Our Photo voltaic System, it seems, is one thing of an oddball. Whereas we’ve rocky planets near the Solar and fuel giants additional out, most stars within the Milky Means harbour one thing completely totally different. They’re worlds between the sizes of Earth and Neptune and orbit nearer to their stars than Mercury does to ours. These tremendous Earths and sub Neptunes are the Galaxy’s most typical planets, discovered round practically each Solar like star ever have studied. Till now that’s.
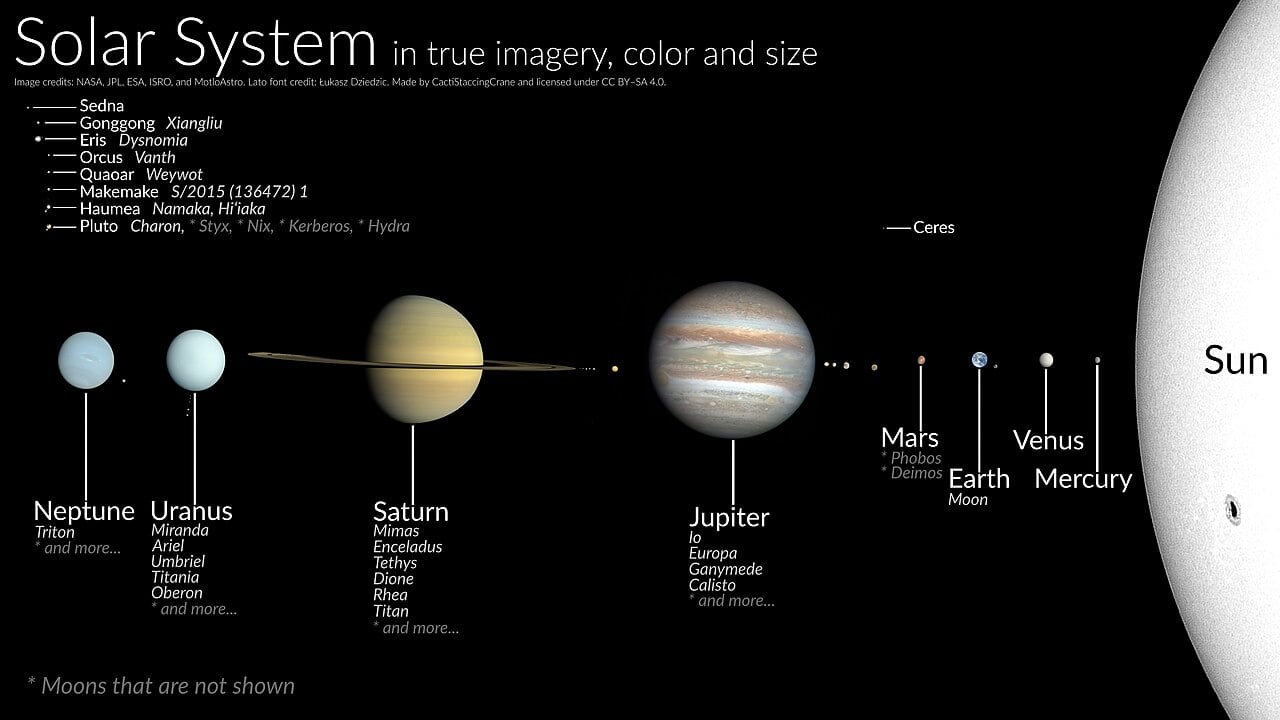 Artist impression of our Photo voltaic System with planets in true color ( Credit score : CactiStaccingCrane)
Artist impression of our Photo voltaic System with planets in true color ( Credit score : CactiStaccingCrane)
A world workforce of astronomers has discovered what they’re calling an important lacking hyperlink, a younger planetary system caught within the act of changing into the Galaxy’s most typical structure. Just like the well-known Lucy fossil that helped bridge apes and people, this technique reveals us precisely how the universe builds its favorite sort of planet.
The important thing lies in V1298 Tau, a younger star simply 20 million years previous, barely a toddler in comparison with our 4.5 billion 12 months previous Solar. 4 large planets circle this star, every between the sizes of Neptune and Jupiter, engaged in what researchers describe as a turbulent section of fast evolution. Over the subsequent few billion years, these bloated worlds will shrink dramatically, reworking into the compact tremendous Earths and sub Neptunes that populate our Galaxy.
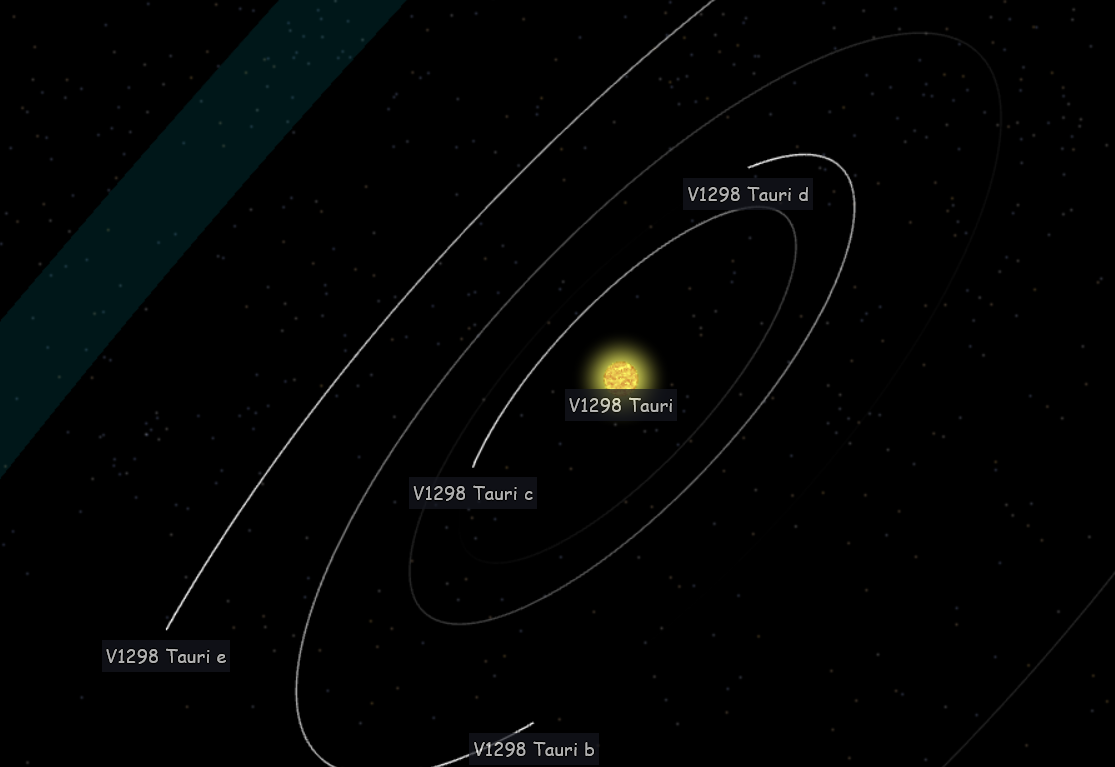 V1298 Tauri system with 4 exoplanets orbiting this younger star (Credit score : Exploration Program and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory for NASA’s Astrophysics Division)
V1298 Tauri system with 4 exoplanets orbiting this younger star (Credit score : Exploration Program and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory for NASA’s Astrophysics Division)
The workforce spent a decade measuring when every planet crossed in entrance of its star in an occasion referred to as a transit. However they weren’t simply trying on the transits themselves, they had been timing tiny irregularities. The planets’ gravitational tugs on one another trigger delicate shifts of their orbital dance, dashing up or slowing down by mere minutes. These Transit Timing Variations allowed the researchers to weigh the planets for the primary time, sidestepping the standard methodology which fails spectacularly with younger, temperamental stars.
The outcomes stunned even the researchers. Regardless of being 5 to 10 instances Earth’s radius, the planets weighed solely 5 to fifteen instances our world’s mass. They’re terribly low density, extra like planetary sized cotton sweet than something we’d recognise as a correct planet.
This puffiness solves a long-standing puzzle. Commonplace planet formation fashions predict that newly shaped worlds must be much more compact. The evaluation reveals that these planets underwent dramatic transformation early on, quickly shedding a lot of their preliminary atmospheres when the fuel wealthy disk round their younger star disappeared. However they’re nonetheless evolving. Over billions of years, they’ll proceed dropping ambiance and contracting considerably.
“We’re basically watching the universe’s most profitable planetary structure within the making” – John Livingston, lead creator from Tokyo’s Astrobiology Centre.
This discovery may additionally clarify why our personal Photo voltaic System lacks the Galaxy’s most typical planets, maybe we merely advanced in a different way, taking a less-travelled cosmic path.
Supply : Astronomers find missing link to galaxy’s most common planets

