Some galaxies within the early universe had been absolute powerhouses, churning out stars at charges that will dwarf the Milky Approach’s modest stellar manufacturing. These “monster galaxies,” buried deep in mud between 10 and 12 billion years in the past, are considered the ancestors of at the moment’s big elliptical galaxies. However what drove them to develop so violently has remained frustratingly unclear.
Ryota Ikeda and his colleagues at Japan’s Nationwide Astronomical Observatory could have simply solved the thriller by discovering there is not a single reply. Utilizing each ALMA and the James Webb House Telescope to watch three monster galaxies within the constellation Sextans, they achieved one thing unprecedented. By evaluating precisely the place stars are forming now with the place they shaped prior to now, all on the similar terribly excessive decision of 0.06 arc-seconds. That is the equal of getting visible acuity 1000 instances higher than human eyesight, sufficient to differentiate options just some thousand gentle years throughout in galaxies billions of sunshine years away.
 Two of the Atacama Massive Millimetre/submillimetre Array (ALMA) 12-metre antennas gaze on the sky on the observatory’s Array Operations Website (AOS), excessive on the Chajnantor plateau at an altitude of 5000 metres within the Chilean Andes (Credit score : ESO)
Two of the Atacama Massive Millimetre/submillimetre Array (ALMA) 12-metre antennas gaze on the sky on the observatory’s Array Operations Website (AOS), excessive on the Chajnantor plateau at an altitude of 5000 metres within the Chilean Andes (Credit score : ESO)
ALMA excels at detecting ongoing star formation hidden behind thick veils of mud, whereas JWST traces the distribution of stars already shaped. When the crew overlaid these complementary views, the three galaxies revealed wildly completely different architectures.
AzTEC-1 exhibits star formation unfold all through the galaxy whereas its present stars cluster tightly on the centre. This sample suggests a serious collision between two massive galaxies funnelled fuel inward, triggering an intense starburst whereas scattering materials throughout the system. The violence of a galactic merger, on this case, acted because the spark.
AzTEC-4 tells a unique story. ALMA reveals elegant spiral arms traced by lively star formation, but JWST exhibits the present stars distributed in a easy disk with out sturdy spiral options. This mix factors to not an exterior set off however to spontaneous star formation pushed by the galaxy’s personal inner gravitational instability.
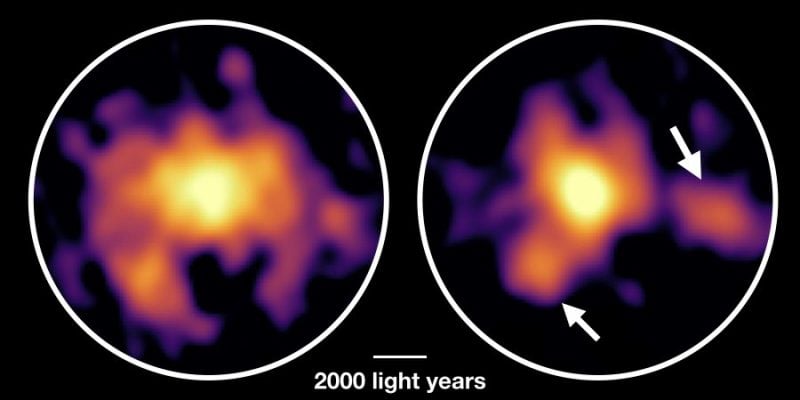 Monster galaxy AzTEC-1 noticed with the ALMA telescope in Chile. ALMA revealed the distribution of molecular fuel (left) and mud particles (proper). Along with the dense cloud within the centre, the analysis crew discovered 2 dense clouds a number of thousand gentle years away from the centre. These dense clouds are dynamically unstable and considered the websites of intense star formation. (Credit score : ALMA/ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)
Monster galaxy AzTEC-1 noticed with the ALMA telescope in Chile. ALMA revealed the distribution of molecular fuel (left) and mud particles (proper). Along with the dense cloud within the centre, the analysis crew discovered 2 dense clouds a number of thousand gentle years away from the centre. These dense clouds are dynamically unstable and considered the websites of intense star formation. (Credit score : ALMA/ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)
AzTEC-8 presents one more state of affairs. Compact star formation concentrates close to the galaxy’s middle in ALMA photos, whereas JWST reveals a way more prolonged stellar distribution peppered with large clumps. This structure suggests a collision with a smaller companion galaxy delivered contemporary fuel to the centre, lighting the fireplace of star formation with out the wholesale disruption of a serious merger.
The invention overturns the earlier assumption that every one monster galaxies grew the identical approach and demonstrates that a number of pathways result in fast progress within the early universe. The crew now plans to broaden their pattern considerably, conducting statistical exams on this variety and exploring what these mechanisms may inform us in regards to the formation of galaxies like our personal Milky Approach.
Supply : Multiple Origins Behind The Extreme Star Formation In “Monster Galaxies”

