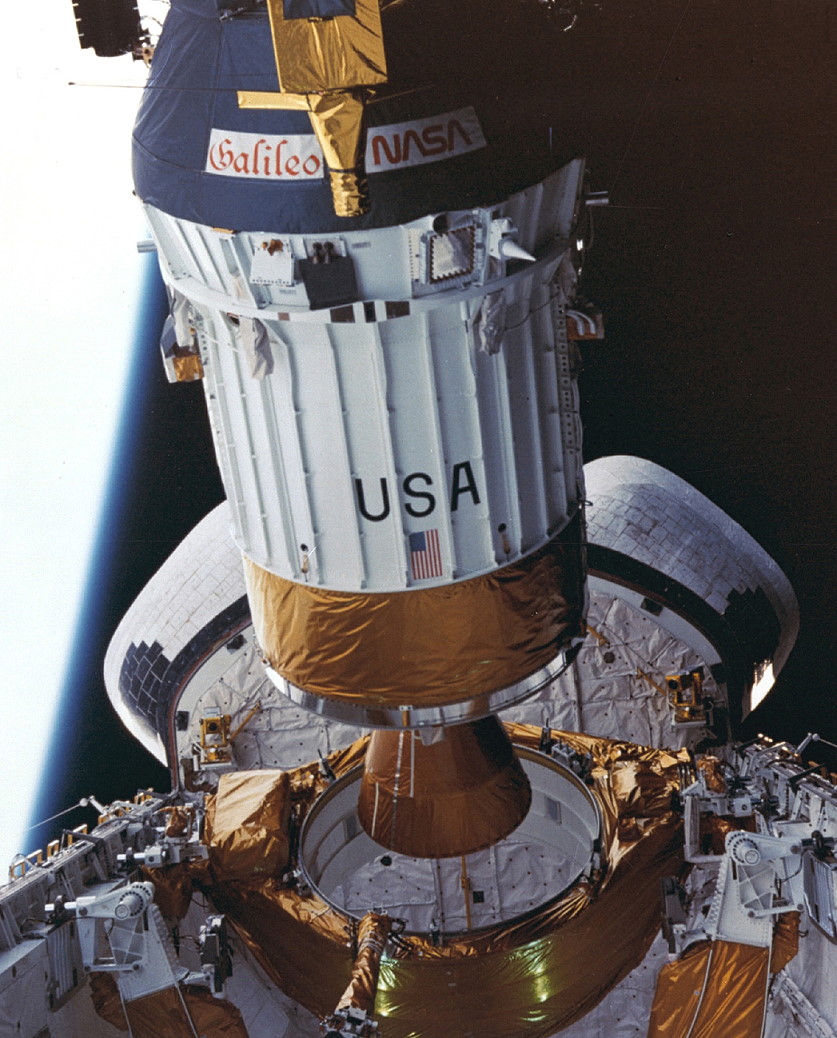

Greater than three many years in the past, Boeing’s Inertial Higher Stage (IUS) and an area probe sure for an additional world drifted silently out of shuttle Atlantis’ cavernous payload bay and into the inky void for a voyage of unprecedented exploration. Emblazoned on its aspect have been two names: “Galileo” in script and “NASA” in block capitals.
For astronaut Shannon Lucid, watching the deployment of the Galileo spacecraft to Jupiter on 18 October 1989, the 2 fonts represented each the romance of journey and the engineering expertise to comprehend a mission to the Photo voltaic System’s largest planet. But Galileo’s journey to the launch pad had been an extended and tortured one and its journey to Jupiter can be longer and more durable nonetheless.
Named in honor of the nice Italian scientist Galileo Galilei, whose endeavors within the early seventeenth century included the invention of Jupiter’s 4 giant moons—Ganymede, Callisto, Europa and Io—the mission obtained Congressional approval in 1977, with plans to launch aboard the shuttle and a Boeing-built IUS in 1981. Nevertheless, issues certifying the shuttle’s predominant engines to operate on the 109-percent energy degree essential to raise Galileo piled uncertainty onto this schedule and the launch made the primary of a number of inexorable slips to the best.
Delayed till 1982 on the soonest, there existed issues that its scientific work at Jupiter may be compromised, with solely 5 orbits of the large planet achievable, moderately than the unique 11. NASA finally switched from the IUS to Basic Dynamics’ extra highly effective, liquid-fueled Centaur-G Prime, though the mission teetered on the point of cancelation for a number of months.

Reassigned for a time to fly on a less expensive IUS, along with an “injection stage” for added propulsion, launch was rescheduled for 1985, however the absence of the Centaur-G Prime meant an extended journey time (5 years as a substitute of two) and a posh flight profile of gravity assists to get to Jupiter. Finally, Galileo shifted again onto the Centaur-G Prime, with launch focused for Might 1986.
Within the meantime, the {hardware} for the mission was taking form. Galileo would turn out to be the primary spacecraft to enter orbit round Jupiter and would deploy an instrumented probe into the planet’s hellish environment. The supersonic parachute for that probe underwent full-scale testing within the fall of 1983 and spacecraft and probe have been built-in in September of that 12 months.
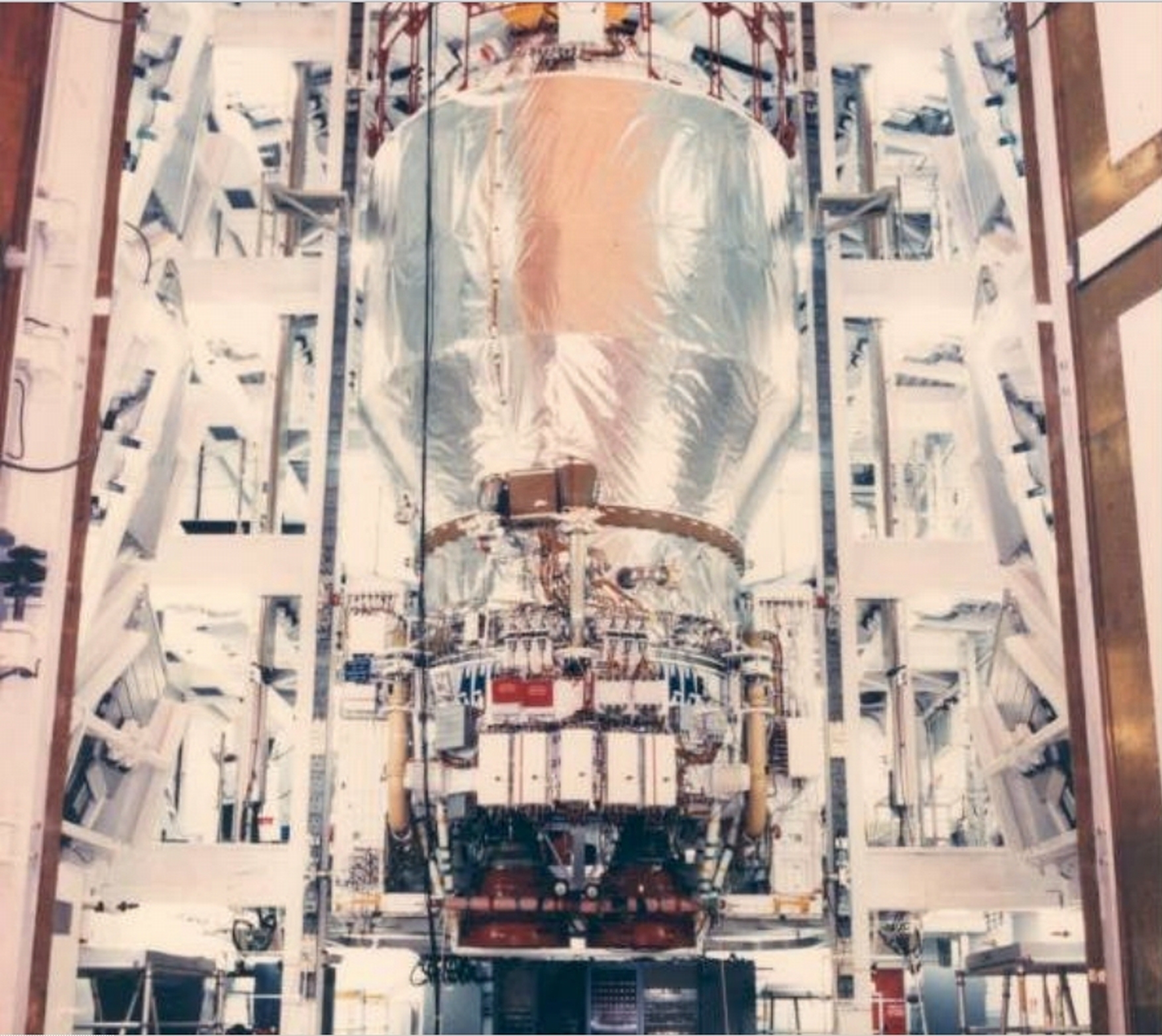
The Centaur-G Prime was full by August 1984 and the mission was taking over the character of a real voyage of exploration, as NASA endorsed different attainable duties for Galileo, together with a flyby of the primordial asteroid Amphitrite. It was acknowledged that an Amphitrite flyby would delay Galileo’s arrival at Jupiter from August to December 1988 and NASA determined to make a last resolution after launch.
Shortly earlier than Christmas 1985, Galileo was trucked overland to the Kennedy House Heart (KSC) in Florida for launch. Then, on 28 January 1986, Challenger exploded throughout liftoff.

The catastrophe irrevocably modified Galileo’s complete future. Speak of returning the shuttle to flight in early 1987 meant the earliest obtainable launch “window” to get to Jupiter didn’t open till June of that 12 months.
However modifications to the shuttle’s twin Stable Rocket Boosters (SRBs)—along with a variety of different enhancements throughout the fleet—pushed that schedule additional to the best and it was not till September 1988 that one other mission flew. Within the meantime, the hazardous Centaur-G Prime had been formally canceled in June 1986 and Galileo, once more, was retargeted to fly atop a safer IUS.

This offered an issue, for the IUS was not highly effective sufficient to ship Galileo on to Jupiter. A fancy flight profile referred to as the “Venus-Earth-Earth Gravity Help” (VEEGA) was conceived.
It envisaged launching in October-November 1989, flying previous Venus in February 1990, twice previous Earth in December 1990 and December 1992 and finally attending to Jupiter in December 1995. The VEEGA profile permitted rendezvous with as much as three asteroids—Ausonia, Gaspra and Ida—and finally the latter pair have been chosen.
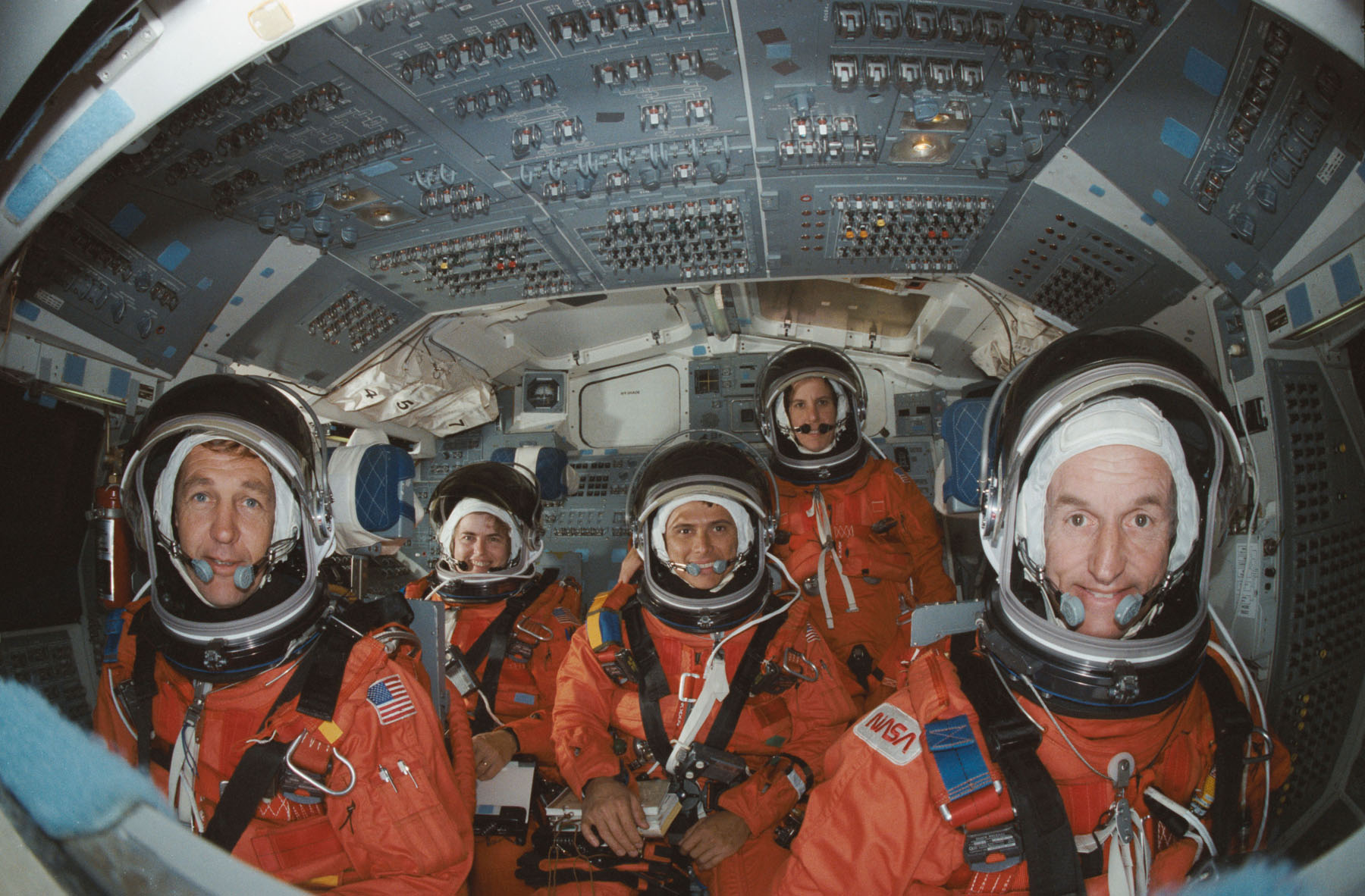

In November 1988, Commander Don Williams, Pilot Mike McCulley and Mission Specialists Shannon Lucid, Franklin Chang-Diaz and Ellen Baker have been assigned to STS-34, the flight scheduled to launch Galileo throughout a six-week-long “window” which opened on 12 October 1989. Nevertheless, extra hassle was afoot, for Galileo’s energy system got here underneath intense media and public scrutiny.
Flying removed from the Solar, using photo voltaic panels was negated in favor of plutonium-fed Radioisotope Thermoelectric Turbines (RTGs), upon which anti-nuclear demonstrators hungrily pounced. Peace marches have been undertaken, mock “demise scenes” enacted and representatives of anti-nuclear teams gathered on the KSC gates to specific their worry {that a} repeat of Challenger might unfold radioactive plutonium throughout the US’ japanese seaboard.
It was not a groundless worry and, certainly, it took last approval from President George H.W. Bush in September 1989 for the launch to go forward. Famous physicist Carl Sagan remarked that “there’s nothing absurd about both aspect of this argument”.
With solely six weeks to launch, timing was tight. And safety was elevated at KSC, as guards armed with M-16 assault rifles and semi-automatic pistols patrolled the perimeter of the launch web site.
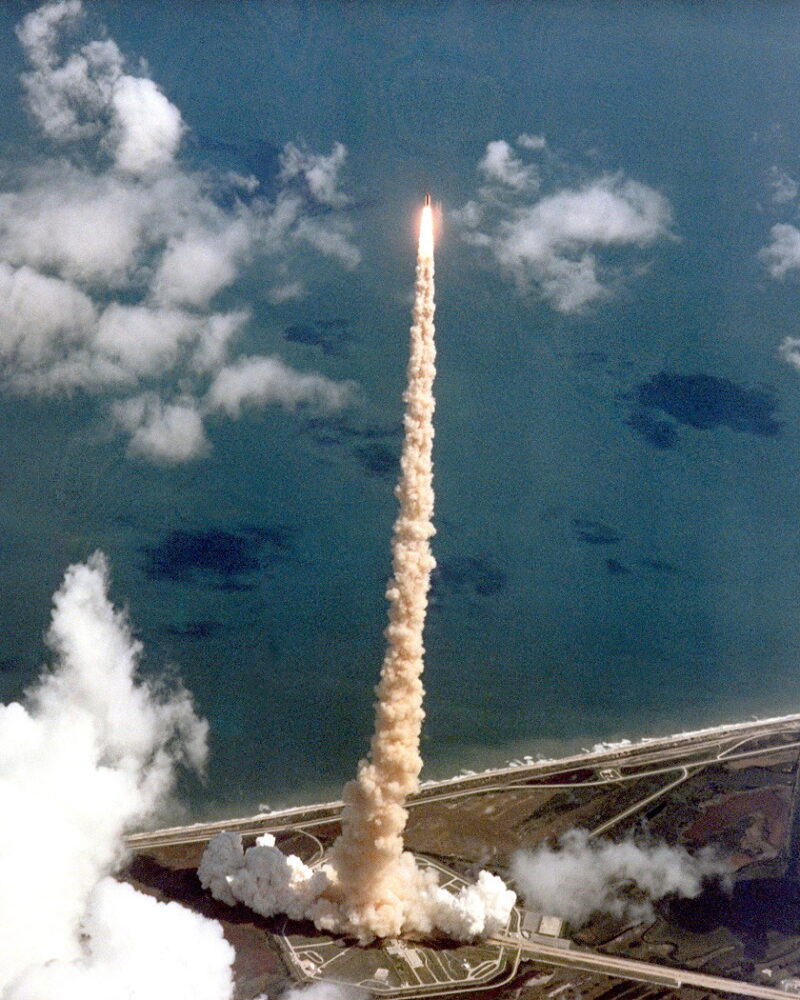

A defective predominant engine controller put paid to Atlantis’ launch on 12 October, while a second try on the seventeenth was scrubbed on account of looming rain showers. Throughout these last days, the final makes an attempt to halt STS-34 have been overturned by the Circuit Court docket of Appeals in Washington, D.C., with Chief Justice Patricia Wald declaring that NASA had correctly compiled all environmental evaluation reviews and, certainly, on the sixteenth, a number of activists have been arrested on the Cape for trespass.
Early on the moist morning of 18 October 1989, Williams led his crew out to Pad 39B and the ready Atlantis. Their launch was postponed by a couple of minutes because the shuttle’s computer systems have been up to date to alter their Transoceanic Abort Touchdown (TAL) emergency web site from rain-soaked Ben Guerir in Morocco to Zaragoza in Spain.
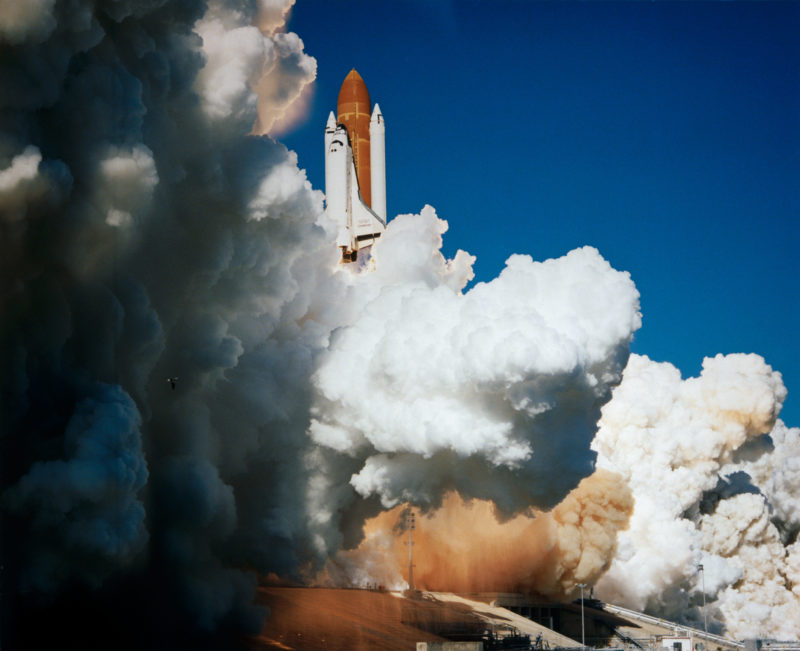
The sheer dynamism of their 12:53 p.m. EDT liftoff got here at 12:53 p.m. EDT got here as a shock to first-time flyer McCulley. At one level, because the shuttle cleared the tower, he turned to Williams and jokingly remarked “You didn’t put together me for this!”
One other factor which got here as surprising was the separation of the dual Stable Rocket Boosters (SRBs), two minutes into ascent. “Within the simulator, there’s a flashbulb that goes off whenever you get to SRB sep,” McCulley stated later, “and in actual life there’s an explosion that goes off, proper in entrance of your face. It was fantastic … however it was stunning!”
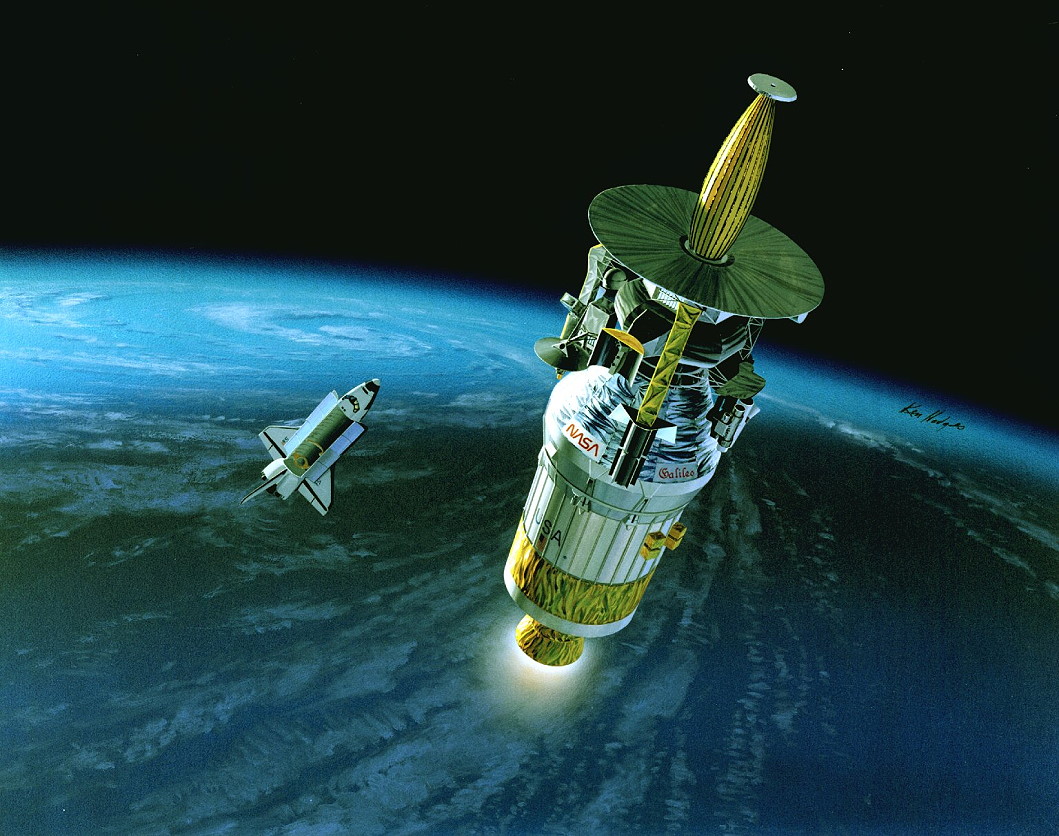

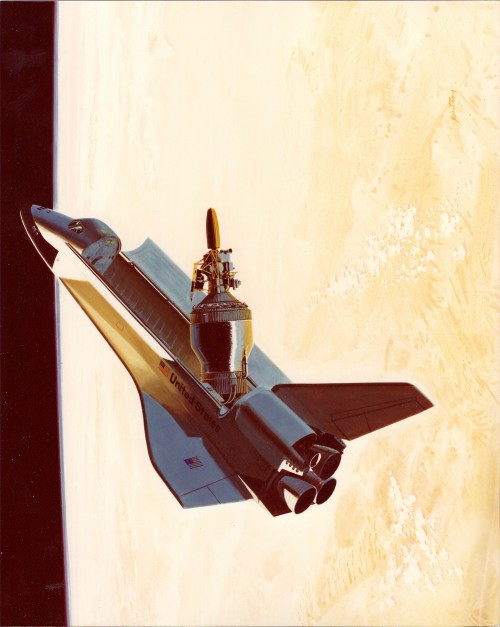
Six hours later, at 7:15 p.m. EDT, underneath the watchful eye of Lucid, the Galileo/IUS combo have been tilted to their deployment configuration in Atlantis’ payload bay and let loose. “Galileo is on its option to one other world,” radioed Williams.
“It’s within the palms of the most effective flight controllers on the earth. Fly safely!” Shortly afterwards, he and McCulley maneuvered the shuttle to a secure distance and the two-stage IUS executed a pair of “burns” to ship Galileo out of Earth orbit and onward to Venus as a part of its VEEGA trajectory to Jupiter.
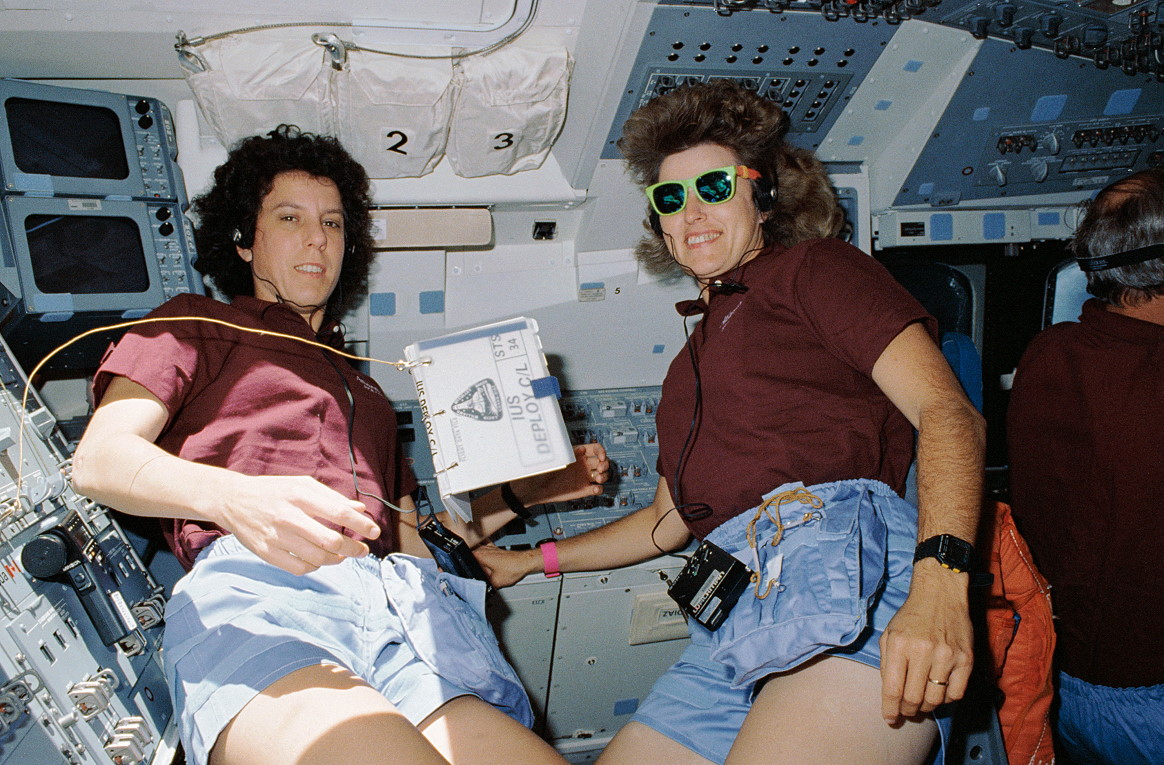

“Each Ellen and I sighed an incredible sigh of reduction,” remembered Lucid of these adrenaline-charged minutes of deployment, “as a result of we figured Galileo was not our concern at that time. We’d gotten rid of it. Happiness was an empty payload bay and we received happier and happier because the IUS and Galileo went additional away from us.”
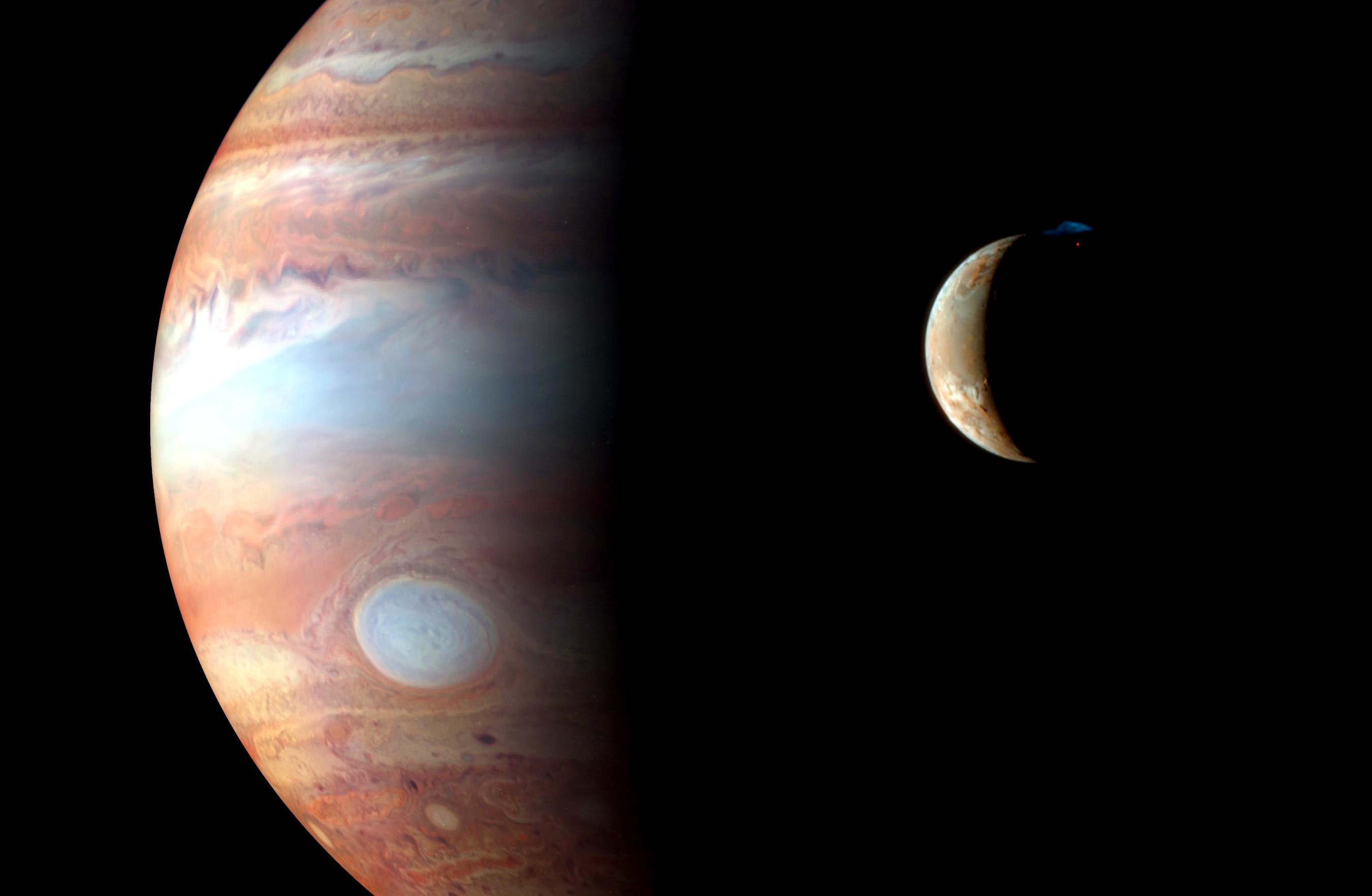
Eighteen months into its cruise, and several other months after its first flyby of Earth, Galileo’s high-gain antenna solely partially unfurled, threatening to wreck the mission. “Workaround” methods have been devised to make use of the low-gain antenna as a substitute, and the spacecraft returned outstanding pictures from Gaspra (in October 1991) and Ida (in August 1993) and, removed from conducting two years of scientific exploration at Jupiter, Galileo spent virtually eight years there.

It measured the chemical composition of the large planet’s environment, immediately noticed its ammonia clouds and mysterious Nice Pink Spot, analyzed the causes and results of volcanism on Io and yielded tantalizing clues for liquid oceans beneath the frozen surfaces of Europa and Ganymede and the extent of Jupiter’s gigantic magnetosphere was mapped and modeled for the primary time. On its option to the planet, in July 1994, Galileo additionally noticed the impression of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 into the Jovian clouds.
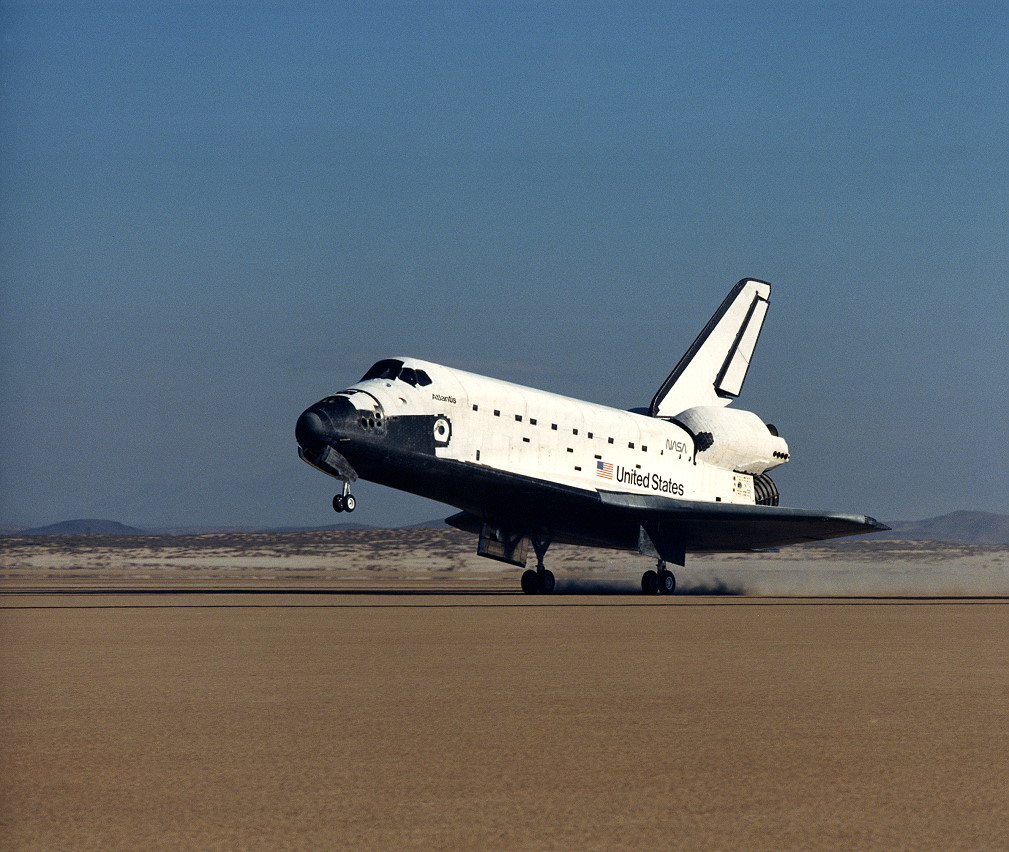
Predicted excessive winds at Edwards Air Pressure Base, Calif., on 23 October prompted NASA to deliver Atlantis house two orbits before deliberate. Williams and McCulley flew their ship to a clean landing at 6:33 a.m. PDT (12:33 p.m. EDT) after 5 days in area. In his thoughts, Williams thought-about STS-34 to have achieved fairly outstanding issues for science. “We knew that Galileo was going to be a lasting program,” he stated. “It was going to be a dwelling, ongoing program and we received to be part of it.”

