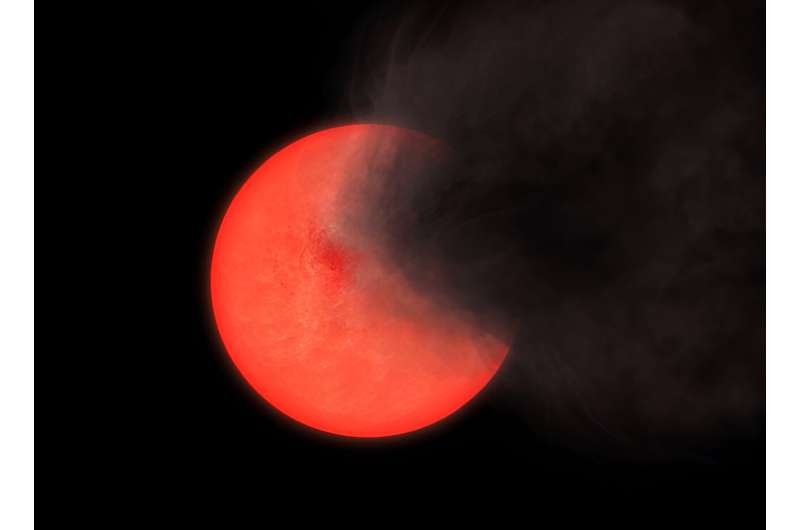

Nearing the top of their life, they sit quietly for lengthy intervals of time, barely noticeable, earlier than immediately puffing out a cloud of smoke.
A mysterious new kind of star nicknamed “outdated smoker” has been found hiding within the coronary heart of our Milky Manner galaxy, astronomers revealed on Friday.
The “peculiar” puffing conduct of those stars has by no means been seen earlier than in such crimson giants, astrophysicist Philip Lucas instructed AFP.
The worldwide staff of scientists behind the invention had not been on the lookout for such outdated stars throughout their 10-year survey, which took in a whole bunch of hundreds of thousands of stars throughout the sky.
As an alternative, they had been utilizing the VISTA telescope within the Chilean Andes to seek for new child stars—referred to as proto-stars—that are vulnerable to frequent, exuberant eruptions.
They noticed 32 proto-stars, “the most important quantity anybody has ever discovered earlier than in a single batch”, stated Lucas, a professor on the UK’s College of Hertfordshire and lead writer of a brand new research.
However lingering within the background was a “good shock”, he added.
‘We do not absolutely perceive’
The outdated people who smoke had been puffing proper within the heart of the Milky Manner, a densely packed and metal-rich area referred to as the Nuclear Stellar Disc.

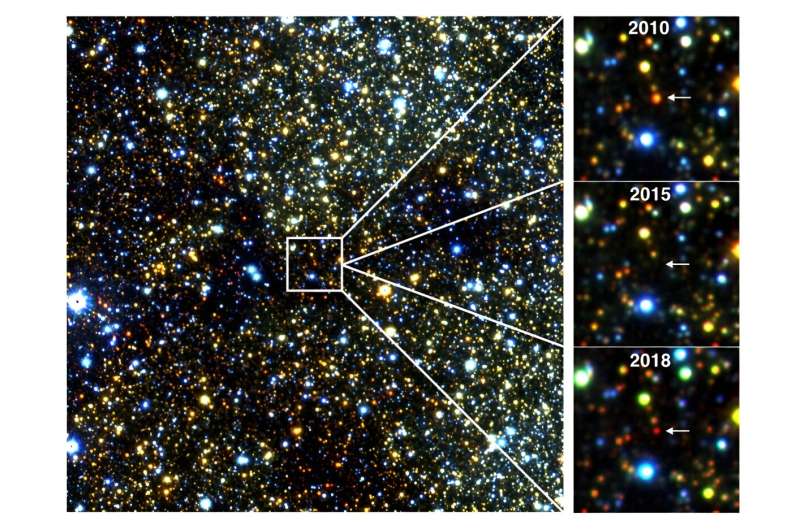
“What was stunning about this new discovery is that we’re seeing stars that had been simply sitting doing nothing in any respect,” Lucas stated.
Then abruptly the celebs would turn out to be between 40 to 100 occasions dimmer, typically so faint that the telescope’s infrared imaginative and prescient might barely spot them.
A few years later, seemingly with out warning, they might return to their former brightness.
“Every part we now have been in a position to study them means that it is a case of stars throwing off puffs of smoke—for causes that we do not absolutely perceive,” Lucas stated.
These smoke puffs are thought to briefly obscure the celebs from our sight.
There are numerous extra “heavy components”—something heavier than hydrogen and helium—on this area of the galaxy, which might create extra mud within the star’s ambiance, Lucas stated.
Precisely what puffs that mud out stays a thriller.
But when this principle is right, then the quantity of matter being thrown off by these stars might play a major function in how heavy components are unfold all through our galaxy—and past, he stated.
Lucas emphasised that these had been simply early greatest guesses.
“We’re simply type of scrabbling round attempting to see what makes probably the most sense,” he stated.
The researchers noticed at the least 21 outdated people who smoke however suspect there are a lot of extra on the market.
The research was printed within the Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Extra data:
Phil Lucas et al, Probably the most variable VVV sources: eruptive protostars, dipping giants within the Nuclear Disc and others, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad3929
Zhen Guo et al, Spectroscopic affirmation of high-amplitude eruptive YSOs and dipping giants from the VVV survey, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad3700
Carlos Contreras Peña et al, On the incidence of episodic accretion in Class I YSOs from VVV, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad3780
Zhen Guo et al, Multi-wavelength detection of an ongoing FUOr-type outburst on a low-mass YSO, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnrasl/slad201
© 2024 AFP
Quotation:
‘Outdated people who smoke’: Unusual new kind of star found in Milky Manner (2024, January 28)
retrieved 28 January 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

