This text was initially printed at The Conversation. The publication contributed the article to House.com’s Professional Voices: Op-Ed & Insights.
Ever been late since you misinterpret a clock? Typically, the “clocks” geologists use thus far occasions will also be misinterpret. Unravelling Earth’s 4.5-billion-year historical past with rocks is hard enterprise.
Living proof: the invention of an historic meteorite affect crater was not too long ago reported within the distant Pilbara area of Western Australia. The unique research, by a distinct group, made headlines with the declare the crater formed 3.5 billion years ago. If true, it could be Earth’s oldest by far.
Because it seems, we would additionally been investigating the identical web site. Our outcomes are published in Science Advances today. Whereas we agree that that is the positioning of an historic meteorite affect, we have now reached totally different conclusions about its age, measurement and significance.
Let’s take into account the claims made about this fascinating crater.
One affect crater, two variations of occasions
Planetary scientists seek for historic impacts to study Earth’s early formation. To date, no one has discovered an affect crater older than the 2.23-billion-year-old Yarrabubba structure, additionally in Australia. (Among the authors from each 2025 Pilbara research had been coauthors on the 2020 Yarrabubba research.)
The brand new contender is positioned in an space known as North Pole Dome. Regardless of the identify, this is not the place Santa lives. It is an arid, sizzling, ochre-stained panorama.
The primary report on the brand new crater claimed it shaped 3.5 billion years in the past, and was greater than 100 kilometers in diameter. It was proposed that such a big affect might need performed a task in forming continental crust within the Pilbara. Extra speculatively, the researchers additionally advised it might have influenced formative years.
Our research concludes the affect truly occurred a lot later, someday after 2.7 billion years in the past. That is no less than 800 million years youthful than the sooner estimate (and we expect it is most likely even youthful; extra on that in a second).
We additionally decided the crater was a lot smaller – about 16km in diameter. In our view, this affect was too younger and too small to have influenced continent formation or formative years.
So how may two research arrive at such totally different findings?
Delicate clues of an affect
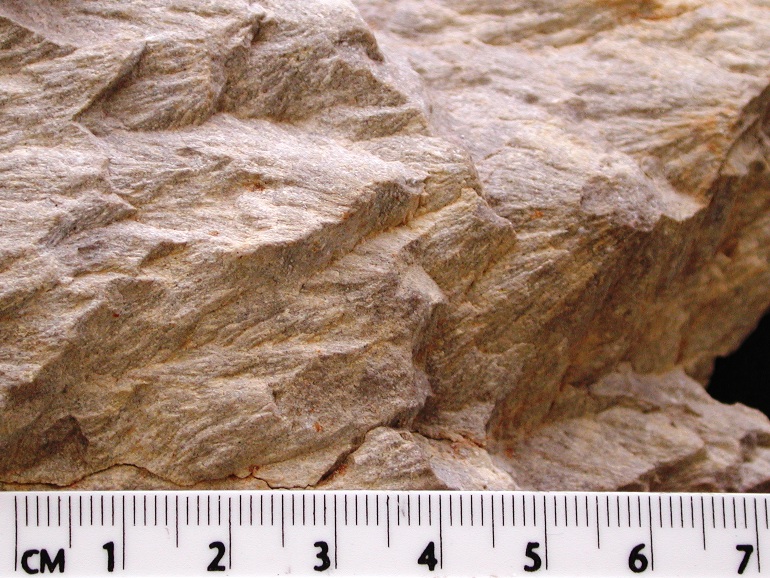
The initially round crater is deeply eroded, leaving solely delicate clues on the panorama. Nonetheless, among the many rust-colored basalts are distinctive telltale indicators of meteorite affect: shatter cones.
Shatter cones are distinctive fossilized imprints of shock waves which have handed by rocks. Their distinctive conical shapes type below temporary however immense strain the place a meteorite strikes Earth.
Each research discovered shatter cones, and agree the positioning is an historic affect.
This new crater additionally wanted a reputation. We consulted the native Aboriginal folks, the Nyamal, who shared the standard identify for this place and its folks: Miralga. The “Miralga affect construction” identify acknowledges this heritage.
Figuring out the timing of the affect
The affect age was estimated by area observations, as neither research discovered materials more likely to yield an affect age by radiometric dating – a technique that makes use of measurements of radioactive isotopes.
Each research utilized a geological precept known as the law of superposition. This states that rock layers get deposited one on high of one other over time, so rocks on high are youthful than these beneath.
The primary group discovered shatter cones inside and beneath a sedimentary layer recognized to have been deposited 3.47 billion years in the past, however no shatter cones in youthful rocks above this layer. This meant the affect occurred throughout deposition of the sedimentary layer.
Their statement gave the impression to be a “smoking gun” for an affect 3.47 billion years in the past.
Because it seems, there was extra to the story.
Our investigation discovered shatter cones in the identical 3.47 billion-year-old rocks, but in addition in youthful overlying rocks, together with lavas recognized to have erupted 2.77 billion years in the past.
The affect needed to happen after the formation of the youngest rocks that contained shatter cones, that means someday after the two.77-billion-year-old lavas.
In the mean time, we do not know exactly how younger the crater is. We will solely constrain the affect to have occurred between 2.7 billion and 400 million years in the past. We’re engaged on relationship the affect by isotopic strategies, however these outcomes aren’t but in.

Smaller than initially thought
We made the primary map exhibiting the place shatter cones are discovered. There are a lot of lots of over an space 6km throughout. From this map and their orientations, we calculate the unique crater was about 16km in diameter.
A 16km crater is a far cry from the unique estimate of greater than 100km. It’s too small to have influenced the formation of continents or life. By the point of the affect, the Pilbara was already fairly previous.
A brand new connection to Mars
Science is a self-policing sport. Claims of discovery are primarily based on knowledge accessible on the time, however they typically require modification primarily based on new knowledge or observations.
Whereas it’s not the world’s oldest, the Miralga affect is scientifically distinctive, as craters shaped in basalt are uncommon. Most basalts there shaped 3.47 billion years in the past, making them the oldest shocked goal rocks recognized.
Previous to affect, these historic basalts had been chemically altered by seawater. Sedimentary rocks close by additionally comprise the earliest well-established fossils on Earth. Such rocks possible lined a lot of early Earth and Mars.
This makes the Miralga affect construction a playground for planetary scientists learning the cratered floor (and possibly formative years) of Mars. It is an simply accessible proving floor for Mars exploration devices and imagery, proper right here on Earth.
This text is republished from The Conversation below a Artistic Commons license. Learn the original article.

