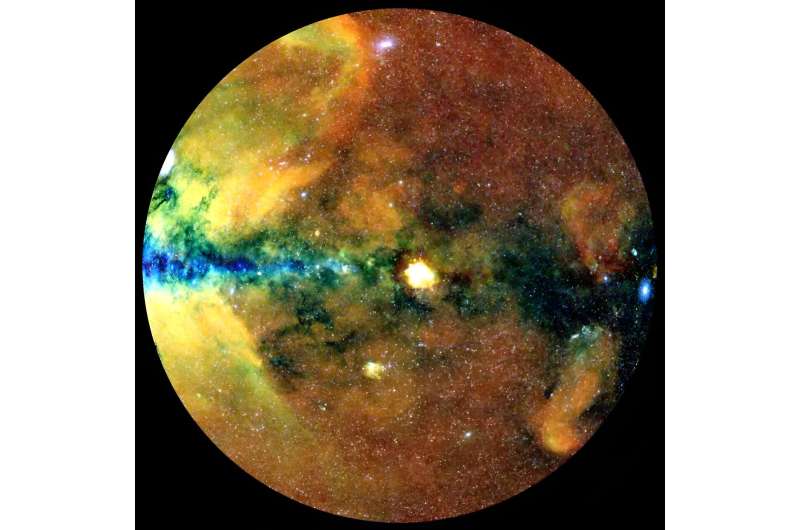
The German eROSITA consortium has launched the information for its share of the primary all-sky survey by the tender X-ray imaging telescope flying aboard the Spectrum-RG (SRG) satellite tv for pc. With about 900,000 distinct sources, the primary eROSITA All-Sky Survey (eRASS1) has yielded the biggest X-ray catalog ever revealed. The work is published within the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Together with the information, the consortium launched a collection of scientific papers describing new outcomes starting from research of the habitability of planets to the invention of the biggest cosmic constructions.
Primarily based on simply the primary six months of observations, eROSITA has already detected extra sources than had beforehand been identified within the 60-year historical past of X-ray astronomy. Now out there to the worldwide science neighborhood, the information will revolutionize our information of the universe at excessive energies.
The eRASS1 observations with the eROSITA telescope had been carried out from 12 December 2019 to 11 June 2020. In probably the most delicate power vary of the eROSITA detectors (0.2-2 keV), the telescope detected 170 million X-ray photons, for which the cameras can precisely measure the incoming power and arrival time.
The catalog was then constructed—after cautious processing and calibration—by detecting concentrations of photons within the sky in opposition to a vivid, large-scale, diffuse background. After eRASS1, eROSITA has continued scanning the sky and collected a number of further all-sky surveys. These information may even be launched to the world within the coming years.
The eRASS1 catalog covers half the X-ray sky, the information share of the German eROSITA consortium. It consists of greater than 900,000 sources, together with some 710,000 supermassive black holes in distant galaxies (energetic galactic nuclei), 180,000 X-ray-emitting stars in our personal Milky Method, and 12,000 clusters of galaxies, plus a small variety of different unique lessons of sources like X-ray-emitting binary stars, supernova remnants, pulsars, and different objects.
“These are mind-blowing numbers for X-ray astronomy,” says Andrea Merloni, eROSITA principal investigator and first creator of the eROSITA catalogue paper. “We have detected extra sources in six months than the large flagship missions XMM-Newton and Chandra have performed in almost 25 years of operation.”
Coordinated with the discharge, the German eROSITA Consortium has submitted virtually 50 new scientific publications to journals, including to the greater than 200 which have already been revealed by the workforce earlier than the information launch.
Many of the new papers seem with chosen discoveries together with an enormous filament of pristine warm-hot gasoline extending between two galaxies and two new “Quasi-Periodically Erupting” black holes. Additional research of how X-ray irradiation from a star might have an effect on the environment and water retention of orbiting planets, and statistical evaluation of flickering supermassive black holes.
“The scientific breadth and affect of the survey is sort of overwhelming; it is arduous to place into a number of phrases,” says Mara Salvato, who as spokesperson for the German eROSITA consortium co-ordinates the efforts of about 250 scientists organized into 12 working teams. “However the papers revealed by the workforce will communicate for themselves.”
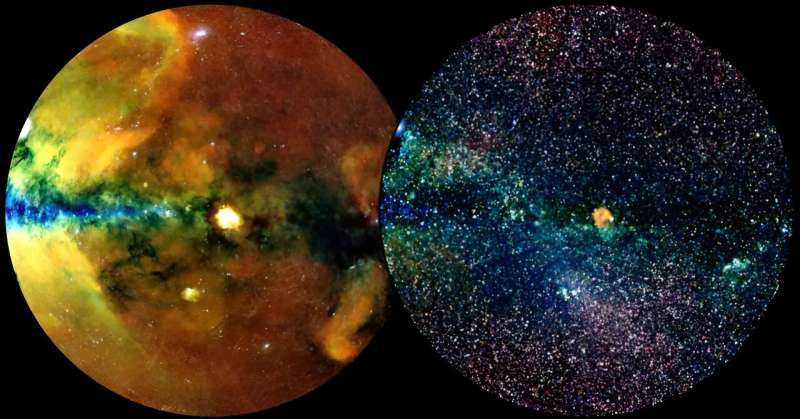
This first eRASS data release (DR1) makes public not solely the supply catalog, however photographs of the X-ray sky at a number of X-ray energies and even lists of the person photons with their sky positions, energies and exact arrival instances.
The software program wanted to research the eROSITA information can also be included within the launch. For a lot of supply lessons, supplementary information from different wavebands has additionally been included into so-called “value-added” catalogs that transcend pure X-ray info.
“We have made an enormous effort to launch high-quality information and software program,” added Miriam Ramos-Ceja, who leads the eROSITA Operations workforce. “We hope it will broaden the bottom of scientists worldwide working with high-energy information and assist push the frontiers of X-ray astronomy.”
“The eROSITA collaboration has performed an impressive job with the information launch and on the identical time publishing all of those superb new outcomes,” says Kirpal Nandra, Director at MPE. “There’s much more to come back from us, and we’re trying ahead to seeing what the remainder of the world will do with the general public information.”
Eager eROSITA-watchers might know that the driving scientific goal that motivated the telescope was to constrain cosmological fashions utilizing clusters of galaxies. The cosmology outcomes, based mostly on an in-depth evaluation of the eRASS1 clusters, will probably be launched in roughly two weeks.
Extra info:
A. Merloni et al, The SRG/eROSITA all-sky survey, Astronomy & Astrophysics (2024). DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202347165
Quotation:
First eROSITA sky-survey information launch makes public the biggest ever catalog of high-energy cosmic sources (2024, January 31)
retrieved 31 January 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

