If aliens are synchronizing their indicators with gentle coming from supernova 1987A, then the seek for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI) is on the case. Scientists with the establishment say they are able to discover such indicators by on the lookout for them on what’s known as the “SETI Ellipsoid.”
About 167,600 years in the past, a blue supergiant star exploded as a supernova within the Massive Magellanic Cloud, which is a small, satellite tv for pc galaxy that neighbors our personal Milky Means. Gentle emanating from that supernova raced by way of area at 299,792,458 meters per second (186,282 miles per second).
Then, on 24 February 1987, it reached Earth.
Associated: Machine studying might assist observe down alien know-how. Here is how
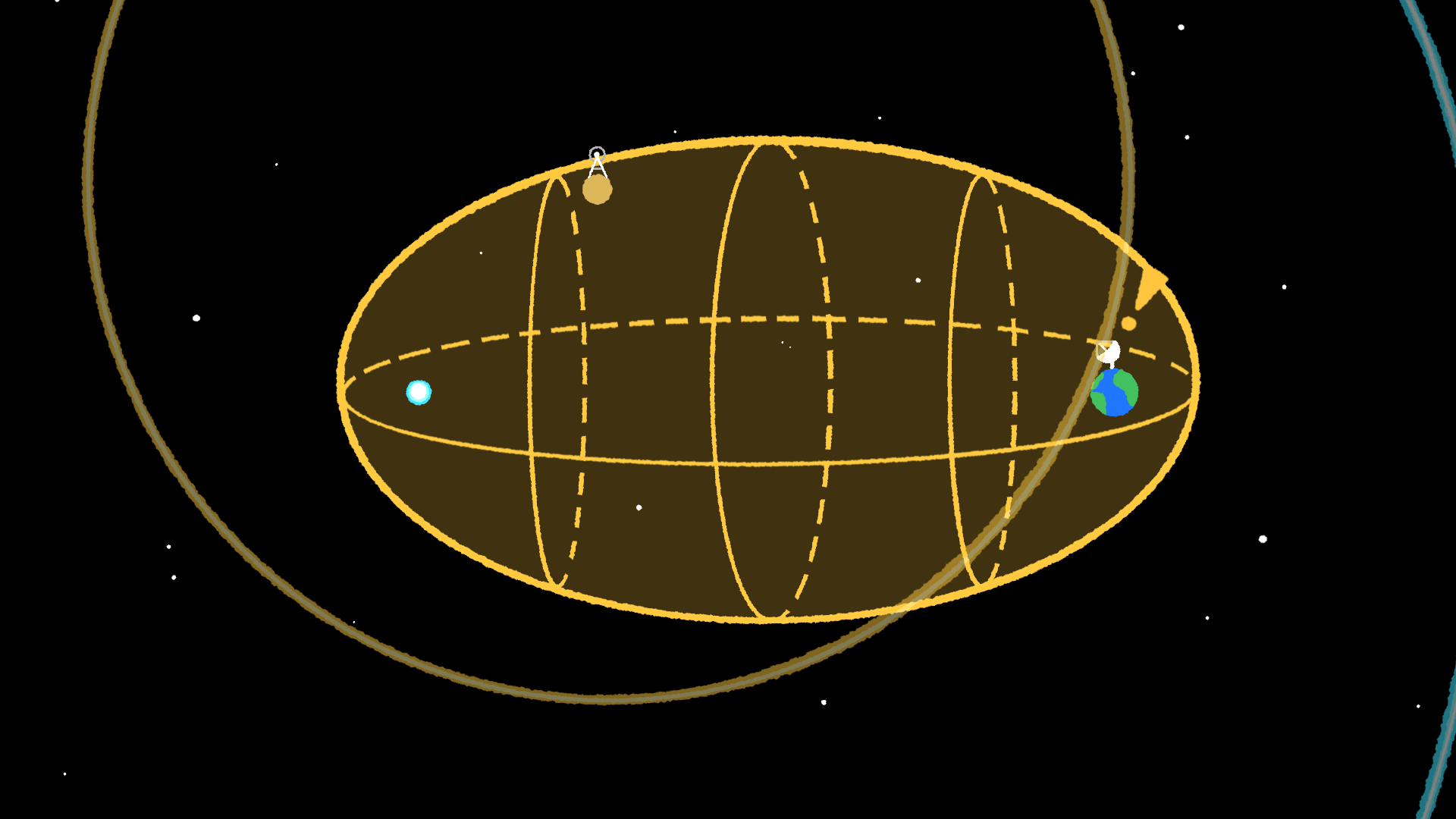
The supernova turned generally known as SN 1987A, and its gentle didn’t cease at Earth. It saved going, deeper and deeper into our galaxy the place different alien life may catch a glimpse. That is the place the idea of the SETI Ellipsoid comes from. It is outlined as an elliptically formed quantity, with Earth at one foci and SN 1987A on the different; its perimeter signifies places the place there was sufficient time for the supernova’s gentle to succeed in a star, and for any technological life on a planet orbiting that star to ship out a sign that might attain us now.
The thought is that we will use the SETI ellipsoid as what’s generally known as a Schelling level, an idea related to recreation concept. It describes a sort of point of interest round which two protagonists — on this case, transmitting aliens and human astronomers watching or listening for his or her indicators — can coordinate their actions with out first speaking their intentions. If that sounds sophisticated, contemplate that SETI has been utilizing Schelling factors ever since Frank Drake’s Mission Ozma, the first-ever SETI search that occurred in April and Might 1960. Drake had looked for radio indicators on the iconic 21 centimeter hydrogen wavelength as a result of he figured aliens would notice our astronomers routinely have a look at that wavelength. Transmitting on such a generally used wavelength, he reasoned, would enhance the possibility of a sign’s detection.
“As Dr. Jill Tarter usually factors out, SETI searches are like on the lookout for a needle in a 9-D haystack,” mentioned Sofia Sheikh of the SETI Institute and the College of California, Berkeley in a statement. “Any method that may assist us prioritize the place to look, such because the SETI Ellipsoid, might doubtlessly give us a shortcut to essentially the most promising elements of the haystack.”
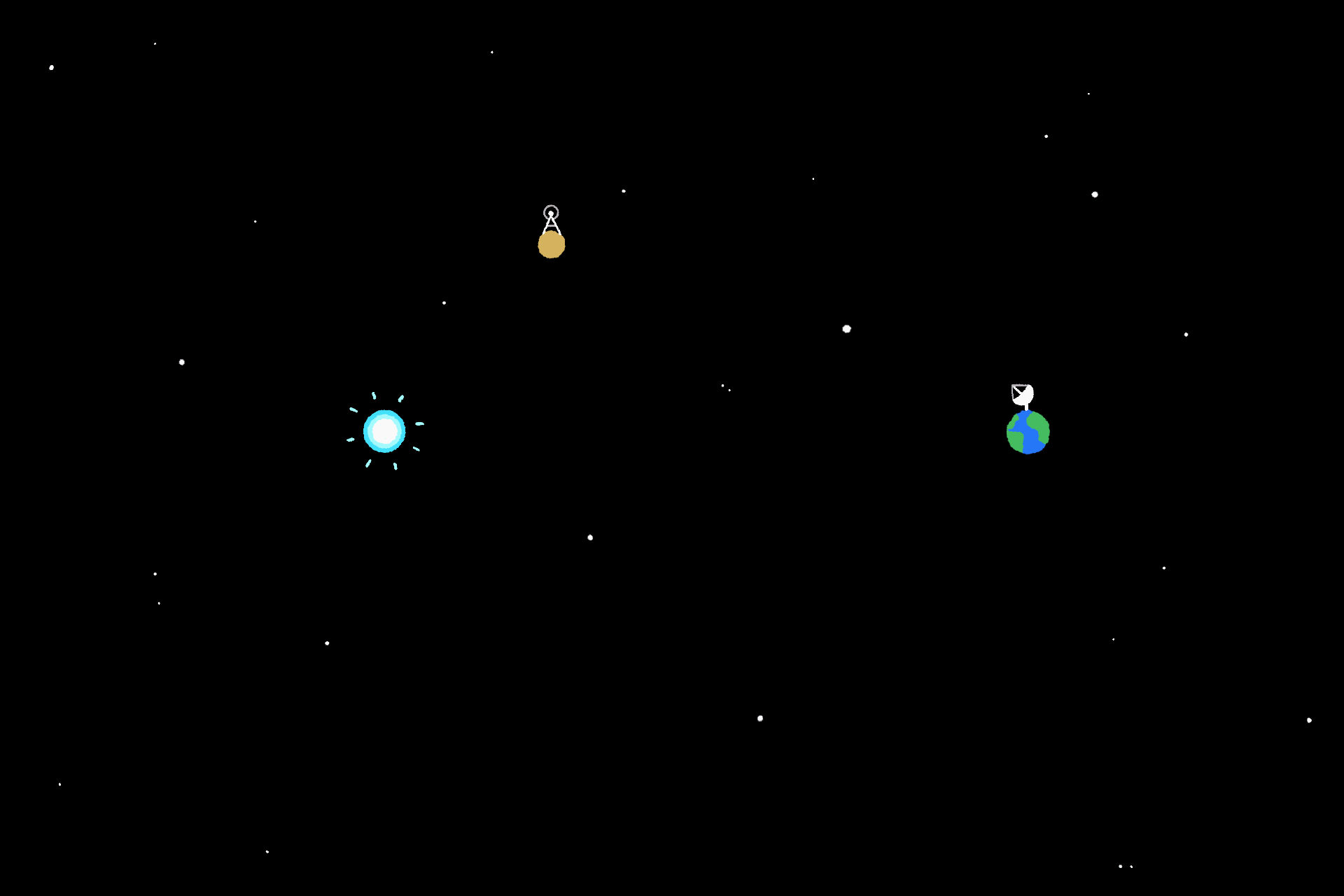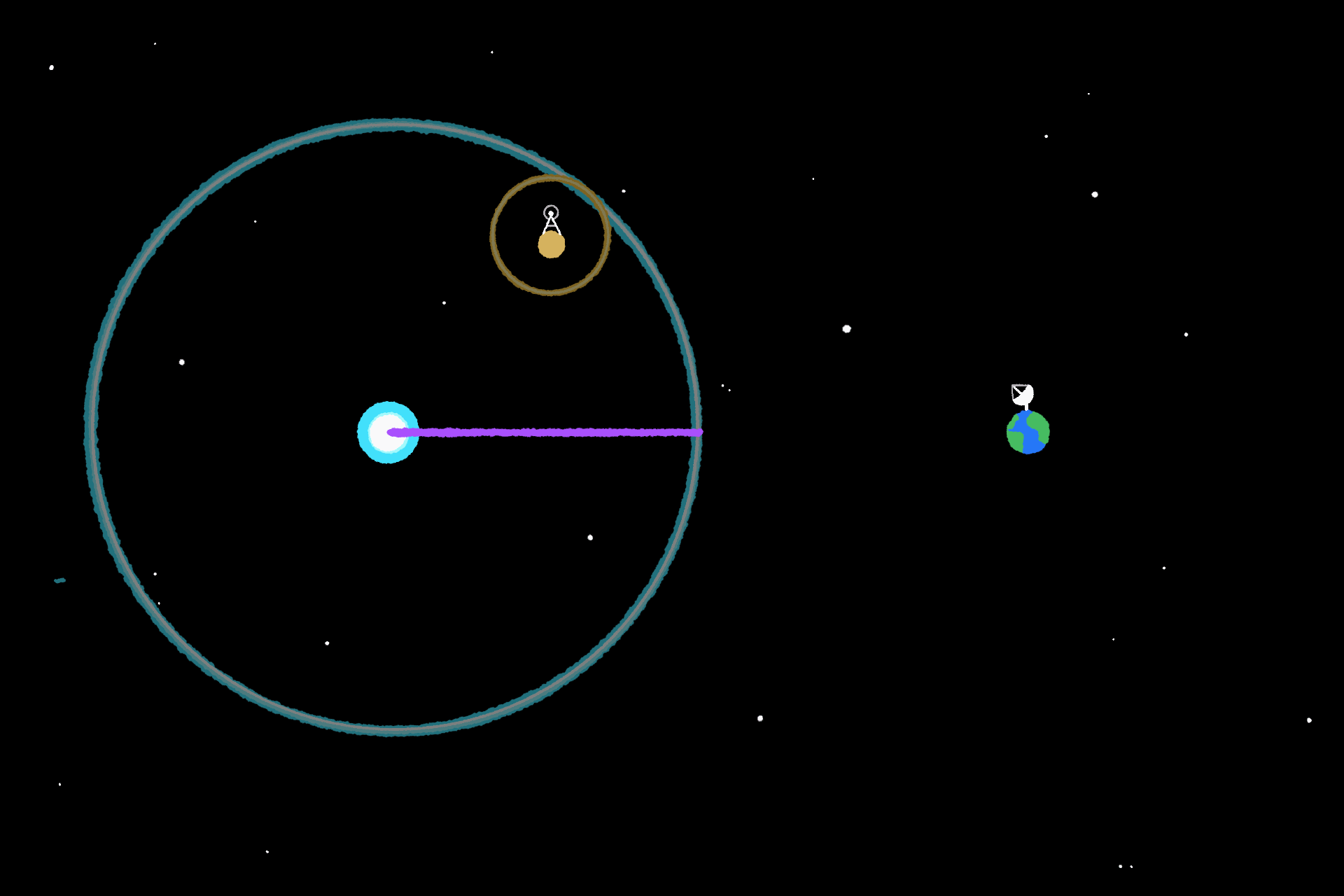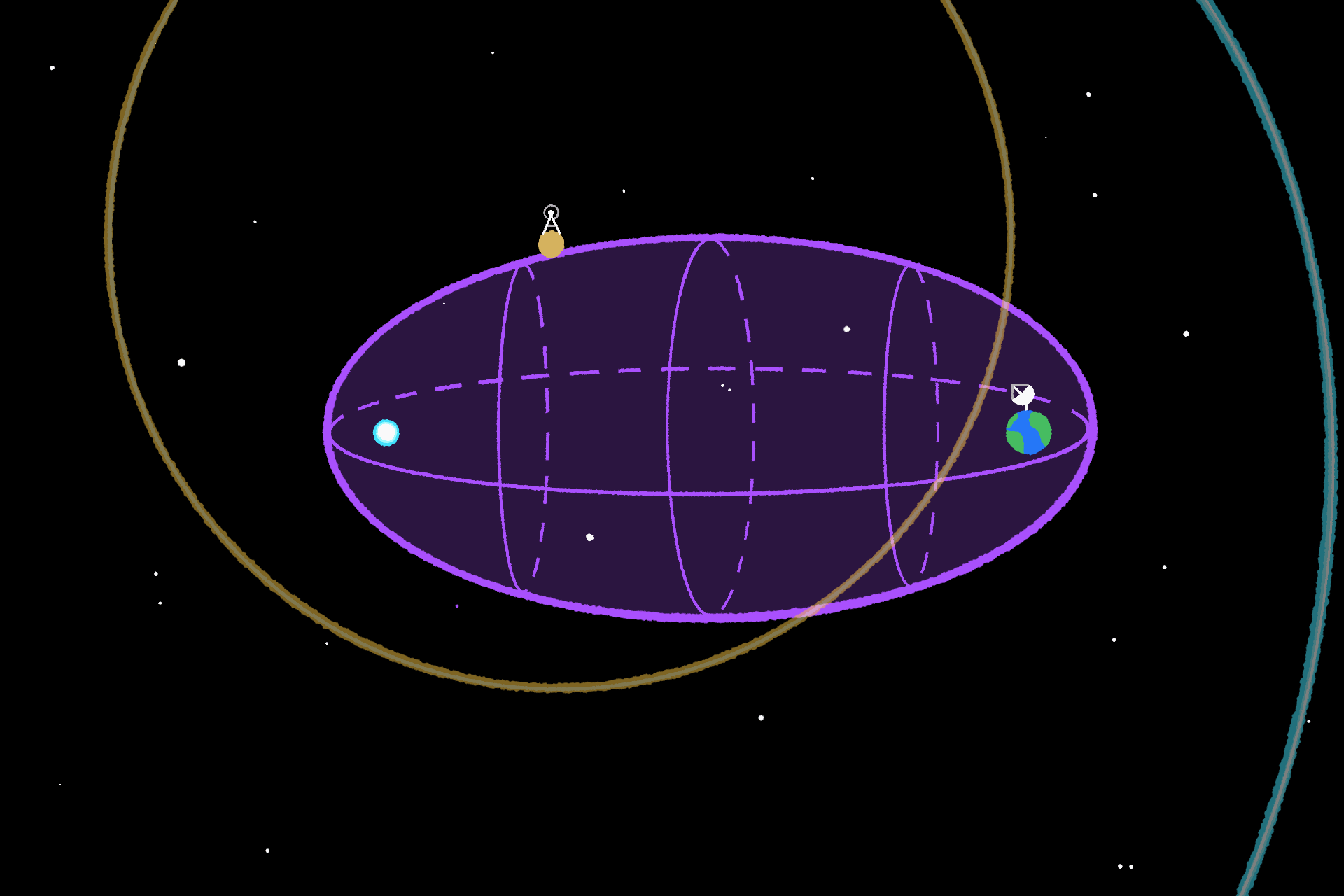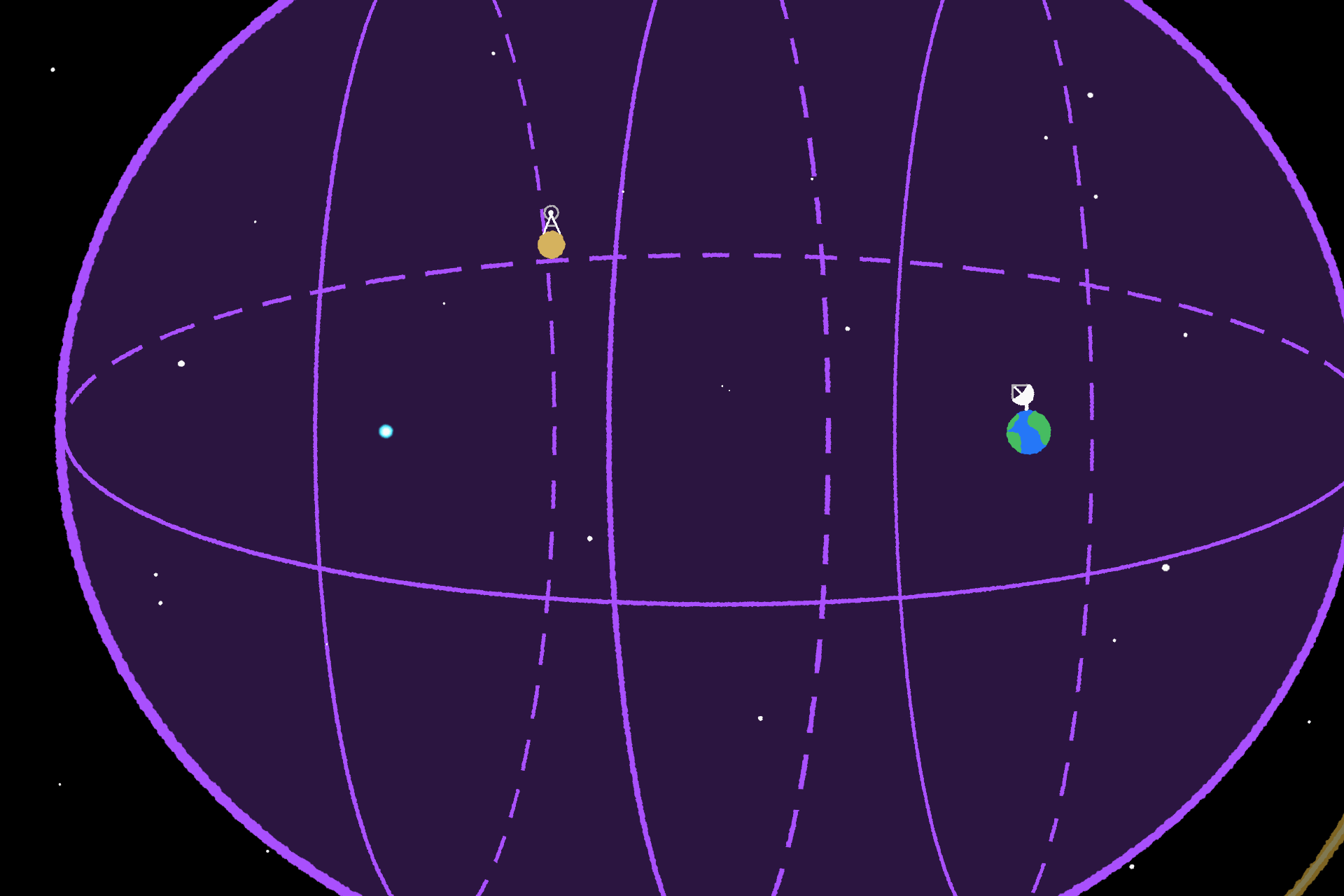
The hope is that technological aliens who’ve seen SN 1987A would synchronize their indicators with it, figuring out that we might be on the lookout for it on the SETI Ellipsoid. Nevertheless, the issue has been that, till very just lately, it has been unimaginable to look the ellipsoid with an inexpensive diploma of accuracy.
To grasp why, let’s check out some SETI and astronomical historical past.
The idea of the SETI Ellipsoid isn’t new. It was first independently described by T. B. Tang within the Journal of the British Interplanetary Society in 1976, and by Soviet astronomer P. V. Makovetskii in 1977. On the time, there have been no apparent targets round which to base a SETI Ellipsoid; Makovetskii proposed utilizing Nova Cygni 1975, which was an outburst of a white dwarf accumulating matter from a companion purple dwarf star, which prompted the system to brighten considerably for a couple of week.
After the invention of SN 1987A, Hungarian astronomer Iván Almár realized it had created a brand new SETI Ellipsoid topic, and in 1994, Argentinian astronomer Guillermo Lemarchand described a search utilizing that ellipsoid. However, uncertainties within the distances of stars close to the ellipsoid’s perimeter had been too nice. Uncertainties in distance correspond to uncertainties in time; if we get the space to a star mistaken by even half a gentle yr, for instance, which means our seek for synchronized indicators can be six months too early or late. And timing could also be every thing with these technosignature hunts.
Solely previously ten years, with the appearance of the European Area Company’s Gaia mission, meant to measure the positions and traits of a billion stars, have astronomers began gleaning distances to stars with the required accuracy to look SN 1987A’s SETI ellipsoid. So, a workforce led by James Davenport of the College of Washington in Seattle mixed the Gaia information with stars on the SETI Ellipsoid which might be within the Steady Viewing Zone of NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite tv for pc (TESS).
TESS spends a yr every celestial hemisphere, and divides these hemispheres up into sectors. TESS gazes at every sector for 27 days, anticipating exoplanetary transits, earlier than transferring on to the following sector. Nevertheless, there is a area round every celestial pole that seems in each sector. That is the Steady Viewing Zone — TESS gathers information from it for a whole yr.
Davenport’s workforce recognized 32 stars within the Steady Viewing Zone which might be on the SETI Ellipsoid, and the yr’s price of knowledge allowed for some leeway in case of any lingering uncertainty of their distances. TESS, being an optical telescope, can solely detect optical indicators and never radio messages. Davenport’s workforce studied the sunshine of the 32 stars over the course of that yr, on the lookout for any anomalies that point out a technological signature. These anomalies might embody a brightening from a laser sign, an unorthodox transit from a man-made construction, and even a man-made outburst mimicking the sunshine curve of SN 1987A. In 1994, Lemarchand recommended on the lookout for a “pretend pulsar” sign, as aliens may know that astronomers can be on the lookout for a pulsar born within the fires of the supernova. (So far, no pulsar has been detected in SN 1987A.)
Suffice to say, Davenport’s workforce discovered no anomalies and due to this fact no proof of aliens was detected. Nevertheless, the SETI Ellipsoid is at all times rising (on the velocity of sunshine, in truth) and it’ll transfer onto different stars sooner or later.
The upcoming PANOSETI (Panoramic SETI) mission, which can repeatedly observe your entire sky seen from Lick Observatory in California and seek for optical and near-infrared laser indicators, might be excellent for probing the SETI Ellipsoid. The Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile is also a recreation changer when it turns into operational later this decade.
“New surveys of the sky present groundbreaking alternatives to seek for technosignatures coordinated with supernovae,” co-researcher Bárbara Cabrales of Smith Faculty in the USA, mentioned within the assertion.
The evaluation of the SETI Ellipsoid and the outcomes from the celebrities in TESS’ Steady Viewing Zone had been described final yr within the The Astronomical Journal.

