Everyone knows folks that appear to defy ageing and seem a lot youthful than they really are. This identical phenomenon occurs in astronomy, too. Some stars simply do not appear to age the identical method different stars do.
Blue Stragglers are puzzling on this regard. Blue Straggler Stars (BSS) had been found a long time in the past and astronomers have been puzzling over them ever since. They get their identify from their place on the Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagram. They’re present in open clusters and globular clusters, and when in comparison with their same-aged cluster-mates, they’re hotter and bluer.
Within the HR diagram, stars discover their place based mostly on their temperatures and luminosities. Foremost sequence stars spend their lives on a diagonal band within the HR diagram. Stars spend most of their lives right here as they fuse hydrogen into helium. Our Solar suits in the course of this band.
However extra huge stars are hotter and brighter, they usually’re discovered within the higher left, whereas smaller stars, that are dimmer and cooler, are discovered on the underside proper.
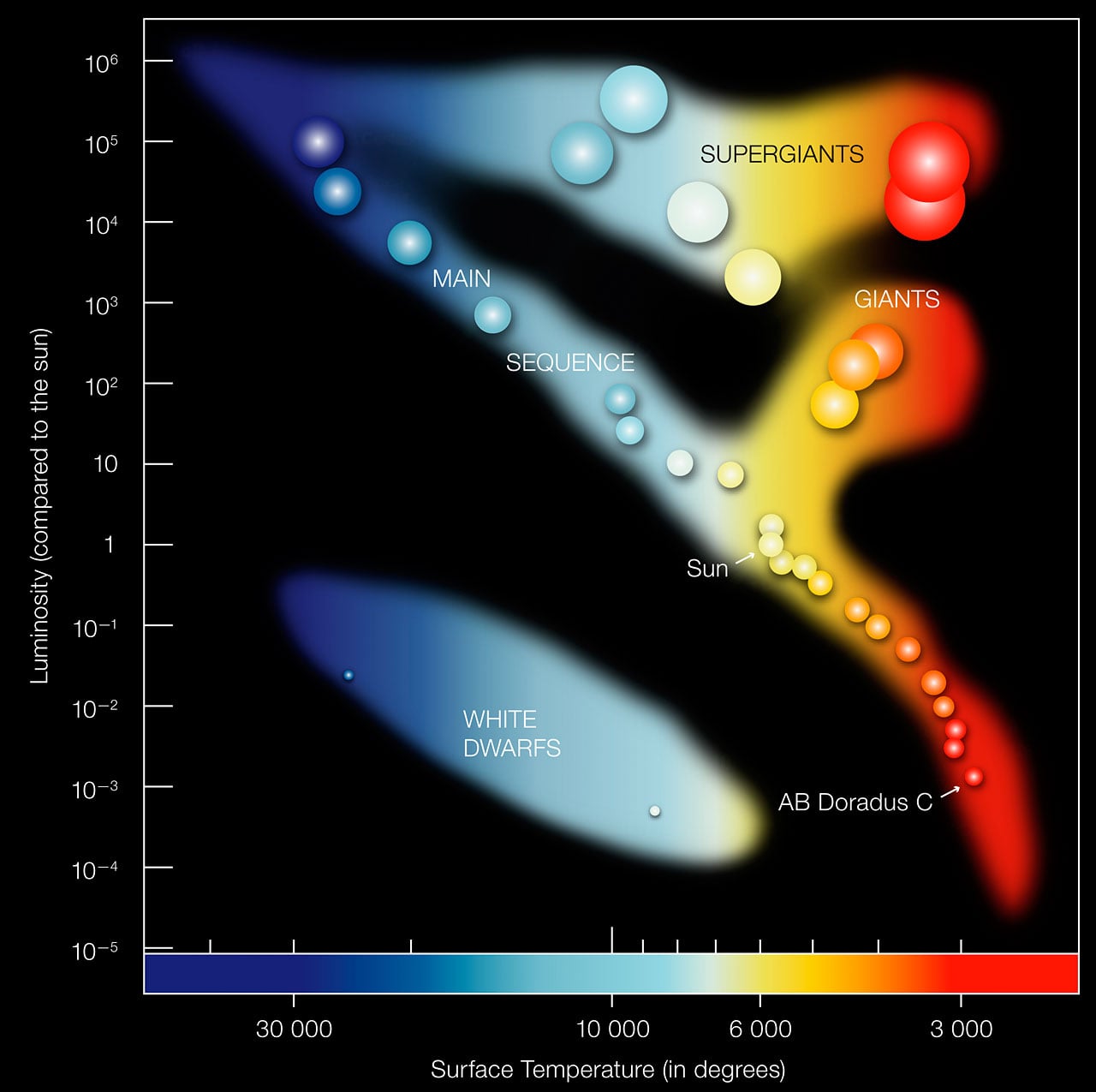 *The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram organizes stars by their temperature and luminosity. Foremost sequence stars are in a diagonal band from the higher left to the decrease proper. Extra huge stars, that are hotter and brighter, are on the higher left. Smaller, dimmer, cooler stars are on the underside proper. Picture Credit score: ESO*
*The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram organizes stars by their temperature and luminosity. Foremost sequence stars are in a diagonal band from the higher left to the decrease proper. Extra huge stars, that are hotter and brighter, are on the higher left. Smaller, dimmer, cooler stars are on the underside proper. Picture Credit score: ESO*
Blue Stragglers are present in globular clusters and are off on their very own within the HR diagram.
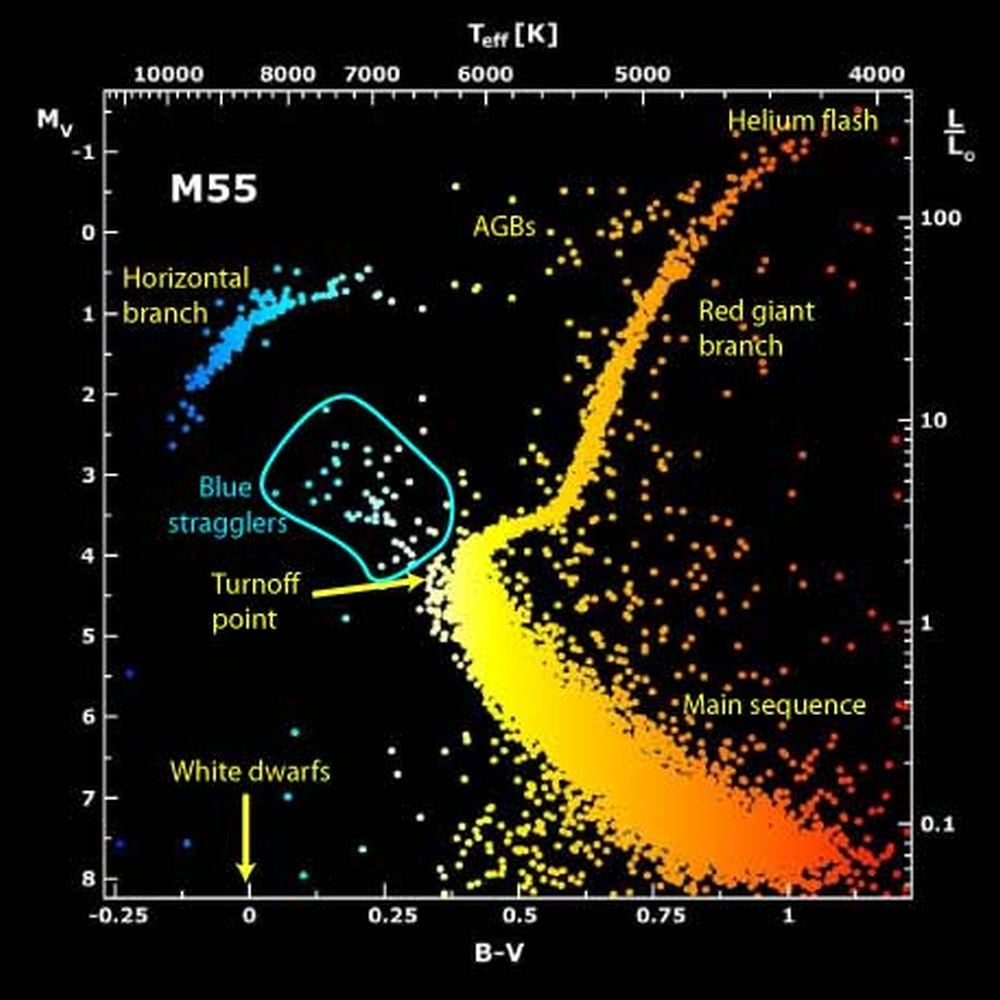 That is an HR diagram for the globular cluster M55. It illustrates how blue stragglers are off on their very own, straggling behind their fellow cluster members. Picture Credit score: NASA APOD Feb twenty third 2001.
That is an HR diagram for the globular cluster M55. It illustrates how blue stragglers are off on their very own, straggling behind their fellow cluster members. Picture Credit score: NASA APOD Feb twenty third 2001.
Globular clusters are historical buildings that include largely older, redder stars. Blue stragglers stand out as a result of they’re hotter and brighter than their fellows. A cluster has a foremost sequence turn-off level, the place stars stop hydrogen fusion and depart the principle sequence to turn out to be giants. However blue stragglers do not conform to this. Whereas the opposite stars turn out to be crimson, swollen, and cooler, blue stragglers keep blue, sizzling, and vivid, despite the fact that they’re the identical age.
The one method they’ll do that is to accumulate further mass in some unspecified time in the future. For many years, astrophysicists have debated how which may occur. There are two competing explanations for the way BSS purchase their further mass.
The primary is through stellar collisions. Two stars and collide after which merge, making a extra huge, hotter, and bluer star. Stars are packed very tightly collectively within the cores of globular clusters, and stellar mergers could be extra possible in this sort of crowded atmosphere.
The second method that BSS might purchase further mass that may delay their keep on the principle sequence is through mass switch. In a binary star association, when one of many stars evolves into a large, it turns into weaker gravitationally and may’t maintain onto its mass. In that case, the first star attracts mass from its companion, accretes it, and thereby turn out to be a blue straggler.
In new analysis, a workforce of astronomers examined BSS in 48 totally different galactic globular clusters (GCC) with the Hubble Area Telescope. They’ve constructed the most important catalogue of blue stragglers ever created, and wished to find out if dense environments in GCCs had been liable for blue stragglers from stellar mergers. A number of the clusters of their work held as few as 12 blue stragglers, and a few had as many as 179, with the overall variety of stragglers reaching 3,419.
Their analysis is titled “A binary-related origin mediated by environmental conditions for blue straggler stars,” and it is revealed in Nature Communications. The lead writer is Francesco Ferraro, a professor within the Division of Physics and Astronomy on the College of Bologna in Italy.
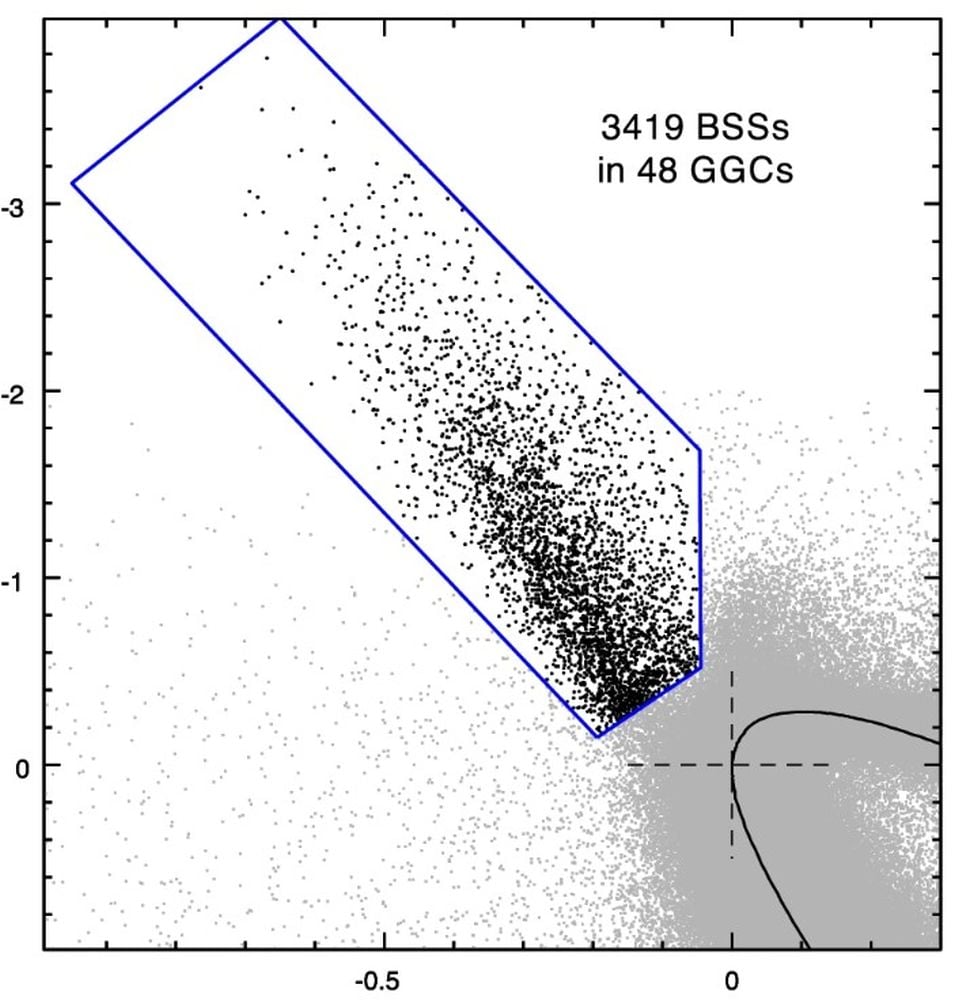 This determine from the research reveals the three,419 blue stragglers within the research, discovered amongst 48 galactic globular clusters. Picture Credit score: Ferraro et al. 2026. NatComm.
This determine from the research reveals the three,419 blue stragglers within the research, discovered amongst 48 galactic globular clusters. Picture Credit score: Ferraro et al. 2026. NatComm.
“Blue stragglers are anomalously huge core hydrogen-burning stars that, in line with the idea of single star evolution, mustn’t exist,” Ferraro and his co-authors write. “They’re suspected to type in mass-enhancement processes, involving binary evolution or stellar collisions.”
“In dynamically energetic techniques like globular clusters, the variety of blue stragglers originated by collisions is predicted to extend with the native density and the speed of stellar encounters,” the researchers clarify.
However that is not what their observations uncovered. Reasonably than discovering extra BSS within the dense heart of globular clusters, they discovered extra in lower-density areas.
“Nonetheless, probably the most intriguing end result comes from the comparability between the BSS particular frequency and different properties characterizing the cluster atmosphere, such because the central density and the collision price,” the researchers clarify of their research. “The truth is, whereas high-density high-collisional environments are anticipated to favor the activation of the BSS collisional channels, we discover as an alternative that the BSS particular frequency decreases in these situations.”
“Extra particularly, in high-density situations, the effectivity of BSS formation/survival is as much as 20 instances decrease than in “peaceable”, low-density environments,” they add.
These outcomes chip away at the concept stellar mergers are the reason for BSS. However they bolster the concept they get their further mass from binary companions. Binary companions usually tend to survive longer within the much less dense areas of globular clusters.
“These findings not solely present that binaries ideally type/survive in low-density environments, but additionally counsel that the general quantity of binary techniques hosted within the mum or dad cluster could possibly be the important thing parameter liable for the noticed BSS populations,” the researchers clarify.
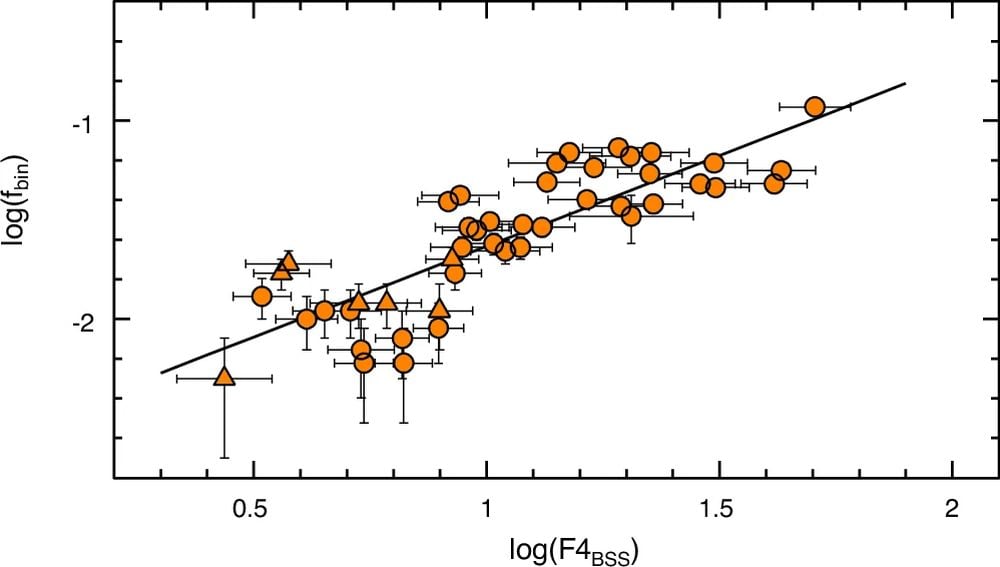 This determine from the analysis reveals the correlation between the fraction of binaries hosted in a galactic globular cluster (y-axis) and the blue straggler particular frequency (x-axis). A stable black line represents the best-fit relation to the info. Picture Credit score: Ferraro et al. 2026. NatComm.
This determine from the analysis reveals the correlation between the fraction of binaries hosted in a galactic globular cluster (y-axis) and the blue straggler particular frequency (x-axis). A stable black line represents the best-fit relation to the info. Picture Credit score: Ferraro et al. 2026. NatComm.
Scientsts are cautious by nature, they usually know that correlation doesn’t equal causation. The authors are fast to level out one thing essential. “The noticed correlations, on their very own, can’t be thought of as irrefutable proofs of the bodily connection between BSSs and binaries,” they write.
However scientists additionally aren’t within the behavior of dismissing patterns that emerge from knowledge. “Nonetheless, the truth that the correlations noticed for binary techniques correctly reproduce these discovered for BSSs, whereas they fail if different sub-populations are thought of, helps the BSS-binary hyperlink,” Ferraro and his fellow authors clarify.
“This work reveals that the atmosphere performs a related position within the lifetime of stars,” stated lead writer Ferraro in a press release. “Blue straggler stars are intimately related to the evolution of binary techniques, however their survival is determined by the situations through which they stay. Low-density environments present the perfect habitat for binaries and their by-products, permitting some stars to seem youthful than anticipated.”
Co-author Enrico Vesperini from Indiana College echoes what Ferraro stated. “Crowded star clusters usually are not a pleasant place for stellar partnerships,” he explains. “The place area is tight, binaries will be extra simply destroyed, and the celebs lose their likelihood to remain younger.”
Stars are formed by their environment, an uncontroversial assertion. However the particulars of how they’re formed just isn’t simply confirmed. This work attracts a hyperlink between the stellar atmosphere and probably the most puzzling varieties of stars on the market. The outcomes may appear counterintuitive, however they’re backed up by a big pattern.
“This work provides us a brand new technique to perceive how stars evolve over billions of years,” stated co-author Barbara Lanzoni, additionally from the College of Bologna in Italy. “It reveals that even star lives are formed by their atmosphere, very like dwelling techniques on Earth.”

