Our seek for exoplanets is targeted on Milky Manner stars. It has been profitable, with greater than 6,000 detected up to now. Scientists are even starting to maneuver past mere detections, and dealing on characterizing different traits of those planets, particularly their atmospheres.
However the Milky Manner (MW) has a confirmed 61 satellite tv for pc galaxies, fairly probably many extra. Many of those smaller galaxies have had their star-forming hydrogen gasoline stripped away via interactions with the MW’s halo. In others, tidal interactions have created streams of stars stretching via house. Nonetheless different satellite tv for pc galaxies are mere remnants, having misplaced most of their stars via merging with the MW. How do these environments have an effect on exoplanets?
To know that, astronomers have to search out exoplanets in these satellite tv for pc galaxies or their remnants. New analysis describes and defines an effort to search out exoplanets in one of many MW’s remnant satellites. It is titled “Searching for Exoplanets Born Outside the Milky Way: VOYAGERS Survey Design,” and it is revealed within the Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. The lead writer is Robert Aloisi, a grad scholar within the Division of Astronomy on the College of Wisconsin-Madison.
“Observations over the previous few a long time have discovered that planets are frequent round close by stars in our Galaxy, however little is understood about planets that shaped outdoors the Milky Manner,” the authors write. “We describe the design and early implementation of a survey to check whether or not planets additionally exist orbiting the remnant stars of historic dwarf galaxies that merged with the Milky Manner, and in that case, how they differ from their Milky Manner counterparts.”
VOYAGERS stands for Views Of Yore – Historical Gaia-enceladus Exoplanet Revealing Survey. It is centered on Gaia-Enceladus (aka Gaia Sausage, Sausage Galaxy, Gaia-Enceladus-Sausage,) which is the remnant of a dwarf galaxy that merged with the MW between 8 and 11 billion years in the past. It is the final main merger within the MW’s historical past. Astronomers have recognized seven of the MW’s globular clusters that was a part of the Gaia Sausage. (The Sausage is just not named for the form of the remnant. It is named for the sausage-like form of the remnant stars when their velocities are plotted on a graph.)
6,000 exoplanets is a big pattern, but it surely’s nonetheless a restricted pattern. Most of them are orbiting primary sequence stars within the MW’s disk. These stars sometimes have metallicities very near the Solar’s, and that is a weak spot within the pattern. “Nonetheless, this census of recognized exoplanet hosts doesn’t absolutely signify the broader range of stars throughout the Universe, together with metal-poor stars from the early Universe and stars present in dwarf galaxies,” the authors clarify. The brand new survey is aimed to deal with this shortcoming.
Metallicity is a important think about each stars and planets, which each type type photo voltaic nebulae. Every nebula has a selected metallicity, which refers to its focus of parts heavier than hydrogen and helium. Metallicity within the Universe will increase as time goes and as generations of stars stay and die, as a result of stars create heavier parts by way of nucleosynthesis. When stars method the tip of their lives, these parts are unfold again out into house to be taken up by the subsequent era of stars, and their planets.
“We speculate that some planets probably shaped within the low-metallicity, high-alpha ingredient setting (parts shaped by fusion of He nuclei) of the early Universe, and this inhabitants could differ in incidence charges and compositions in comparison with these discovered in additional not too long ago shaped stars within the Milky Manner disk,” the authors write. Excessive-alpha parts embody oxygen, neon, sulphur, and magnesium. They’re produced on shorter timescales by stars that explode as core-collapse supernovae in solely thousands and thousands of years.
Our 6,000 exoplanets have revealed some patterns in exoplanet formation. There are fewer planets with lots bigger than Jupiter round low-metallicity stars, and in distinction, the incidence charges for exoplanets of Neptune mass and smaller do not appear to rely upon metallicity in any respect. Exoplanet scientists additionally know that sub-Neptune mass planets have decrease densities when shaped round low-metallicity stars. In one other connection between exoplanets and stellar metallicity, short-period super-Earths are comparatively uncommon round low-metallicity stars.
This all elements right into a better understanding of exoplanet habitability. The query is, how do these patterns relate to stars and exoplanets in remnant satellite tv for pc galaxies?
“Looking for planets in GES (Gaia-Enceladus Sausage) presents an intriguing alternative, because it stays unclear how planets type in environments outdoors the Milky Manner and the way low-metallicity situations affect these processes,” the researchers clarify.
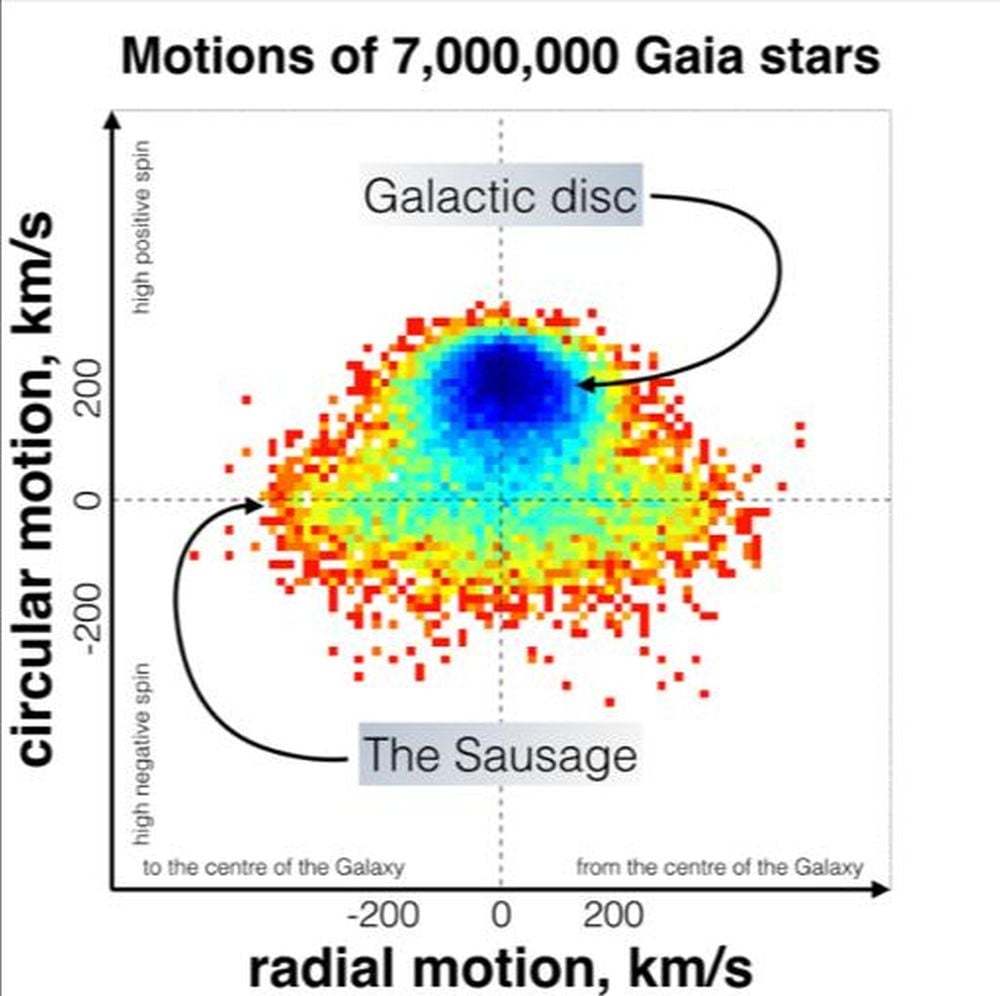 This determine exhibits the Gaia-Sausage construction detected by the ESA’s Gaia satellite tv for pc in velocity house. (Credit score: V. Belokurov et al. 2018, MNRAS, 478, 611).
This determine exhibits the Gaia-Sausage construction detected by the ESA’s Gaia satellite tv for pc in velocity house. (Credit score: V. Belokurov et al. 2018, MNRAS, 478, 611).
VOYAGERS will use the radial velocity (RV) technique to review primary sequence stars and barely advanced stars within the GES. The primary objective is to search out exoplanets shaped in low-metallicity environments separate from the MW. There are greater than 47,000 stars which might be recognized as GES stars, and the researchers began with them. Then they filtered them out and had been left with a mere 156 stars that had been appropriate for exoplanet detection resulting from their brightness and different properties. The celebrities had been additional screened for his or her suitability for RV observations, and by the tip of the rigorous evaluation and screening, they had been left with 22 stars within the GES.
“A key objective of our survey isn’t just to detect planets that had been born outdoors the Milky Manner, but in addition to be a primary probe of their inhabitants and to see whether or not there are vital variations between GES planets and Milky Manner planets,” the authors write. The survey can be centered on sub-Neptune mass exoplanets.
VOYAGERS is just partially full. “Our objective is to acquire 160 observations for every GES goal,” the authors write. “We’ve got accomplished 778 observations.” With 22 targets and 160 observations every, that provides as much as 3,520, so the survey is just 22% full.
The analysis crew say that their future observations will concentrate on 10 primary sequence stars to expedite their outcomes, whereas additionally observing the remaining targets throughout much less optimum observing situations.
“Additional, the survey is designed such that if we detect no planets, we will decide with confidence that incidence charges for Neptune-mass exoplanets are considerably decrease for GES targets than incidence charges for stars born within the Milky Manner,” the authors write.
If that seems to be true, it helps the metallicity speculation in planet formation. One of many issues the speculation states is that metal-rich stars usually tend to type big planets as a result of there’s extra heavy parts for them to type their giant cores.
Star formation, metallicity, and exoplanet formation are all items in a big, advanced puzzle. As these items discover their appropriate locations within the puzzle, we’ll study extra about potential habitability and the prospects of life elsewhere. Discovering Neptune mass planets in these low-metallicity environments would deliver the puzzle one tiny step nearer to completion.
“If we uncover a number of planets orbiting these historic, low-metallicity stars, the survey outcomes will lengthen our understanding of when and the place planets and probably life can evolve within the Universe,” the authors conclude.

