It’s a scientific consensus that water as soon as flowed on Mars, that it had a denser ambiance, that means that it was as soon as liveable. Sadly, roughly 4.2 to three.7 billion years in the past, Mars’ rivers, lake, and world ocean started to vanish as photo voltaic wind slowly stripped its ambiance away. For scientists, the query of how lengthy it remained liveable has been the topic of ongoing inquiry. Whereas some scientists keep that Mars ceased being liveable billions of years in the past, latest analysis means that it skilled durations of habitability that lasted for eons.
This contains latest findings by NASA’s Curiosity rover, which has been exploring the Gale Crater on Mars to be taught extra concerning the planet’s previous. In keeping with new research by scientists at New York College Abu Dhabi (NYUAD), there may be proof that billions of years in the past, historic sand dunes inside the crater progressively was rock by interacting with underground water. Their findings, which had been revealed within the Journal of Geophysical Research – Planets, point out that Mars could have been liveable for much longer than anticipated.
The analysis was led by Dimitra Atri, the Principal Investigator of NYUAD’s Heart for Astrophysics and House Science (CASS) with help by fellow CASS researcher Vignesh Krishnamoorthy. They had been joined by Analysis Instrumentation Scientist James Weston of NYUAD’s Core Expertise Platforms, Postdoctoral Affiliate Marieh B. Al-Handawi of NYUAD’s Good Supplies Lab, and Professor Panče Naumov of NYUAD’s Heart for Good Engineering Supplies, the Analysis Heart for Surroundings and Supplies, and NYU’s Molecular Design Institute.
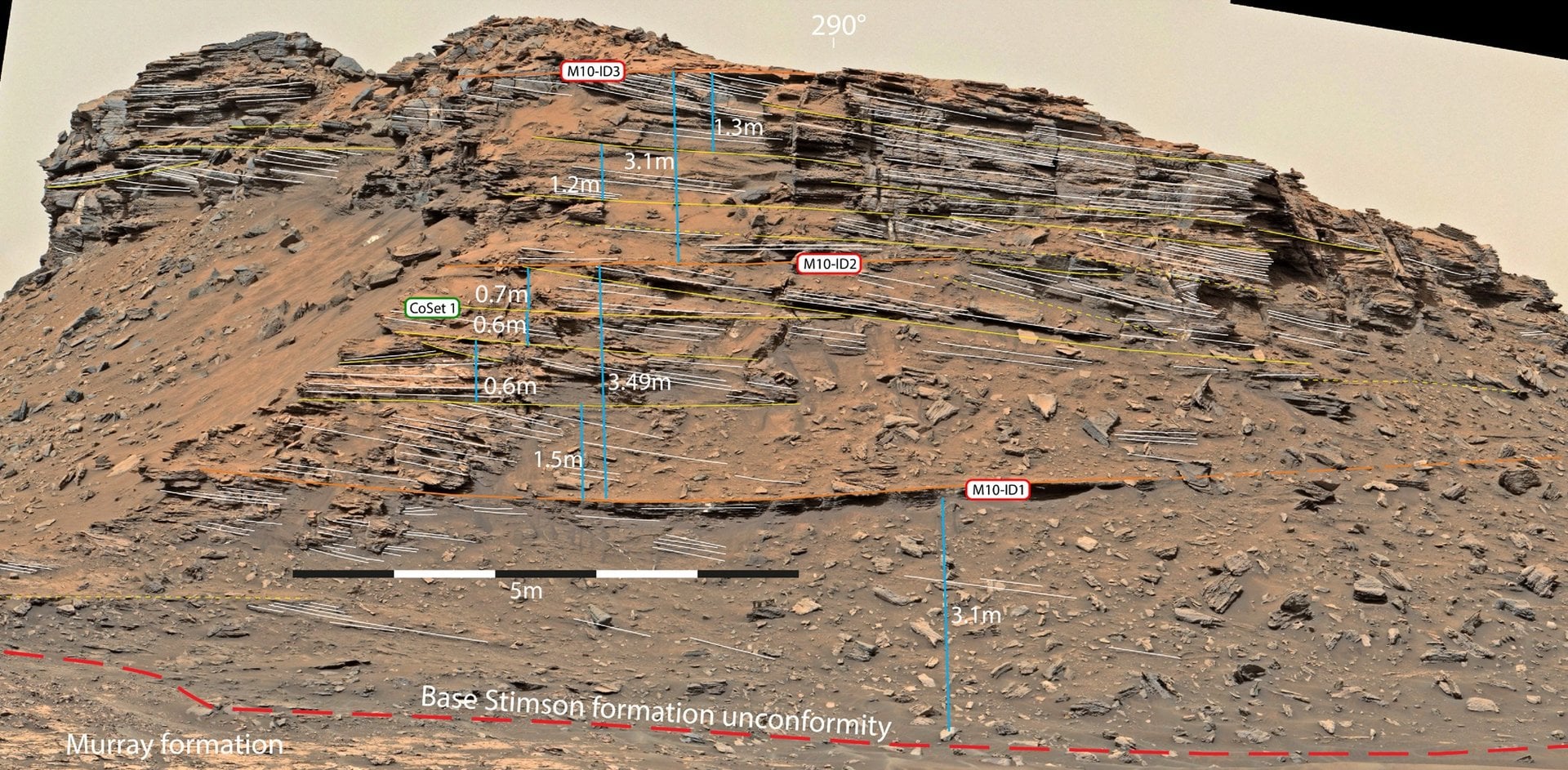 *Mastcam mosaic of the Stimson Formation, which fashioned by means of interplay with underground water. Credit score: MSL/NASA/JPL-Caltech*
*Mastcam mosaic of the Stimson Formation, which fashioned by means of interplay with underground water. Credit score: MSL/NASA/JPL-Caltech*
For his or her examine, the group examined dunes within the Stimson Formation (SF), a system of wind-blown (aeolian) sand and sedimentary rock within the Gale Crater. The Curiosity rover has noticed proof of those “lithified” formations (i.e. sediments that hardened into stone) at this location on a number of events. Given the pervasive dry situations within the Gale Crater, these formations probably fashioned through the Noachian Interval (ca. 4.1 to three.7 billion years in the past) when in depth flooding is believed to have taken place, which included rivers that flowed into the Gale Crater.
The group accessed this information by means of the Mars Science Laboratory’s (MSL) Curiosity Notebook, which offers entry to data gathered by Curiosity‘s devices. They then in contrast this information to discipline research of rock formations within the desert atmosphere of the United Arab Emirates (UAE), that are additionally identified to have fashioned within the presence of water. They decided that the SF was the product of late-stage aqueous exercise, that means they fashioned from interplay with groundwater from the close by mountain.
They additional discovered that this interplay left behind minerals resembling gypsum, gentle sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO4) that can also be present in Earth’s deserts. This newest analysis echoes related findings offered by Krishnamoorthi and Atri final 12 months on the Tenth International Conference on Mars, which passed off from July twenty second to twenty fifth at Caltech in Pasadena, California. In that examine, they examined information collected on the Greenheugh Pediments (GP), a close-by dune formation with equally lithified rock deposits.
In each circumstances, the researchers imagine that these dunes and their techniques of underground water led to the creation of those curious formations, which may have vital implications within the seek for previous (and current) life on Mars. On Earth, sandstone deposits include a number of the oldest proof of life on Earth, together with communities of microorganisms that bind sediment and trigger minerals to precipitate. Primarily based on these terrestrial analogues, Atri and Krishnamoorthi’s group imagine that lithified deposits within the Gale Crater may include the preserved stays of historic micro organism.
This newest analysis not solely offers new perception into how Mars developed and transitioned to the extraordinarily chilly and dry atmosphere we see there immediately. It additionally means that these websites could be good candidates for future missions that may proceed the seek for life on Mars.
Additional Studying: NYU Abu Dhabi

