One of the crucial perplexing discoveries in fashionable astronomy has been discovering supermassive black holes, some weighing billions of instances greater than our Solar, in galaxies that fashioned lower than 750 million years after the Massive Bang. They seem to have grown impossibly quick, difficult our understanding of how black holes type and evolve.
The normal path for black gap formation entails stellar collapse, the place a large star dies and go away behind black holes sometimes weighing only a few instances greater than the Solar. However for these stellar remnants to develop into billion photo voltaic mass giants within the early universe would require feeding at unattainable charges for exceptionally lengthy durations.
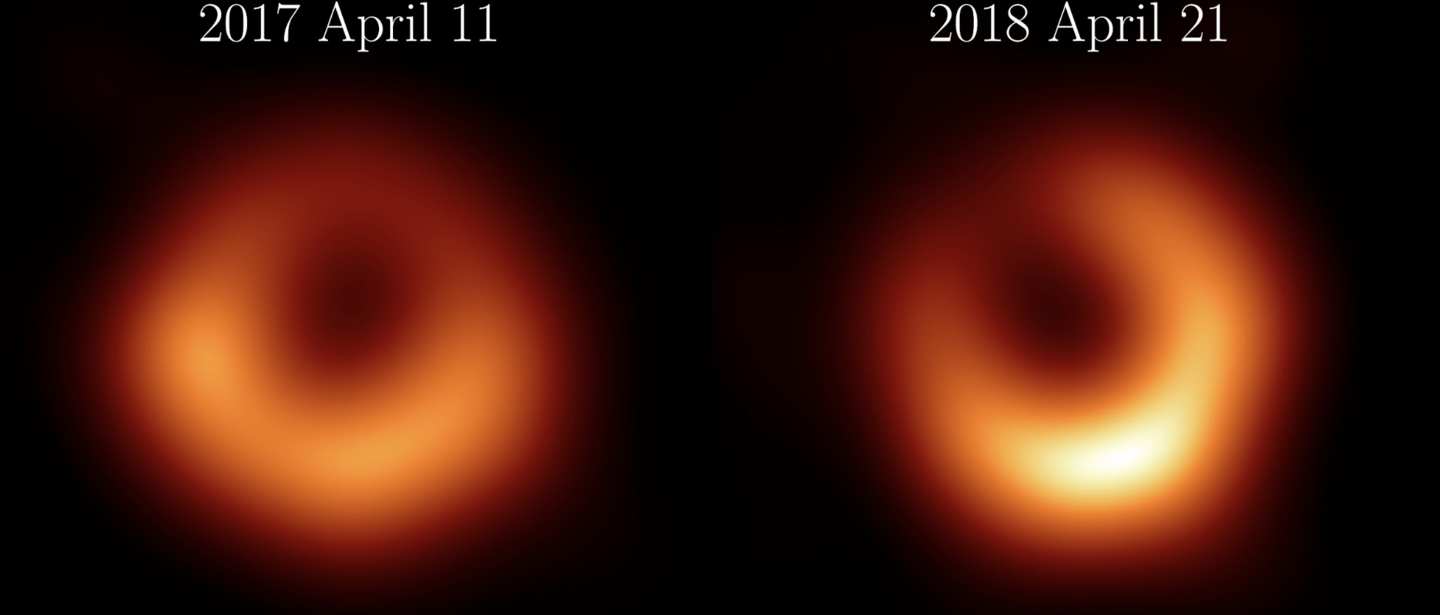 Picture exhibiting the adjustments within the black gap on the centre of the galaxy often called M87 (Credit score : NASA/JPL)
Picture exhibiting the adjustments within the black gap on the centre of the galaxy often called M87 (Credit score : NASA/JPL)
A staff of scientists could have discovered a strategy to spot supermassive black holes when they’re forming by in search of a specific kind of sunshine they emit throughout their violent beginning course of. Enter the “Direct Collapse” situation, a proposed mechanism the place huge clouds of primordial gasoline collapse instantly into supermassive black gap seeds with out first forming stars. This course of might create intermediate mass black holes weighing 100,000 to 10 million photo voltaic lots, offering a way more cheap start line for speedy progress into supermassive black holes.
The New analysis by Yang Luo1 and Isaac Shlosman, means that these precursors to the universe’s most huge black holes might be detectable as they type, probably fixing considered one of astronomy’s largest mysteries. The important thing requirement for direct collapse course of is sustaining the gasoline at atomic hydrogen’s cooling temperature of about 10,000 Kelvin, stopping the fragmentation that might result in star formation as an alternative. Below these circumstances, huge gasoline clouds can collapse instantly into dense cores that ultimately turn out to be black gap seeds.
The analysis focuses on detecting a particular kind of sunshine known as Lyman-alpha emission which occurs when hydrogen atoms take up and re-emit ultraviolet radiation. Throughout direct collapse, this emission represents one of many major cooling processes, carrying away power because the gasoline cloud contracts.
 The New Horizons sky map proven Lyman-alpha emission centred on the anti-Solar course (Credit score : G. Randall Gladstone)
The New Horizons sky map proven Lyman-alpha emission centred on the anti-Solar course (Credit score : G. Randall Gladstone)
Earlier fashions assumed spherical collapse, which might lure the photons and destroy them via quantum processes. Nonetheless, the researchers suggest a extra lifelike situation involving rotating gasoline that varieties an accretion disk across the central mass focus. This creates a bi-conical outflow sample, basically funnels alongside the rotation axis the place radiation can escape.
Utilizing subtle laptop simulations and radiation switch calculations, the duo found that substantial fractions of Lyman-alpha photons can escape via these outflow channels. For a pre-supermassive black gap object at redshift 10 (when the universe was solely about 500 million years outdated), greater than 95% of the Lyman-alpha radiation might escape and probably be detected.
The analysis exhibits that the James Webb Area Telescope’s NIRSpec instrument may be capable of detect these indicators with its multi-object spectroscopy mode and about 10,000 seconds of statement time.
 NIRSpec previous to set up on the James Webb Area Telescope and with out its Optical Meeting Cowl (Credit score : Astrium GmbH)
NIRSpec previous to set up on the James Webb Area Telescope and with out its Optical Meeting Cowl (Credit score : Astrium GmbH)
What makes this discovery notably thrilling is that the Lyman-alpha emission from direct collapse objects ought to have distinctive traits that distinguish them from different celestial sources. The researchers discovered that these pre-supermassive black gap objects would produce extremely uneven spectral traces with prolonged pink tails, options not sometimes seen in regular galaxies or established quasars.
The flexibility to detect these objects would open a brand new window into the early universe’s most dramatic occasions. Not like fashioned supermassive black holes surrounded by vibrant accretion disks, these pre-black gap objects could be comparatively metal-free, representing really primordial circumstances.
One essential facet of this analysis is timing. The direct collapse course of and related Lyman-alpha emission seemingly happens throughout a comparatively transient section earlier than the central object turns into a real black gap. This slender detection window emphasises the significance of systematic surveys to catch these objects throughout their formation.
If confirmed via observations, this analysis might basically change our understanding of how the universe’s most huge black holes fashioned, offering direct proof for probably the most unique situations in theoretical astrophysics. The primary detection of a direct collapse object via its Lyman-alpha emission would characterize a serious milestone in understanding the origins of supermassive black holes that formed the construction of the early universe.

