A couple of years in the past, asteroid mining was all the fad. With the business area sector quickly rising, the dream of commercializing area appeared nearly imminent. Principally, the notion of getting platforms and spacecraft that would rendezvous and mine Close to Earth Asteroids (NEAs), then return them to space-based foundries, was proper up there with sending business crews to Mars. After an excessive amount of hypothesis and ventures going beneath, these plans have been positioned on the again burner till the expertise matured and different milestones could possibly be achieved first.
Nonetheless, the dream of asteroid mining and the “post-scarcity” future it will deliver stays. Along with the necessity for extra infrastructure and technical improvement, additional analysis is required to find out the chemical composition of small asteroids. In a recent study, a group led by researchers from the Institute of House Sciences (ICE-CSIC) analyzed samples of C-type (carbon-rich) asteroids, which account for 75% of recognized asteroids. Their findings show that these asteroids could possibly be an important supply of uncooked supplies, presenting alternatives for future useful resource exploitation.
The group was led by Dr. Josep M. Trigo-Rodríguez, a Theoretical Physicist from the Institute of House Sciences (ICE) and the Catalonian Institute of House Research (IEEC) in Barcelona. He was joined by PhD pupil Pau Grèbol-Tomàs (additionally from the ICE and IEEC), Dr. Jordi Ibanez-Insa (Geosciences Barcelona), Prof. Jacinto Alonso-Azcárate (Universidad de Castilla-La Mancha), and Prof. Maria Gritsevich (College of Helsinki and the Institute of Physics and Know-how, Ural Federal College. Their work is detailed in a paper that can seem on Jan. 2nd within the *Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society* (MNRAS).
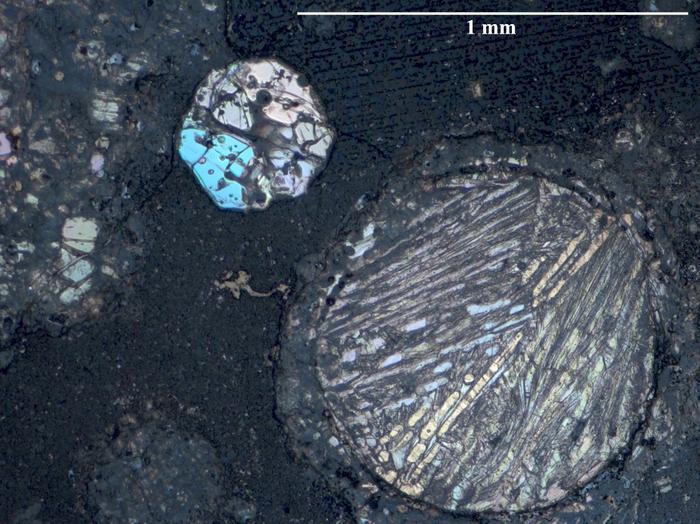 Mirrored gentle picture of a skinny part of carbonaceous chondrite meteorite from NASA’s Antarctic assortment. Credit score: ICE-CSIC/J.M.Trigo-Rodríguez et al. (2025)
Mirrored gentle picture of a skinny part of carbonaceous chondrite meteorite from NASA’s Antarctic assortment. Credit score: ICE-CSIC/J.M.Trigo-Rodríguez et al. (2025)
Carbonaceous chondrites (C chondrites) fall to Earth often, although they’re hardly ever retrieved for research by scientists. Except for accounting for less than 5% of all meteorites, their fragile nature usually causes them to fragment and be misplaced. So far, nearly all of these retrieved have been present in desert areas, together with the Sahara and Antarctica. The Asteroids, Comets, and Meteorites analysis group at ICE-CSIC, which Trigo-Rodriguez leads, investigates the physicochemical properties of asteroids and comets and is the worldwide repository for NASA’s Antarctic meteorite assortment.
On this newest research, the analysis group chosen and characterised the asteroid samples, which have been then analyzed by Professor Jacinto Alonso-Azcárate on the College of Castilla-La Mancha utilizing mass spectrometry. This allowed them to find out the exact chemical composition of the six most typical lessons of C chondrites, offering beneficial data on whether or not useful resource extraction might be potential sooner or later. Mentioned Trigo-Rodríguez in a Spanish Nationwide Analysis Council (CSIC) press release:
The scientific curiosity in every of those meteorites is that they pattern small, undifferentiated asteroids, and supply beneficial data on the chemical composition and evolutionary historical past of the our bodies from which they originate. At ICE-CSIC and IEEC, we focus on growing experiments to raised perceive the properties of those asteroids and the way the bodily processes that happen in area have an effect on their nature and mineralogy. The work now being printed is the end result of that group effort.
Realizing the abundance of fabric in asteroids is significant, as they’re extremely heterogeneous. Whereas they’re sometimes grouped into three classes: C-type (carbonaceous), M-type (metallic), or S-type (silicaceous), asteroids are additionally categorized by spectral traits and orbit. As well as, asteroids are basically materials left over from the formation of the Photo voltaic System and are closely influenced by their lengthy evolutionary historical past (ca. 4.5 billion years). As such, understanding the exact composition of asteroids is crucial to figuring out the place totally different sources (water, ores, and many others.) are more likely to be situated.
 *Credit score: ESO*
*Credit score: ESO*
In line with the group’s outcomes, mining undifferentiated asteroids (believed to be the progenitor of chondritic meteorites) is way from viable. The research additionally recognized a kind of asteroid wealthy in olivine and spinel bands as a possible goal for mining operations. The group additionally famous that water-rich asteroids with excessive concentrations of water-bearing minerals ought to be chosen. Within the meantime, they emphasize the necessity for extra sample-return missions to confirm the determine of progenitor our bodies earlier than mining will be realized. Mentioned Trigo-Rodríguez:
Alongside the progress represented by pattern return missions, firms able to taking decisive steps within the technological improvement essential to extract and gather these supplies beneath low-gravity situations are really wanted. The processing of those supplies and the waste generated would even have a major impression that ought to be quantified and correctly mitigated.
This, they argue, would require the event of large-scale assortment methods and strategies for extracting sources in microgravity. “For sure water-rich carbonaceous asteroids, extracting water for reuse appears extra viable, both as gas or as a major useful resource for exploring different worlds,” stated Trigo-Rodríguez. “This might additionally present science with better information about sure our bodies that would someday threaten our very existence. In the long run, we might even mine and shrink doubtlessly hazardous asteroids in order that they stop to be harmful.” As Grèbol-Tomàs added:
Finding out and deciding on most of these meteorites in our clear room utilizing different analytical strategies is fascinating, notably due to the range of minerals and chemical parts they comprise. Nonetheless, most asteroids have comparatively small abundances of treasured parts, and due to this fact the target of our research has been to grasp to what extent their extraction can be viable. It feels like science fiction, however it additionally appeared like science fiction when the primary pattern return missions have been being deliberate thirty years in the past.
In any case, the advantages of asteroid mining are immense, which is why the topic has gained such traction prior to now decade. Along with treasured metals, many asteroids are a supply of water ice that could possibly be used to fabricate gas for deep-space missions and water for ingesting and irrigating crops. This is able to imply lowered reliance on resupply missions from Earth, permitting robotic and crewed missions to attain better self-sufficiency. By relocating mining and manufacturing to cislunar area and the Most important Asteroid Belt, humanity would additionally cut back the environmental impression these industries have on Earth.
Whereas public enthusiasm for asteroid mining has cooled over the previous decade, many ventures right now are researching and growing the required expertise. Equally, area businesses like NASA and JAXA have carried out sample-return missions which have revealed an incredible deal in regards to the scientific and materials wealth asteroids might comprise.
Within the close to future, China’s Tianwen-2 mission will rendezvous with an NEA and a Most important Asteroid Belt comet. Although it could be many a long time (or longer) earlier than an trade for space-based sources emerges, there are numerous ready to get in on the bottom flooring.

