barely. Generally the beam is pointed proper at you and seems very vivid, and typically it’s pointed a bit to both facet of you and it seems dimmer. The quantity of sunshine isn’t actually altering, but it surely appears to be like like it’s.
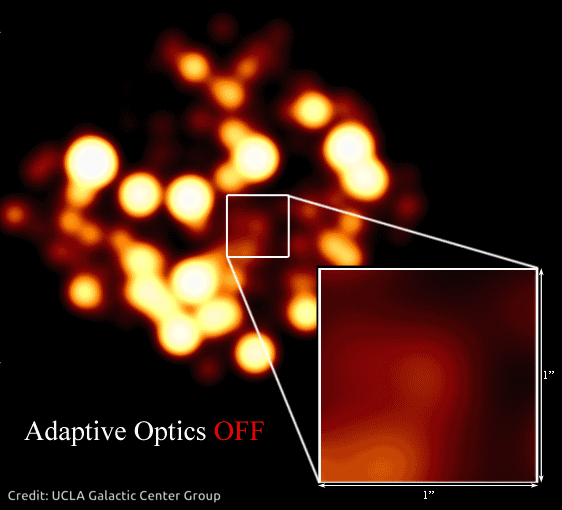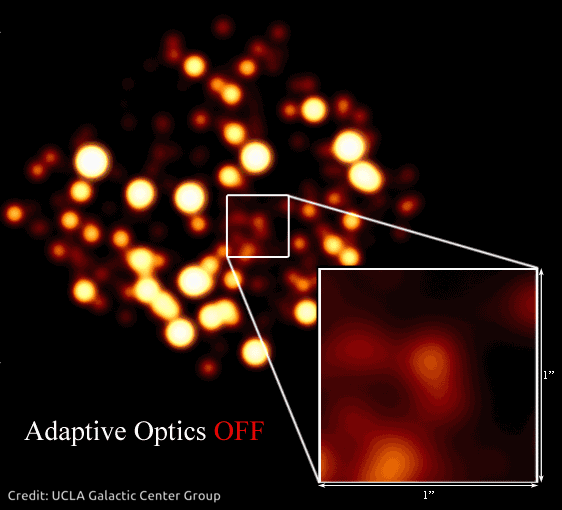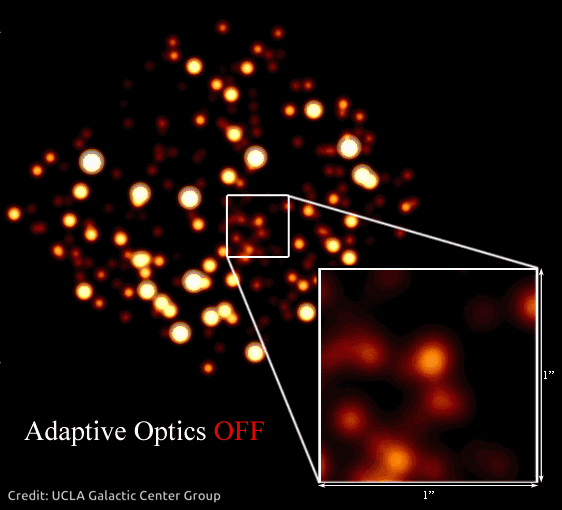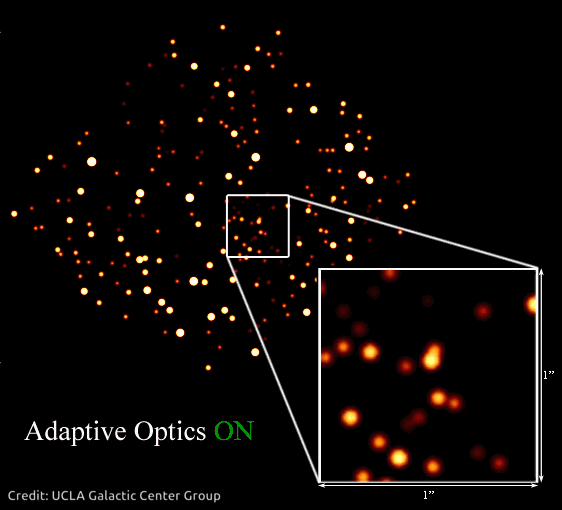
This impact creates an issue for ground-based telescopes. As a substitute of seeing sharp pictures, astronomers get fuzzy photos. Particular tech often known as adaptive optics helps resolve photos of area so astronomers can see issues extra clearly. It’s even helpful for telescopes which are in area, above Earth’s ambiance, as a result of tiny imperfections of their optics can blur pictures, too.
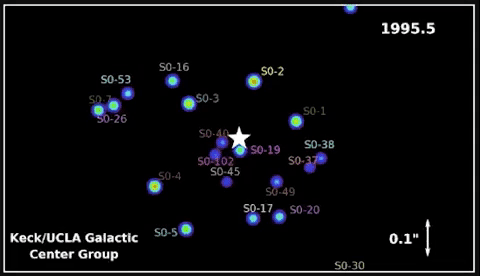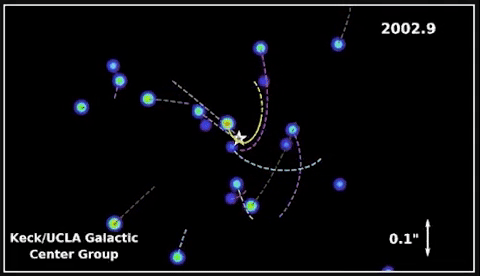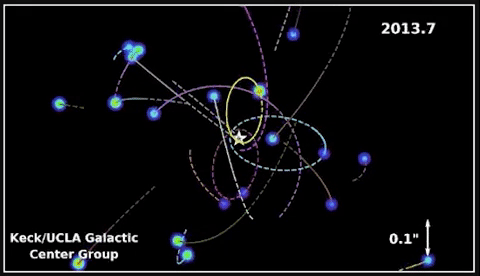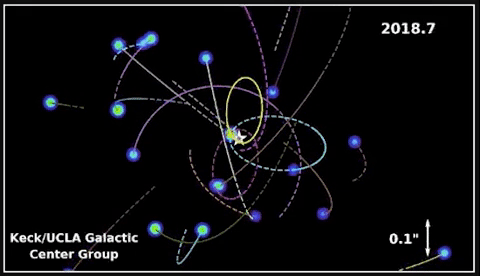
In 2020, Andrea Ghez was awarded a share of the Nobel Prize in Physics for devising an experiment that proved there’s a supermassive black gap embedded within the coronary heart of our galaxy – one thing Hubble has proven is true of almost every galaxy in the universe! She used the W. M. Keck Observatory’s adaptive optics to trace stars orbiting the unseen black gap.
A girl named Nancy Grace Roman, who was NASA’s first chief astronomer, paved the best way for telescopes that research the universe from area. An upcoming observatory named in her honor, the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, will use a particular form of adaptive optics in its Coronagraph Instrument, which is a expertise demonstration designed to dam the glare from host stars and reveal dimmer orbiting planets.
Roman’s Coronagraph Instrument will come outfitted with deformable mirrors that can function a type of visible “autocorrect” by measuring and subtracting starlight in actual time. The mirrors will bend and flex to assist counteract results like temperature modifications, which may barely alter the form of the optics.
Different telescopes have taken photos of huge, younger, vivid planets orbiting far-off from their host stars as a result of they’re often the simplest ones to see. Taking tech that’s labored properly on ground-based telescopes to area will assist Roman {photograph} dimmer, older, colder planets than every other observatory has been in a position to to date. The mission might even snap the primary actual {photograph} of a planet like Jupiter orbiting a Sun-like star!
Discover out extra in regards to the Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope on Twitter and Facebook, and study the person from which the mission attracts its identify.
Be certain that to comply with us on Tumblr to your common dose of area!