Within the distant previous, the Photo voltaic System was rife with impacts and collisions. Thousands and thousands of rocky objects zoomed chaotically by way of the system, smashing into one another in collisional cascades. Over time, a lot of them finally turned a part of the rocky planets. What’s left of the house rocks are largely gathered in the principle asteroid belt.
However some are in any other case hidden in troublesome to look at places. Sadly for all times on Earth, among the most troublesome to identify ones are near us. They’re hidden within the Solar’s glare and are uncomfortably near our Earthly dwelling.
A scientist on the Carnegie Institute for Science has found a brand new asteroid in our neighbourhood. It is title is 2025 SC79 and it is the most recent member of the Atira asteroid group. These are near-Earth asteroids with orbits completely inside Earth’s orbit. Atiras are the least quite a few group of near-Earth objects and 2025 SC79 is the thirty ninth member.
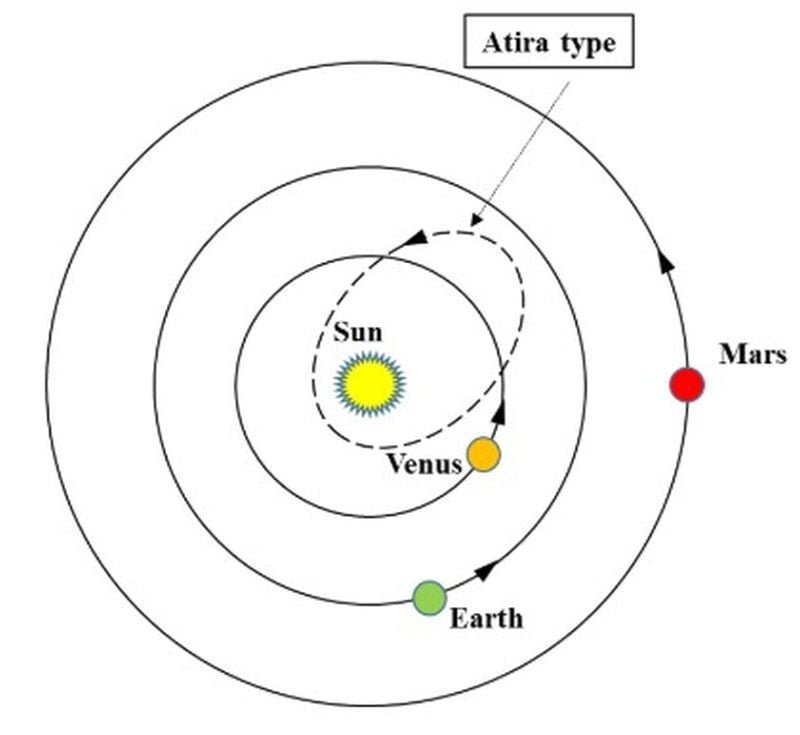 Atira asteroids comply with orbits completely inside Earth’s orbit. Picture Credit score:
Atira asteroids comply with orbits completely inside Earth’s orbit. Picture Credit score:
These objects are difficult to identify as a result of their meager gentle is drowned out by the Solar’s overpowering glare. This new house rock is barely the second identified object with an orbit completely inside Venus’ orbit. It additionally crosses Mercury’s orbit, and completes a visit across the Solar in solely 128 days. It has the third shortest orbital interval of any asteroid, with the 2 quickest ones each having an orbital interval of solely 115 days. For comparision, Mercury’s orbital interval is barely 88 days.
Carnegie Science astronomer Scott S. Sheppard found the asteroid on September 27 with the Darkish Power Digital camera on the Nationwide Science Basis’s Blanco 4-meter telescope. That telescope searches for killer asteroids, and 2025 SC79 actually qualifies. 2025 SC79 is about 700 metres (2,300 ft) in diameter. Whereas small in comparison with the Chicxulub impactor that ended the dinosaurs, that measurement asteroid would nonetheless create a catastrophic affect on a continental scale. Relying on the place it landed, it might kill billions of individuals and animals.
The sighting was later confirmed with two different telescopes: the NSF’s Gemini telescope and Carnegie Science’s Magellan telescopes.
 *This artist’s illustration reveals an asteroid hiding within the Solar’s glare. Picture Credit score: DOE/FNAL/DECam/CTIO/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/J. da Silva/Spaceengine CC BY 4.0*
*This artist’s illustration reveals an asteroid hiding within the Solar’s glare. Picture Credit score: DOE/FNAL/DECam/CTIO/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/J. da Silva/Spaceengine CC BY 4.0*
“Probably the most harmful asteroids are essentially the most troublesome to detect,” Sheppard defined in a press release. “Most asteroid analysis finds these objects at the hours of darkness of night time, the place they’re best to identify. However asteroids that lurk close to the Solar can solely be noticed throughout twilight—when the Solar is nearly to rise or set. If these ‘twilight’ asteroids strategy Earth, they might pose severe affect hazards.”
There’s much more to study 2025 SC79 however that should wait. It is disappearing behind the Solar for a number of months. As soon as it reappers, astronomers will study it for extra detailed data. Its composition is a crucial query, because it’s surviving publicity to the Solar’s intense warmth. Additional observations may make clear the asteroid’s origins. It could have been dislodged from the principle asteroid belt by some means after which captured by the Solar.
“Lots of the Photo voltaic System’s asteroids inhabit one in every of two belts of house rocks, however perturbations can ship objects careening into nearer orbits the place they are often tougher to identify,” Sheppard concluded. “Understanding how they arrived at these places will help us shield our planet and in addition assist us study extra about Photo voltaic System historical past.”

