What truly occurs to a spacecraft throughout its fiery final moments? That is the important thing query for the European House Company’s (ESA) Harmful Reentry Evaluation Container Object (Draco) mission.
ESA has greenlit this system that can create a extremely advanced reentry of a spacecraft particularly constructed to dive into Earth’s environment whereas loaded with a wide range of sensors.
Last moments
ESA is strongly backing an ambitious Zero Debris approach, an undertaking that aims to prevent more space debris by attempting to lower the risk that spacecraft will produce debris from collisions.
As part of that, ESA scientists are studying what happens when satellites burn up. Reentry science is an essential element of what’s dubbed “design for demise” efforts, said Holger Krag, ESA Head of Space Safety.
“We need to gain more insight into what happens when satellites burn up in the atmosphere as well as validate our re-entry models,” Krag said in an ESA statement targeted on the Draco initiative.
“That is why the distinctive knowledge collected by Draco will assist information the event of latest applied sciences to construct extra demisable satellites by 2030,” mentioned Krag.
Pressure gauge
Draco’s sensors will probably be measuring temperatures, gauging the pressure on the assorted components of the satellite tv for pc itself, and register the encompassing strain. 4 extra cameras will probably be pointing on the spacecraft to observe the destruction and gather contextual data.
Deliberate for 2027, the Draco satellite tv for pc is anticipated to tip the scales at between 330 to 440 kilos (150-200 kilograms). Concerning the measurement of a washer, Draco would purposely pile-drive itself over an ocean uninhabited space just a few 12 hours after being put into Earth orbit.

Fiery frenzy
Outfitted with 200 sensors and 4 cameras to report its fiery frenzy, the 1.3 foot diameter (40 centimeters) capsule would retailer knowledge safely onboard. As soon as its parachute is deployed, Draco would hook up with a geostationary satellite tv for pc, outputting its knowledge.
Based on ESA planners, there will probably be a few 20-minute window to transmit telemetry earlier than it splashes down into the ocean, concluding the Draco mission’s task.
If all goes properly, Draco would gather “real-world knowledge” on what happens as area {hardware} takes the warmth, shatters and scatters throughout reentry. It is a course of that researchers can solely mimic immediately on Earth in wind tunnels or through laptop fashions.
“Understanding how completely different supplies behave as they fritter away,” ESA explains, “might assist engineers design satellites that absolutely disintegrate, leaving nothing behind in orbit or within the environment.”
Ablation merchandise
The case for Draco knowledge is front-and-center clarify area particles specialists.
“Reentries create a number of points for basic area sustainability,” mentioned Aaron Boley, a professor on the College of British Columbia for physics and astronomy and co-director of the Outer House Institute.
If uncontrolled, they impose casualty dangers to individuals on the bottom and in plane in flight, Boley advised House.com, and might additional be disruptive to air site visitors ought to there be sudden airspace closures in response to the reentries.
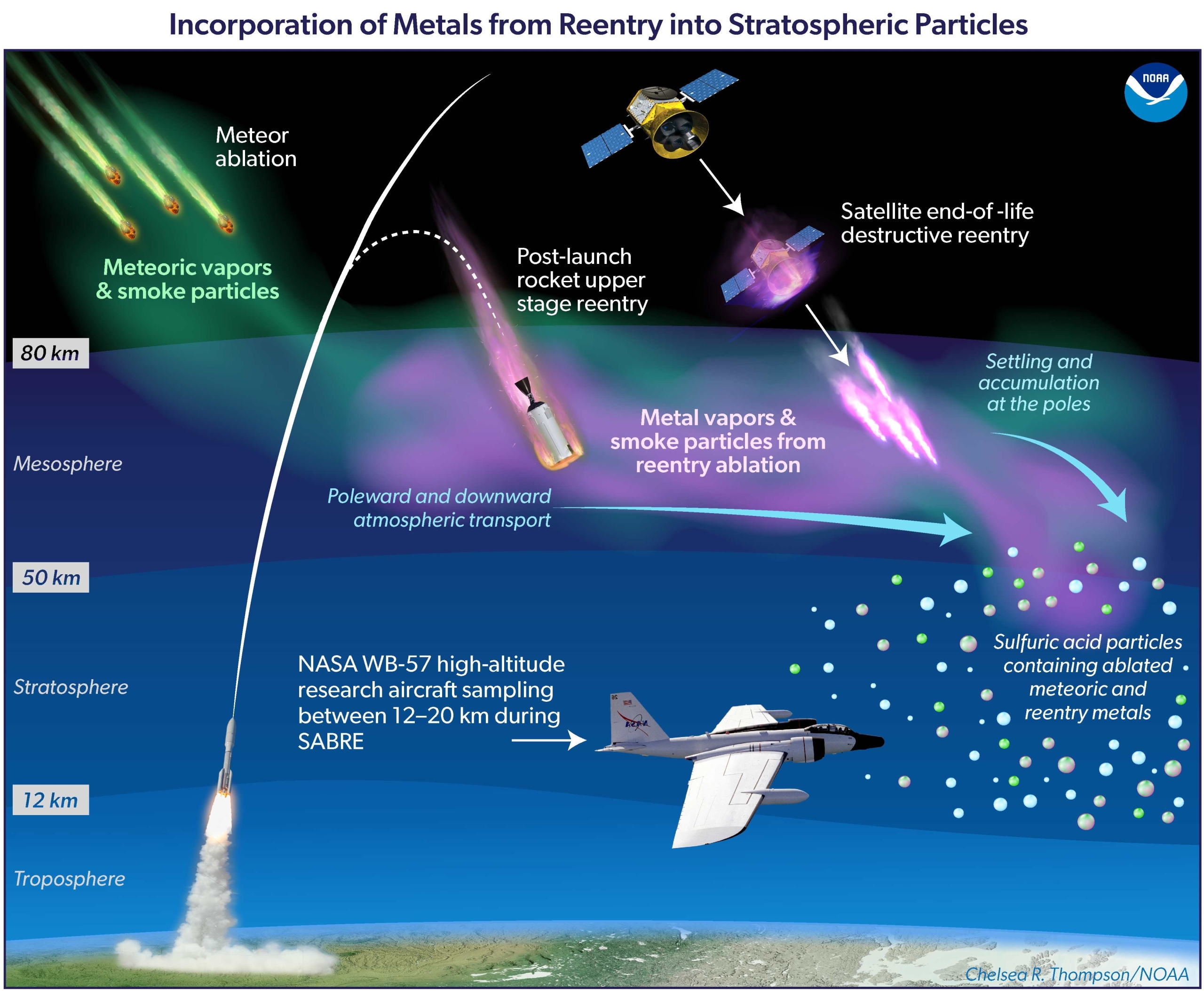
“Additionally they deposit ablation merchandise straight into the higher environment,” Boley mentioned.
One strategy to addressing casualty dangers is to design spacecraft to demise completely, however this exacerbates the environment air pollution downside, mentioned Boley. “Furthermore, reentry ablation fashions are insufficiently verified due partly to limits on lab testing.”
Advanced issues: security and air pollution
Experiments that may monitor the on-the-spot demise of a satellite tv for pc and the forms of emission merchandise which might be produced upon reentry are very helpful for addressing the interconnected and sophisticated issues of security and air pollution, Boley added.
Whereas not collaborating within the Draco mission, Boley mentioned that characterizing the forms of ablation merchandise “is of excessive precedence” as doing so permits investigators “to higher perceive how reentry emissions will have an effect on higher environment aerosols and related chemistry, with implications for ozone, local weather stability, higher environment polar clouds, and atmospheric transmission,” mentioned Boley.
Piece of the puzzle
Leonard Schulz is a researcher on the Technische Universität Braunschweig’s Institute of Geophysics and Extraterrestrial Physics in Braunschweig, Germany.
Additionally not engaged in ESA’s Draco initiative, Schulz mentioned that the outcomes of the enterprise can be eagerly awaited.
“In-situ measurements are one necessary piece of the puzzle lacking to higher perceive damaging spacecraft re-entry and its results on the environment,” he advised House.com.
“I sit up for the outcomes of this mission. Hopefully, it could possibly function a pathfinder for in-situ observations of spacecraft fragmentation and particularly their ablative habits,” mentioned Schulz.
Related knowledge
Related in view is Luciano Anselmo, a researcher on the House Flight Dynamics Laboratory inside the Nationwide Analysis Council’s Institute of Info Science and Applied sciences in Pisa, Italy.
Draco will probably be a single spacecraft reentry, with a particular trajectory, mass, and design, Anselmo mentioned.
Not concerned within the Draco program, Anselmo advised House.com that the experiment goals to be as consultant as potential and, if profitable, will enable for the gathering of loads of related knowledge.
“This knowledge couldn’t solely show to be way more typically relevant than one would possibly initially assume,” mentioned Anselmo, “however might additionally reveal one thing surprising, fostering new strains of investigation.”

